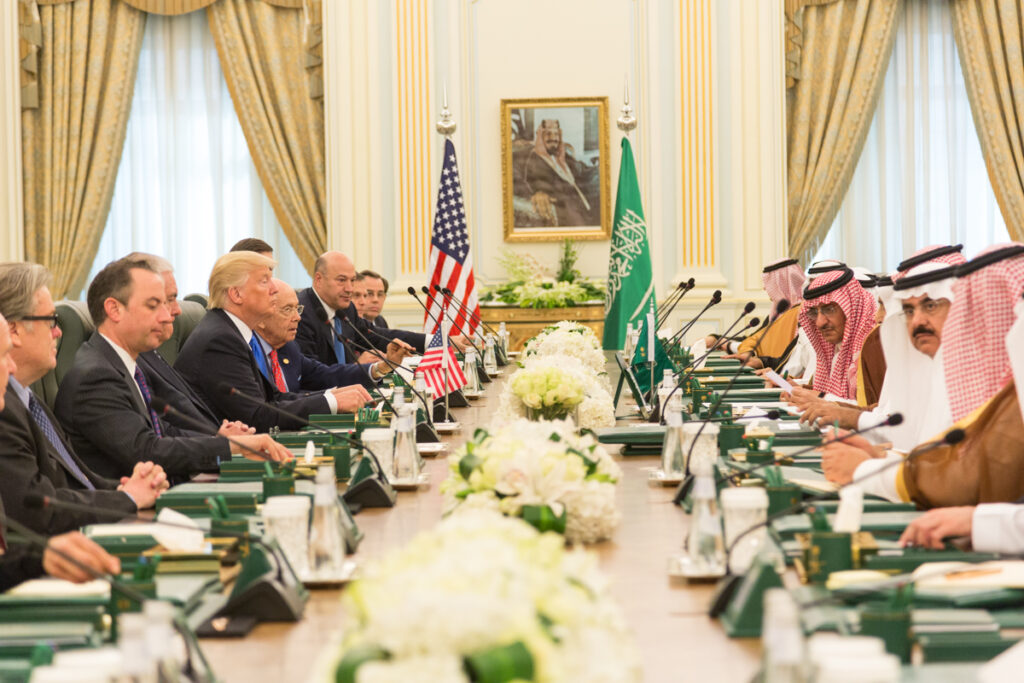
President Donald Trump is traveling to the Gulf states this week in a visit aimed at negotiating business deals rather than wading into geopolitical issues. Here are four ways this strategy may play out.
STAY CONNECTED
Sign up for PowerPlay, the Atlantic Council’s bimonthly newsletter keeping you up to date on all facets of the energy transition.
1. Investment in US energy and manufacturing
Last month, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) committed to investing $1.4 trillion in the United States over the next decade. Some of the investments in the package have already been announced, including a recent commitment by Emirates Global Aluminum to fund the construction of a smelter in the United States. If built, it would be the country’s first new aluminum smelter in thirty-five years and could potentially double US production. Trump will likely push the UAE to announce additional plans to invest in US manufacturing, infrastructure, and energy production, with petrochemicals, steel, and battery production likely targets.
Trump is expected to press Saudi Arabia to announce where it intends to invest the $600 billion that Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman committed to during a post-inauguration call in January. Just like during his first term, Trump said that if Saudi Arabia agreed to large purchases of US products, he would make the country his first foreign visit. Now, he will look to hammer out the specifics, which will likely include purchases of military equipment in addition to investments in infrastructure, technology, and mining.
2. Nuclear energy cooperation
Saudi Arabia has tried to start a domestic nuclear power program since 2006. It has signed multiple agreements with various contractors and consultants—but with very little progress other than a small research reactor in Riyadh due to come online soon. Saudi Arabia has engaged with Chinese companies to explore domestic uranium mining and enrichment—a potentially problematic move from the perspective of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) because it can easily lead to weapons production.
However, there are signs that Saudi Arabia is now interested in complying with IAEA standards. Last August, Riyadh agreed to IAEA spot inspections designed to ensure that weapons are not being developed, potentially paving a pathway for cooperation with the United States. Last week, the Trump administration announced that it was dropping the Biden administration’s demand that Saudi Arabia normalize relations with Israel as a condition for civil nuclear cooperation negations, putting Saudi nuclear power back on the table. At stake may be commitments from Saudi Arabia to use US companies and American-made materials to build future reactors, as well as deals to supply Saudi-produced critical minerals to US customers.
3. Pumping more oil
Trump has been extremely vocal about his desire to lower oil prices. While US producers don’t want to see prices fall below the sixty dollars per barrel range (breakeven prices in the most productive shale basins are currently in the low to mid sixty dollars per barrel range), consumers would welcome lower gasoline prices this summer. Middle East producers seem eager to help, as OPEC+ recently committed to increase production by 411,000 barrels per day in June and is expected to recommit to gradually put more oil on the market at its ministerial meeting at the end of May. It is unlikely that Trump will press the Gulf countries to make additional commitments, but he will expect them to follow through—and will likely say so to the press.
4. LNG purchases
Trump is likely to push Gulf countries to expand their orders for US liquefied natural gas (LNG). Kuwait and Iraq already import US LNG and Bahrain just received its first cargo last month. Both Kuwait and Bahrain want to buy more LNG to meet high domestic electricity demand over the summer while natural gas outputs decline. Trump should push them to sign long-term offtake agreements with US LNG companies rather than rely on spot market purchases. This will ensure that these countries continue buying US gas even when more LNG become available from nearby Qatar, which is expanding its production.
This should be an easy sell to Kuwait, which is already in talks with the Australian company Woodside to buy a 40 percent stake in its Louisiana LNG terminal. Kuwait is aiming to secure LNG supplies from this project, but even with assistance from the Trump administration, it won’t be fully operational until the early 2030s. Trump should push Kuwait to sign additional offtake agreements, with the idea that if Kuwait does find itself oversupplied with LNG in the future, it can always resell cargos on the spot market.
Strategically, announcing at least two new LNG agreements with Middle Eastern countries will help the Trump administration’s position as it presses Europe to move forward with long-term offtake agreements for US LNG. Europe has been dragging its feet over concerns about emissions reporting, even though Europe needs US gas to replace the Russian LNG it currently buys. Trump can use LNG deals with Middle Eastern consumers to pressure Europe to commit to US purchases before winding down imports of Russian LNG. This would also help Trump pressure Russia to negotiate on Ukraine, as it would further squeeze Moscow’s income.
It isn’t just business
The focus of Trump’s visit to the Middle East may be on strengthening economic ties, but it is tough to ignore the backdrop of rising geopolitical tensions, particularly regarding Israel, Iran, and the Houthis. Business, trade, and energy markets are important to both the president and the leaders of the Gulf countries he will be meeting, but so are security and diplomacy. In Trump’s mind, business and geopolitics operate in tandem and everything is up for negotiation. It should not come as a surprise to see energy deals, trade negotiations, sanctions enforcement and even weapons sales materialize in concert.
MEET THE AUTHOR
RELATED CONTENT
OUR WORK

The Global Energy Center develops and promotes pragmatic and nonpartisan policy solutions designed to advance global energy security, enhance economic opportunity, and accelerate pathways to net-zero emissions.
Image: President Donald Trump and members of the U.S. delegation participate, Saturday, May 20, 2017, in a bilateral meeting with King Salman bin Abdulaziz Al Saud and Saudi Arabia officials at the Royal Court Palace in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. (Official White House photo by Shealah Craighead)