What you should know
- $617 million: The Nicaraguan government reports that hurricanes Eta and Iota caused damage worth $617 million and economic losses of $121 million.
- $7 trillion: The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development predicts most economies will be smaller at the end of 2021 than the end of 2019. The OECD also announced lockdowns to contain the COVID-19 pandemic have shrunk global GDP by $7 trillion.
- 21 percent: The Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) reports that infections from the HIV virus rose 21 percent between 2010 and 2019 in Latin America. PAHO Director Carissa Etienne says COVID-19 is expected to exacerbate the HIV problem in the region.
- 1.5 million: The week of November 23 saw 1.5 million new COVID-19 cases in the Americas, marking the highest weekly numbers since the start of the pandemic. The Americas is now home to more than 25 million cases and over 700,000 deaths. Below are this week’s latest figures.
Quarantine + reopening plans
Countries are taking divergent approaches to the holiday season, with some opting to relax containment measures and others implementing curfews and restrictions.
- The Brazilian state of São Paulo imposed stricter social distancing measures, further restricting the opening hours and capacities of bars, restaurants, and shopping malls.
- Bolivia announced the full resumption of economic activities, beginning December 1, but biosecurity measures, including capacity restrictions, remain in place.
- Chilean President Sebastián Piñera urged citizens to take precautionary measures to avoid another wave of COVID-19 cases. The government is expected to announce new restrictions for the holidays.
- Peruvian authorities extended the state of emergency until the end of the year but reduced the nationwide curfew by one hour.
- On November 29, the Maduro regime announced the nationwide curfew will be lifted for December.
- The Grenadian government is expected to increase the penalties for individuals who breach quarantine regulations. Current regulations include a fine and six months in jail.
- Uruguayan President Luis Lacalle Pou announced new measures to stop the spread of COVID-19, including requiring all public employees to work from home, the suspension of indoor sports and the closure of gyms, and restricted hours for bars and restaurants. The measures will remain in effect until December 18.
International travel restrictions
- Argentines and permanent residents will be required to present a negative PCR test to enter the country but will no longer be required to quarantine upon arrival. Buenos Aires unveiled a plan to resume domestic and international tourism. Long-distance bus services will gradually resume on December 8 and flights will begin on December 15.
- On December 1, Bolivia opened its borders to tourists and residents alike. Travelers must present a negative PCR test.
- The CDC issued a very high-risk warning for Mexico, urging Americans not to travel to the country as COVID-19 cases continue to rise.
- The Peruvian government is expected to authorize international flights up to fourteen hours this week, in effect, authorizing flights to Europe.
Economies in focus
Economic Impact
- The OECD published a new report predicting an 8 percent decline in regional GDP. Argentine, Mexican, and Colombian economies are expected to see the biggest drops with 13 percent, 9 percent, and 8 percent respectively.
- The Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean estimates that Nicaragua’s economy will contract by 6 percent as a result of hurricanes Eta and Iota and the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Moody’s predicts that the devastation and economic impact of hurricanes Eta and Iota will place additional pressure on the credit ratings of Central American countries.
- Chile’s unemployment rate eased for a third consecutive month, falling to 12 percent for August through October, but it remains significantly higher than the same period the previous year.
- The Central Bank of Ecuador estimates the economy will grow by 3 percent in 2021 as a result of increased spending and the recovery of remittances.
Economic Relief
- The Central American Bank for Economic Integration approved two loans totaling $400 million to Panama to alleviate the impact of COVID-19.
- The Mexican Ministry of Finance announced a second infrastructure investment package of 29 projects funded by the government and private sector valued at $11.4 billion. President Andrés Manuel López Obrador also announced that he would extend tax breaks for communities on the southern and northern borders until 2024.
- The Inter-American Development Bank (IDB) issued a $50 million loan for micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises in Brazil’s southern states, to preserve jobs and the companies’ financial stability amid the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The IDB also approved a $50 million loan for members of the Organization of Eastern Caribbean States to support their responses to the health, social, and economic consequences of the pandemic.
- The World Bank will provide Guyana with a $7.5 million loan to strengthen the country’s health system and COVID-19 tracking capabilities.
- CAF-Development Bank of Latin America extended a long-term credit of $500 million to Costa Rica for its COVID-19 response.
- The government of the Republic of Korea announced $700,000 in humanitarian assistance to three countries affected by Hurricane Iota – Colombia, Honduras, and Nicaragua.
Resilience, recovery + renewal
COVID-19 represents one of the greatest ever shocks to our economies and, in consequence, to the business models of financial institutions and the way they do business.
While many changes to business processes and operations were already taking place prior to the pandemic, COVID-19 has given many added impetus and urgency. Decision-makers must choose between adapting a wait-and-see approach or implementing more proactive strategies to safeguard and, if possible, grow their businesses.
Baker McKenzie’s Finding the Balance series seeks to map the post-pandemic environment that financial institutions need to navigate as we move to the new normal. It looks at how different industry sectors are experiencing profoundly distinct impacts on their balance sheets and markets, with very different timescales and pinch points. The series also considers how the global economy will be impacted directly and indirectly in the years ahead.
Drawing on analysis and resources from beyond the legal sector — media commentary, economic analysis, consultancy, political insight — and reflecting Baker McKenzie’s clients’ own views on what’s happening to their businesses in various jurisdictions and areas of business, Baker McKenzie’s legal experts consider the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead for financial institutions.
You can find additional resources, including links to Baker’s FInsight podcast here, and its Financial Institutions Hub, with the latest news, events and publications on financial services hot topics can be found here.
Health + innovation
- The United Kingdom has become the first country to approve a COVID-19 vaccine after UK regulators granted emergency use authorization to the vaccine developed by Pfizer and BioNTech. US approval of the same vaccine is expected shortly after a Food and Drug Administration (FDA) review on December 10.
- On November 30, Moderna announced it had filed for an emergency use authorization (EUA) for its COVID-19 vaccine from the FDA. The FDA will review the Moderna vaccine on December 17.
- On November 26, AstraZeneca acknowledged that an error during trials of its COVID-19 vaccine resulted in higher efficacy rates in a group that mistakenly received 1 ½ vaccine doses instead of the intended two. Furthermore, the group that mistakenly received the dose did not include anyone over the age of 55. AstraZeneca announced additional international studies will be run to examine the dose regimen among more participants.
- On November 25, the Ecuadorian government announced it will purchase and import 16 million doses of a COVID-19 vaccine from AstraZeneca, Pfizer, and Moderna. Health Minister Juan Carlos Zevallos expects the first shipment of 50,000 doses is expected to arrive in the first quarter of 2021. Ecuador is also part of the COVAX vaccine facility.
- Also on November 25, China’s Sinopharm submitted an application to Chinese authorities to market its COVID-19 vaccine based on trial results. China has five other domestically produced COVID-19 vaccines in phase three trials in at least 16 countries.
Country Focus
- Brazil: Amidst the world’s third-most cases and second-most deaths, Brazilian municipal elections concluded on November 29 after a six-week delay due to the pandemic. The elections involved 500,000 city council candidates and 19,000 mayoral candidates in more than 5,570 municipalities. Although voting in Brazil is mandatory, abstention reached 29 percent according to the Organization of American States, which could possibly be explained by the pandemic.
- Colombia: According to a UN High Commissioner for Refugees report dated December 1, an average of 400 Venezuelans transiting on foot enter Colombia daily via informal crossing points in Arauca and Cúcuta.
- Mexico: After reaching a new daily record of additional COVID-19 cases on November 27 (12,081 additional cases in a day), World Health Organization Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus raised concerns over Mexico’s management of the pandemic. Mexico has the world’s fourth highest death toll and over 1 million confirmed cases. The government has repeatedly said real numbers are likely significantly higher than official figures.
- Trinidad and Tobago: Trinidad and Tobago signed a $64 million development aid funding agreement with the European Union (EU), developed in partnership with the Ministry of Planning and Development and the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB). The Caribbean Industrial Research Institute (CARIRI) will be the key implementing partner of the program, which seeks to drive economic growth and jobs in a socially and environmentally sustainable way.
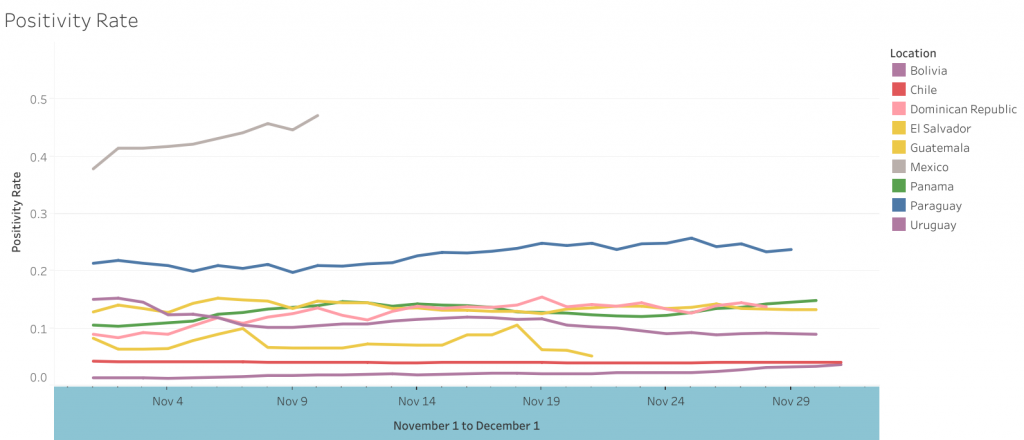
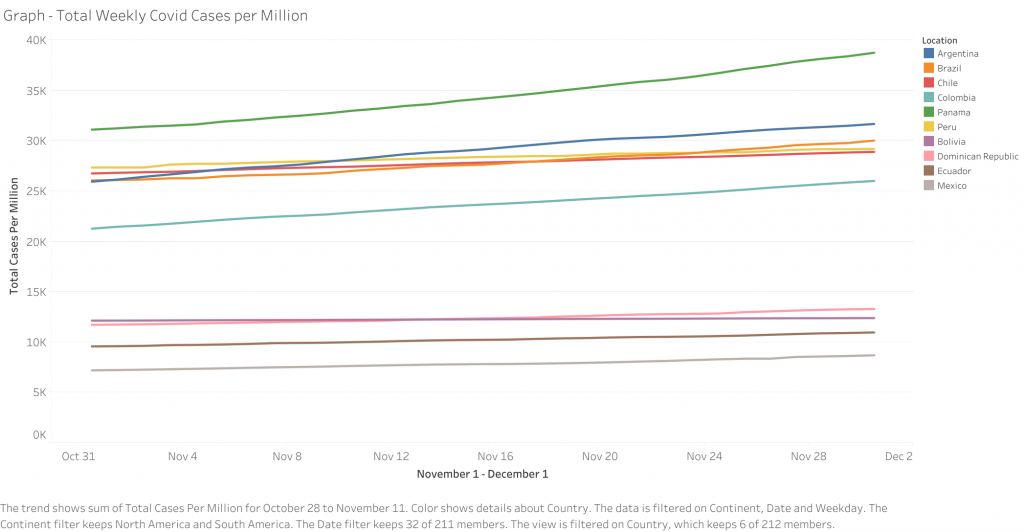
By the numbers
- Cases by country: Brazil (6,388,526) #3 worldwide, Argentina (1,432,570) #9 worldwide, Colombia (1,324,792) #10 worldwide, Mexico (1,122,362) #11 worldwide, Peru (965,228) #15 worldwide, Chile (552,864) #21 worldwide, Ecuador (193,673) #40 worldwide, Panama (167,311) #43 worldwide, Bolivia (144,810) #46 worldwide, Dominican Republic (144,302) #47 worldwide, Source: worldometers.info
- Prevalence rate (total cases per million people): Aruba (45,551) #11 worldwide, Panama (38,524) #14 worldwide, Argentina (31,576), Brazil (29,996) #30 worldwide, Peru (29,105) #32 worldwide, Chile (28,818) #33 worldwide, Costa Rica (27,412) #34 worldwide, Colombia (25,921) #29 worldwide, Bahamas (19,105) #56 worldwide, Saint Martin (18,413) #59 worldwide, Source: worldometers.info
- Deaths per capita (deaths per million people): Peru (1,086) #3 worldwide, Argentina (858) #9 worldwide, Mexico (824) #12 worldwide, Brazil (816) #14 worldwide, Chile (804) #15 worldwide, Bolivia (763) #18 worldwide, Ecuador (760) #19 worldwide, Colombia (723) #22 worldwide, Panama (713) #23 worldwide, Aruba (421) #37 worldwide, Source: worldometers.info
Quick take
Sponsored By

