As the European Union (EU) prepares to unanimously extend its economic sanctions on Russia when they expire on July, it is a good opportunity to take a closer look. After Russia´s illegal annexation of Crimea and interference in Eastern Ukraine, the U.S. and the EU enacted economic sanctions in a coordinated manner, which were followed by other Allies and partners like Canada and Australia.
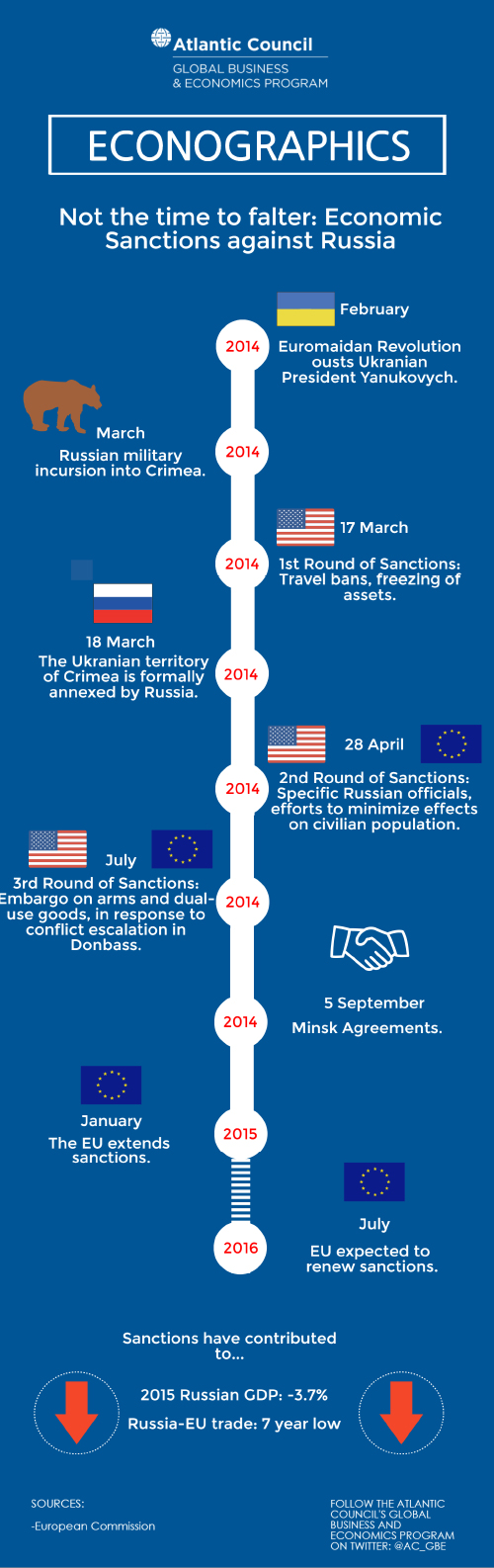
There are three types of economic sanctions. The first limits access to Western financial markets for certain Russian state-owned enterprises in the banking, energy, and defense sectors. The second prohibits exports to Russia of designated high-technology oil exploration and production equipment. Finally, an embargo was put on place on exports to Russia of certain military and dual-use goods.
Although the effect of sanctions is hard to calculate on its own, it certainly contributed to the severe contraction of the Russian economy, which fell 3.7 per cent in 2015, the worse figure in six years. Lifting of the sanctions hinges upon Russia delivering on its commitments in the Minsk agreements, but implementation has stalled for months.