Complicated history helps Russian narratives about Ukraine find a foothold in the Middle East
This is one chapter of the DFRLab’s report, Undermining Ukraine: How Russia widened its global information war in 2023. Read the rest here.
More than a decade after the revolutions collectively known as the Arab Spring, several countries in the Middle East and North Africa are undergoing democratic backsliding and a return to authoritarian rule, including Egypt under President Abdel Fattah al-Sisi, Libya under General Khalifa Haftar, and Tunisia under President Kais Saied. This trend and some shifts in sentiments about the West in these and other MENA countries have given Russia openings to undercut Western influence in the region and frame Ukraine as a Western puppet, using its state media and public diplomacy to influence opinion.
This is playing out in the context of growing internal polarization in many countries in the region and, among the citizenry, rising disenchantment with the West and democracy as a workable governing system for them. These developments enable Russia to offer an alternative alliance to authoritarian leaders who aim to diversify their country’s resources and reduce reliance on the West and the United States in particular.
Russian state media has had a presence in the Arab World since the 2007 launch of Russia Today Arabic (now just RT Arabic), and its influence expanded with the 2014 start of Sputnik Arabic, which maintains a regional office in Cairo. Today, RT Arabic is one of the region’s top three most-watched news broadcasters after Al Arabiya and Al Jazeera. As reported in the DFRLab’s previous Undermining Ukraine report, Russia signed cooperation agreements with local media in Egypt, Algeria, and Morocco to formalize official cooperation on joint projects and information exchanges.
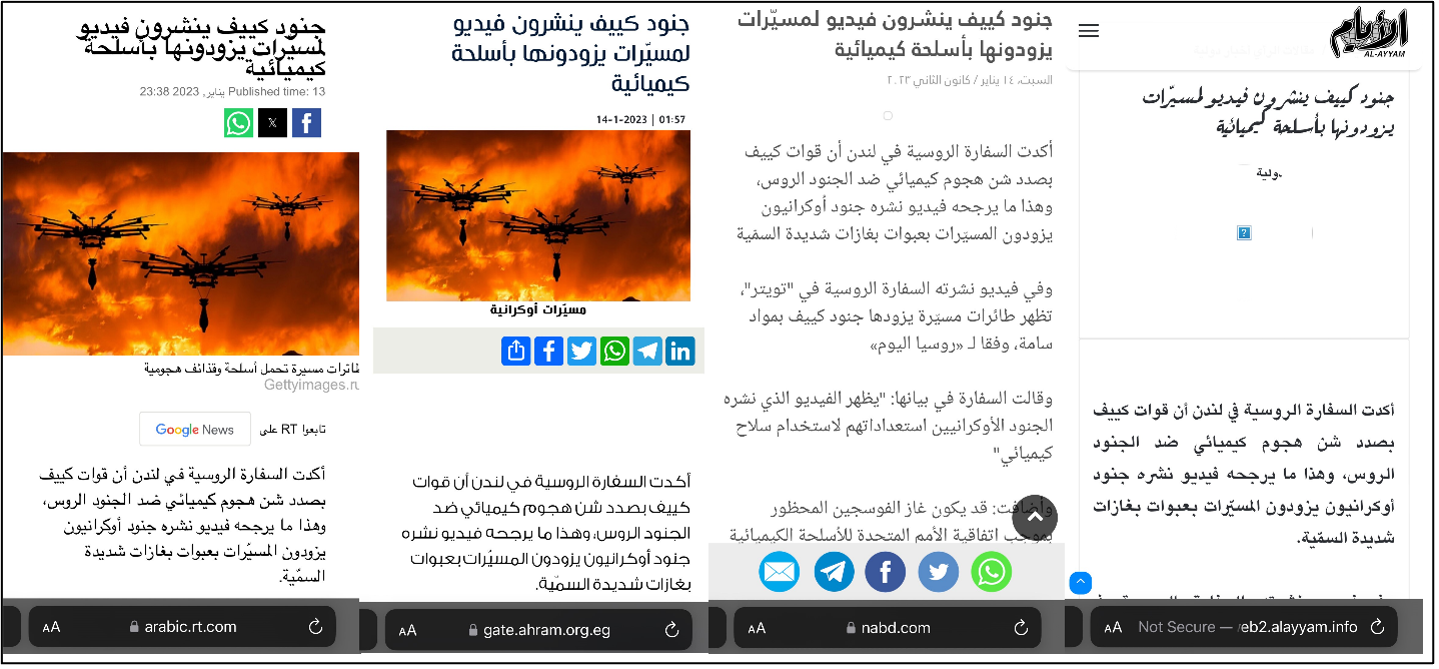
Some Arabic-speaking media outlets post the exact text of articles published on RT Arabic’s website, allowing for the spread of narratives promoted by state-run Russian media to Arabic speakers. A short RT article from January 13, 2023, pushing claims that Ukrainian soldiers were carrying chemical weapons, was posted verbatim on the news websites of Egypt’s Al-Ahram, Yemen’s Al-Ayyam, and Dubai-based news aggregator Nabd. An August 2023 RT Arabic article repeating Putin’s claim that the ban on Russian media was due to the West’s fear of the truth was also reposted by Yemen’s Al-Ayyam and Emirati newspaper Al Khaleej. An article published in state-aligned Syria’s Al-Watan and Egypt’s Al-Ahram in September quoting State Duma Member Anna Kuznetsova saying that the “Kyiv regime uses the same methods used by the terrorist organization ISIS [Islamic State group] to recruit children” was originally published in RT Arabic.
By cooperating with local media, Russia is able to spread its propaganda to a broader audience in the Arab world. The narratives amplified by Russian state media and local media partners are framed in a way that appeals to audiences in the region and their complicated history with the West. In line with authoritarian Arab leaders’ statements about the West’s interest in their countries, local media amplify narratives suggesting that the West attempts to demonize Russia in order to maintain Arab nations’ reliance on the West. Additionally, narratives about Zelenskyy being a puppet of the West and Putin standing up to them appeal to many in the Arab populations who viewed their former authoritarian leaders as puppets supported by the West at their own expense. Moreover, regional audiences point to Western hypocrisy in considering Russia’s war in Ukraine with a different lens than the US invasion of Iraq or Israel’s actions in the Gaza Strip.
As Western states imposed a ban on RT and Sputnik and blocked their YouTube channels to minimize the impact of their propaganda, Russian media was further emboldened in the region as it became increasingly considered an alternative source of information after decades of Western influence in their countries. While there is some sympathy expressed online among Arabic speakers for the Ukrainian people, there is also support for Russia and Putin expressed by media and individuals, resulting from internal polarization and disenchantment with democracy and the West.
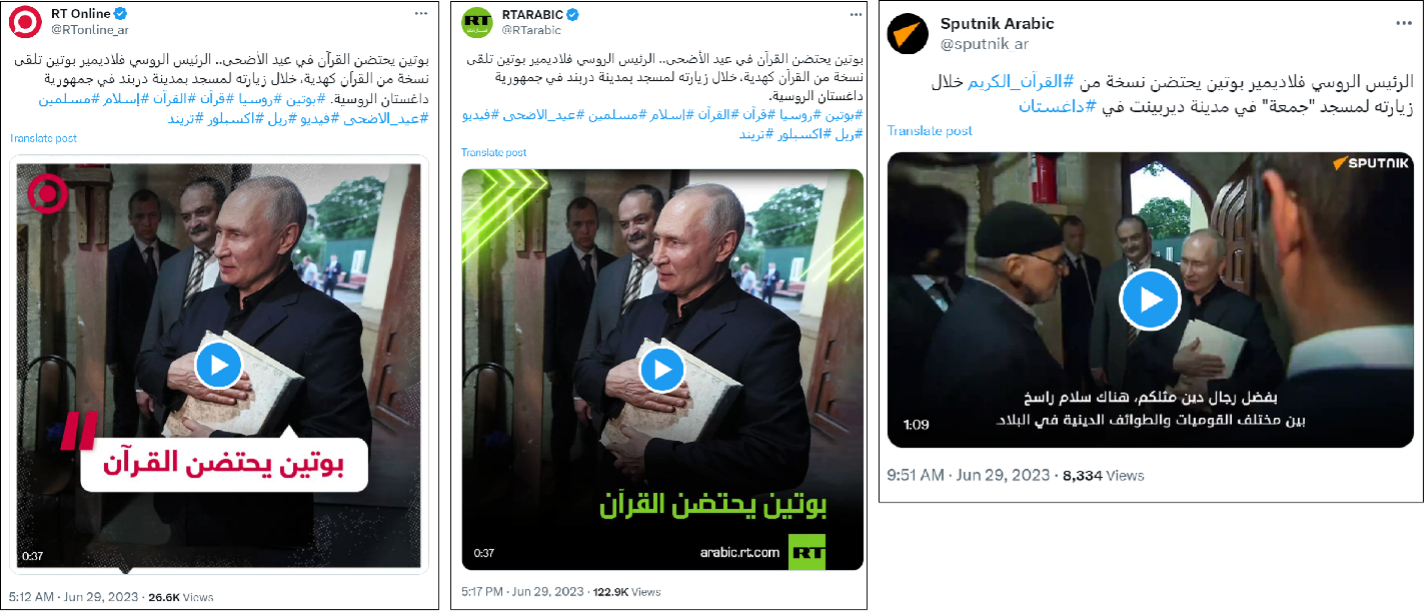
Russian media and its social media accounts capitalize on such resentment toward Western countries to gain support for Russia in the region. The X accounts of Sputnik and RT Arabic produce more content than BBC Arabic and Al Jazeera, regularly posting content that appeals to Arab audiences. For instance, on June 29, 2023, one day after an incident of Quran burning in Sweden, the three X accounts posted similar videos showing Putin holding the Quran during a visit to a mosque in the city of Derbent, Russia, while criticizing Western countries like Sweden for allowing the burning of the holy book.
Arabic-speaking journalists and influencers promoting pro-Russia narratives
X also serves as a major social media platform for several Arabic-speaking Russian state media personalities as well as unaffiliated online influencers. Many of these accounts with large followings consistently post news content aligned with the Kremlin’s preferred narratives. There are differences between the two groups, however, as affiliated journalists openly state their ties to Russian media and use their real identities, while influencer accounts appear to more frequently use stolen images and show signs of coordinated posting and engagement.
The DFRLab identified and analyzed thirty accounts of influencers and self-proclaimed journalists boasting large follower counts and posting Arabic content, mostly in the form of news updates. These accounts often promoted similar pro-Russia, anti-Western messaging and celebrated partnerships between Russia and Arab nations. Specifically, the accounts created content that would resonate more with an Arab audience and sometimes expand on regional resentment toward Western countries, accusing them of double standards following their pro-Ukraine narratives.
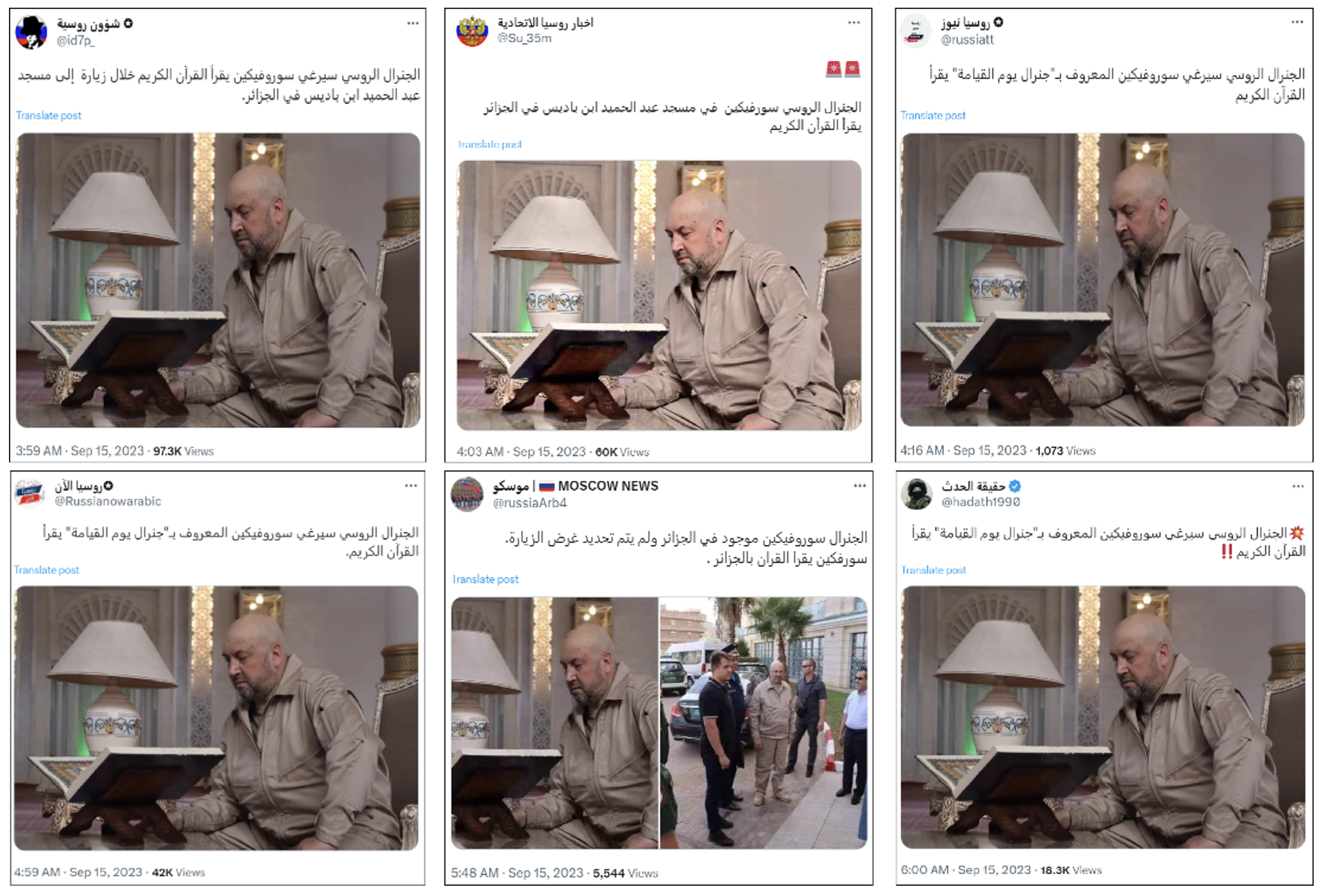
An analysis of the accounts revealed several suspicious indicators, including similarities in how they present themselves and the content they post. The bios of twenty-three of thirty accounts highlighted interest in Russian news, Russia-Ukraine news, or general political and war news. Many of the accounts often published similar posts on the same day or within a short window. One example showed accounts attempting to attract interest from Arab and Muslim users after Russian general Sergei Surovikin visited Algeria, with six accounts using very similar text and the same photo of Surovikin reading the Quran in an Algerian mosque, all published within a two-hour period on September 15, 2023.
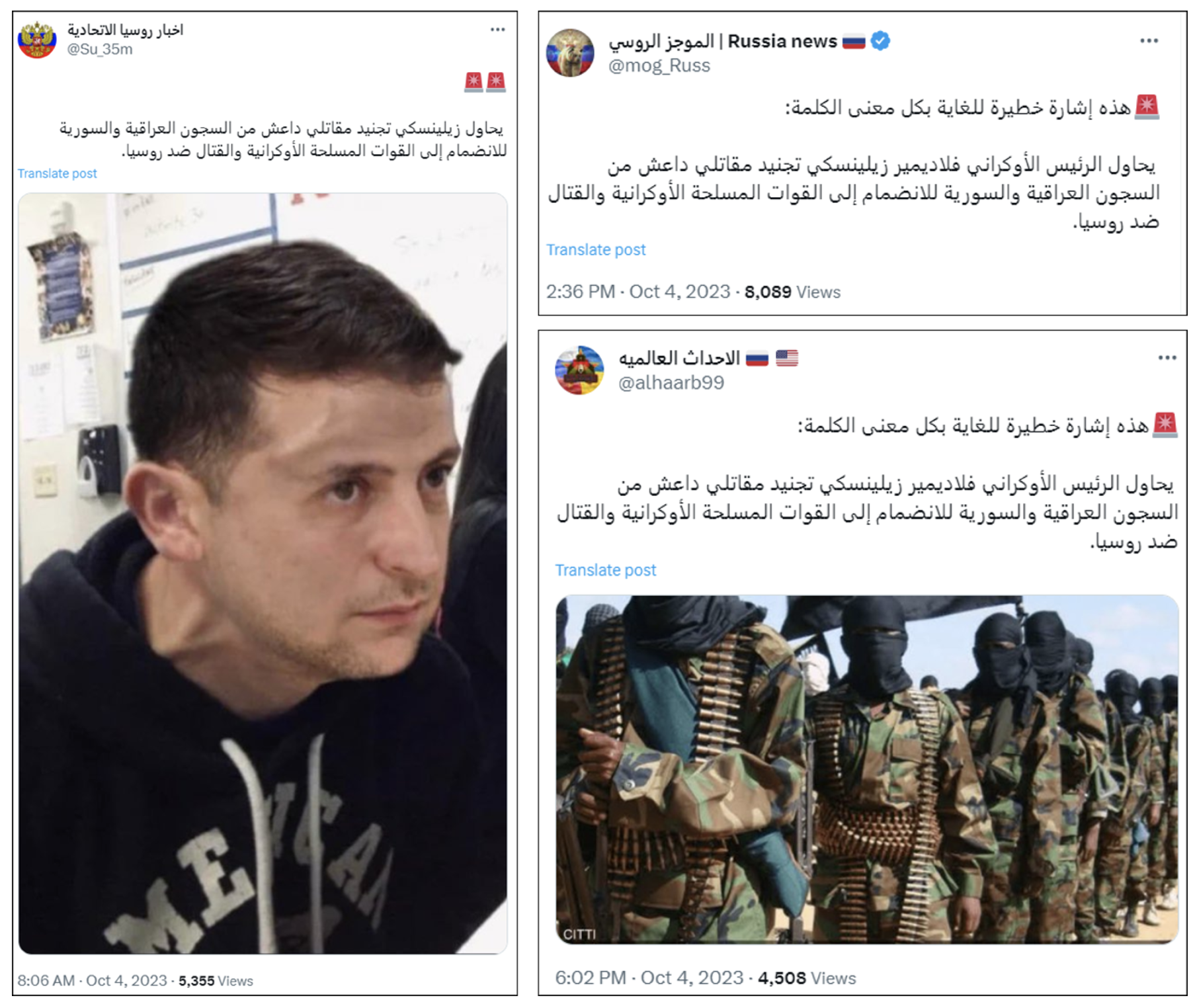
These X accounts routinely promoted disinformation related to the Russia-Ukraine war as well. In one example, on October 4, 2023, three accounts used identical or nearly identical text falsely claiming that Zelenskyy was attempting to recruit Islamic State fighters held in Iraqi and Syrian prisons to join the Ukrainian army in its fight against Russia.
The DFRLab also noticed some degree of coordination between some of the accounts, such as liking, retweeting, and replying to each other’s tweets. For instance, reviewing @russiaArb4’s post engagement revealed many retweets from the same three accounts. Moreover, some of the accounts created posts to promote other accounts and asked users to follow them.
Several of the identified accounts appeared focus on retweeting other accounts, alongside retweeting specific and possibly new Arabic media accounts. This apparent coordination around retweeting could be seen in the almost identical timelines with the same set of retweets between accounts.
Furthermore, five accounts that claimed to be either media figures or Russian citizens living in Russia or somewhere else had additional suspicious indicators. According to monitoring tool Twitter ID Finder, four of these accounts were created in October 2022: three on October 20—two of them just twenty minutes apart—and one on October 28. A reverse image search also confirmed that four of these accounts reappropriated publicly available images of attractive women as their avatars. This tactic appears to be similar to one previously used by a set of pro-Russia accounts, as documented by the Institute for Strategic Dialogue, in an attempt to target Arab male users to follow and engage with them.
Russian public diplomacy in the region
As in Latin America, Russia uses the social media presence of its diplomatic missions in the Middle East and North Africa to promote its preferred narratives about the war in Ukraine. Most of the diplomatic missions post updates to their official Facebook and X accounts at varying frequencies, focusing on diplomatic affairs with the host country. Most repost content from other diplomatic missions and the Russian Foreign Ministry’s English, Russian, and Arabic X accounts about international affairs and the war in Ukraine, routinely posting falsehoods and exaggerations about the war. These include describing the war as a “special military operation” or fighting Nazis in Ukraine.
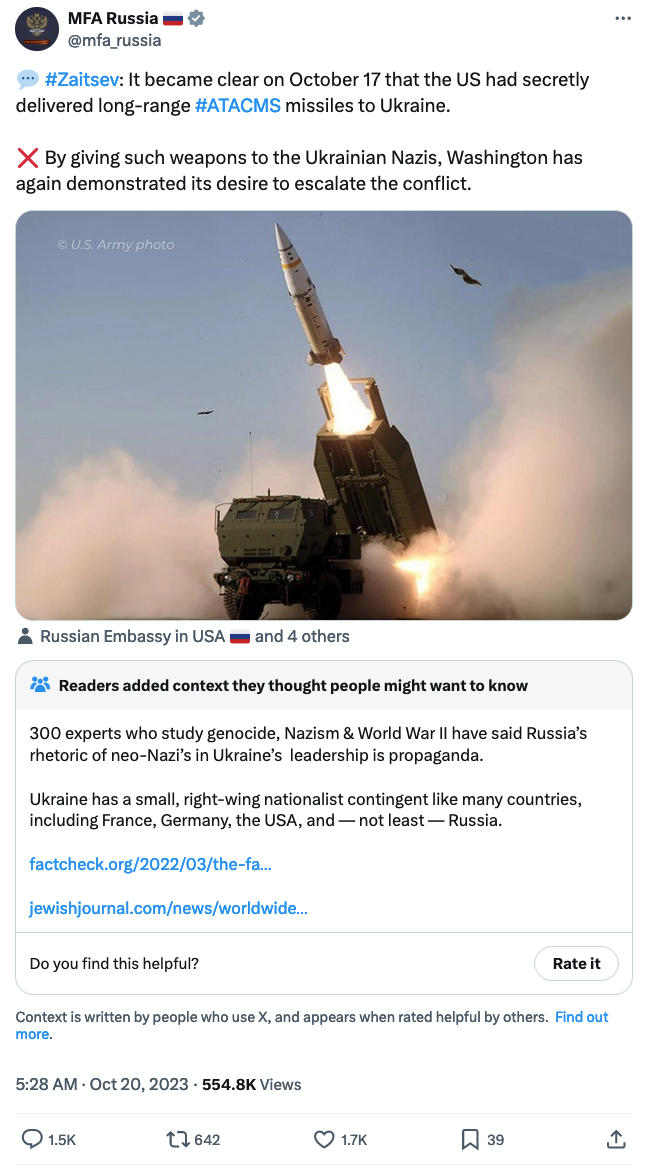
The X and Facebook accounts of Russia’s diplomatic mission in Egypt post regular international affairs updates. The accounts posted regularly about Ukraine throughout 2023 with the hashtag #الحق_مع_روسيا (“Russia is right”). Among its posts, Russia’s embassy in Egypt posted statements to Facebook about “Ukrainian Nazis” allegedly firing missiles at a hospital in Pervomaisk, Ukraine, using US-provided High Mobility Artillery Rocket System (HIMARS) missiles. Economic and military ties between Russia and Egypt have strengthened in recent years, especially as the latter’s government seeks to reduce its dependence on the United States, which provides Egypt with $1.3 million in annual military assistance. Egypt currently imports the majority of its wheat from Russia and has been working with Russia to construct a Russian-built nuclear plant since 2022.
The increased cooperation and aligning of economic and military priorities between the governments of Egypt and Russia allows the latter to be more aggressive in promoting its narratives to Egyptian audiences through its official channels and getting positive engagement with social media users. The embassy’s messaging about the war in Ukraine sometimes plays on anti-Western sentiment among some audiences.
On February 24, 2023—the first anniversary of Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine—the Russian embassy in Egypt tweeted a statement from the ambassador expressing gratitude to Egypt for “fully understanding the reasons for the confrontation over Ukraine and for supporting Russia despite the torrents of lies about our actions launched by the West.”
In September of that year, the embassy posted about a US announcement that Russia characterized as providing tanks to “Ukrainian Nazis” and depleted uranium shells to “expose our land to radioactive pollution. Exactly what they did in Iraq.” Russian diplomatic missions reference the Iraq War as part of its strategy to capitalize on anti-Western sentiment fueled by lingering distrust of the United States.
Diplomatic missions also capitalize on holidays and other public events by posting statements promoting Russian narratives. For example, the Russian embassy in Egypt evoked its fight against “Nazis” in Ukraine in a tweet on Defenders of the Homeland Day, then repeated the same rhetoric in another tweet on Russia’s Victory Day.
The Russian embassy in Algeria posted a statement from its ambassador on the occasion of Russia Diplomats’ Day, suggesting that the West was engaging in an “open anti-Russia campaign,” adding, “In a time like now when we witness tremendous pressure on Russia by the so-called ‘collective West,’ it becomes clear who our real friends are.” The ambassador also posted on Russia’s Victory Day, saying that “our great Homeland will win this time, will once again rid the world of fascism and Nazism.”
In other posts, Russian diplomatic missions in the region promoted narratives related to specific incidents of concern to Muslim audiences, such as a post from the Russian Embassy in Egypt showing a picture of a praying hand and a copy of the Quran with a tweet condemning the alleged burning of the Quran by Ukrainian soldiers. The post stated that the soldiers did so, knowing there are Muslims fighting in the Russian army, referring to a video that appears to show Ukrainian soldiers burning copies of the Quran.
Related content

The Atlantic Council’s Digital Forensic Research Lab (DFRLab) has operationalized the study of disinformation by exposing falsehoods and fake news, documenting human rights abuses, and building digital resilience worldwide.
Image: Russian Minister of Foreign Affairs Sergey Lavrov addresses the Doha Forum, in Doha, Qatar, on December 10, 2023. Photo by Balkis Press/ABACAPRESS.COM


