Retaliation and resistance: China’s economic statecraft in a Taiwan crisis
Table of contents

Chinese economic statecraft in a Taiwan crisis: Tools and applications
China’s capacity to circumvent financial sanctions and G7 economic statecraft
Using international Renminbi networks to circumvent sanctions
Current scope of Renminbi internationalization
Policy constraints on expansion of Renminbi financial networks
Responding to G7 economic statecraft in a crisis
Assessing China’s capacity to respond to G7 statecraft
Financial statecraft and consequences
Preventing escalation in economic warfare
Executive summary
Beijing has watched carefully as Western allies have deployed unprecedented economic statecraft against Russia over the past two years. Our report from June 2023 modeled scenarios and costs of Group of Seven (G7) sanctions in the event of a crisis in the Taiwan Strait. However, that report largely left unanswered a critical question: How would China respond?
This report examines China’s ability to address potential US and broader G7 sanctions, focusing on its possible retaliatory measures and its means of sanctions circumvention. We find that reciprocal economic statecraft measures would exact a heavy financial toll on the G7, China itself, and the global economy. Crucially, however, we also find that China is developing capacities that are making its economy more resilient to Western sanctions.
We consider the use of economic statecraft tools in two main scenarios: a moderate escalation over Taiwan limited to the United States and China that remains short of military confrontation, and a more severe scenario with G7-wide restrictions targeting Chinese firms and financial institutions. For each, we consider China’s potential responses to adversarial economic statecraft in terms of retaliatory action (including restrictions on economic activity within China and China’s potential actions abroad) and attempts to circumvent G7 sanctions.
We arrive at seven key findings:
- China’s economic statecraft toolkit is quickly expanding. In the past five years, China has used a range of formal and informal statecraft tools, including tariffs, import bans, boycotts, and inspections, to punish firms and countries for their stances on Taiwan and other sensitive issues. In anticipation of the potential for more extensive foreign sanctions, China has also been legislating to equip itself with an expanded toolkit to respond. This scope of options distinguishes China from Russia, which had prepared for additional sanctions in a less organized fashion, and presents a significantly more difficult challenge for Western economic statecraft.
- China’s statecraft toolkit is heavily weighted toward trade and investment rather than financial statecraft. We assess that in a moderate scenario where US exports to China are curtailed, more than $79 billion worth of US goods and services exports (such as automobiles and tourism) would be at risk. In a higher-escalation scenario involving G7-wide sanctions against China, around $358 billion in G7 goods exports to China could be at risk from the combination of G7 sanctions and Chinese countermeasures. On the imports side, we estimate that the G7 depends on more than $477 billion in goods from China which could be made the target of Chinese export restrictions. Regarding investment, at least $460 billion in G7 direct investment assets would be at immediate risk from the combined impact of G7 sanctions and retaliatory measures by Beijing. By comparison, China has limited financial tools available to directly influence G7 economies. What restrictions China imposes on capital outflows are likely to be driven more by financial stability concerns rather than attempts to coerce.
- China will face steep short- and medium-term costs if Beijing deploys economic statecraft tools. China would face high economic and reputational costs from using economic statecraft tools, especially in a high-escalation scenario. While export restrictions would be one of China’s most impactful economic statecraft tools, it would also be among the costliest options for China. Over 100 million jobs in China depend on foreign final demand, and nearly 45 million of these jobs depend on final demand from G7 countries. In a high-escalation scenario, most of these jobs would at least temporarily be put at risk. Even in a moderate-escalation scenario, China’s viability as a destination for foreign investment would dramatically decline, with implications for China’s exchange rate and domestic financial stability.
- China may prefer to avoid tit-for-tat retaliation for strategic reasons. As a result of the major costs to its citizens, China is unlikely to follow a tit-for-tat approach but will target sectors where it can inflict asymmetric pain, particularly through the use of export controls or trade restrictions on critical goods such as rare earths, active pharmaceutical ingredients, and clean energy inputs (e.g., graphite). China’s political objectives in a Taiwan crisis are unlikely to be served with a completely reciprocal response to G7 sanctions.
- China will likely attempt to divide the G7 and thereby limit the impact of sanctions. In scenarios where the United States alone imposes sanctions on China, Beijing has more opportunities to circumvent sanctions using targeted retaliatory measures against the United States, but not other G7 countries. The G7 has varied relations with and commitments to Taiwan, and a significant proportion of firms, particularly in Europe, continue to see China as a critical export destination. In addition, China may use positive inducements to encourage countries across the Group of Twenty (G20) to stay neutral. Beijing may also leverage its large bilateral lending with a range of emerging and developing economies to attempt to circumvent or not implement G7 sanctions.
- China is seeking to create resiliency to sanctions by developing alternatives to the dollar-based financial system, including renminbi-denominated transaction networks. Renminbi-based networks are never likely to replace the US dollar-denominated global financial system. However, the gradual expansion of these networks can help Beijing find alternative mechanisms for maintaining access to financing and trade transactions even in the event of far reaching Western sanctions or trade restrictions. A rapidly growing number of domestic and cross border payment projects are being designed with the possibility of Western sanctions in mind.
- The timing of any crisis can significantly alter the impact of statecraft tools, for both the G7 and Beijing. Western efforts to de-risk and shift supply chains in the next five years may reduce Beijing’s “second strike” statecraft capacity over time. At the same time, China’s renminbi-based financial networks will expand in scope and liquidity, providing Beijing with more options to mitigate Western sanctions.
Introduction
The prospect of a crisis over Taiwan has generated intense discussion in recent years, as other unthinkable scenarios in global affairs have become depressingly manifest. Russia’s invasion of Ukraine presented the United States and its allies with a need to quickly escalate economic sanctions and other tools of statecraft against Russia as part of a broader political response. As tensions in the Taiwan Strait have risen, the policy community began asking whether similar tools could be used to deter China in a Taiwan crisis scenario. Senior leaders in China increasingly reference risks from Western sanctions in policy remarks, and Beijing has reportedly conducted its own assessments of China’s vulnerabilities to Western economic sanctions.1Zongyuan Zoe Liu, “China’s Attempts to Reduce Its Strategic Vulnerabilities to Financial Sanctions,” China Leadership Monitor, March 1, 2024, https://www.prcleader.org/post/china-s-attempts-to-reduce-its-strategic-vulnerabilities-to-financial-sanctions; Reuters, “$2.6tn could evaporate from global economy in Taiwan emergency,” August 22, 2022, https://asia.nikkei.com/static/vdata/infographics/2-dot-6tn-dollars-could-evaporate-from-global-economy-in-taiwan-emergency/.
As tensions have risen within the US-China bilateral relationship, policymakers and analysts have started to actively discuss the potential use of sanctions, export controls on critical technologies, and China’s retaliatory responses. These economic statecraft tools are now being considered as options within a broader multilateral strategy toward China, without fully considering the consequences for cross-strait stability or the global economy. Over the last two years, economic warfare has become more plausible, even if military engagement still seems remote.
In June 2023, Rhodium Group and the Atlantic Council GeoEconomics Center published a report that found that the Group of Seven (G7) would likely consider a wide range of economic measures to deter or punish China in a Taiwan-related crisis scenario.2Vest and Kratz, Sanctioning China in a Taiwan Crisis. While that report highlighted what tools might be considered and their direct costs to the global economy, it largely set aside questions about China’s own economic statecraft tools and responses. This report aims to fill that gap and discuss China’s potential responses to G7 sanctions or other tools of statecraft.
While still extremely costly in economic terms, these tools are nonetheless likely to be considered in a crisis since the costs of war are far higher. But unless the US-China political tensions over Taiwan can be managed, these lines between economic and military warfare will be blurred in any crisis scenario, with economic statecraft tools appearing as plausible and manageable responses.
This is exactly why understanding China’s potential responses to US and allied statecraft is so important. Understanding China’s capacity for economic coercion and circumvention can help refocus policy debate around credible and effective deterrence of both broader military conflict and the steady escalation of tensions from more limited crisis scenarios. Just as theories of nuclear deterrence account for the concept of second-strike capabilities, so too must we consider economic retaliatory measures in assessing the deterrence character of sanctions.3See also the discussion of sanctions and deterrence theory in Chapter 6 of Henry Farrell and Abraham Newman, Underground Empire: How America Weaponized the World Economy (New York: Henry Holt and Co., 2023). Recent actions by Beijing to establish export controls on critical raw materials and other critical inputs reveal that Beijing is practicing and refining its use of economic leverage, but the contours of China’s ability, willingness, and channels for action are not well understood.
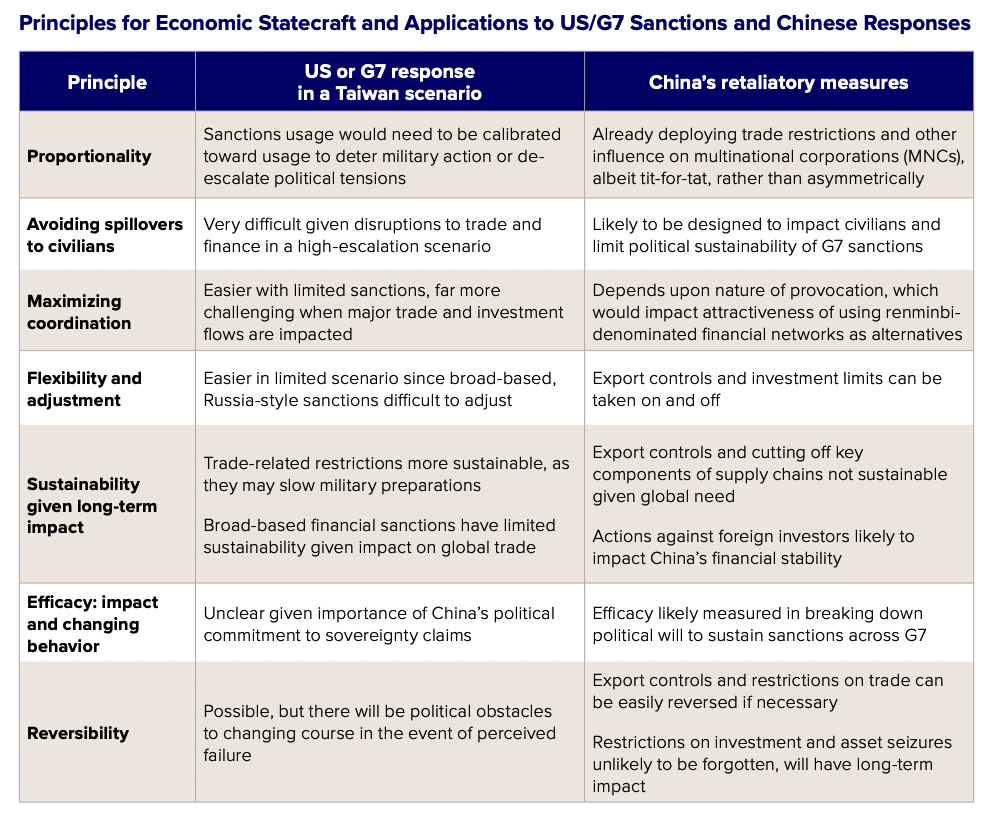
A February 2024 Atlantic Council policy brief by a senior US official (at the time out of government) with deep experience in this domain outlined seven principles for the effective use of economic statecraft.4Daleep Singh, “Forging a positive vision of economic statecraft,” New Atlanticist, Atlantic Council, February 22, 2024, https://www.atlanticcouncil.org/blogs/new-atlanticist/forging-a-positive-vision-of-economic-statecraft/. While these principles focus on US options, the framework can also be used to evaluate the effectiveness of China’s policy instruments.
Designing and implementing a set of economic statecraft instruments in a Taiwan crisis scenario to achieve political objectives requires clarity on the trade-offs involved among these principles, and where benefits will outweigh costs. In a Taiwan crisis, decisions will need to be made quickly, making it critical to understand China’s potential response. While China’s retaliatory tools can inflict significant short-term economic pain, and China’s leaders may not be considering the same principles as outlined in the table below, Beijing will also struggle to mount an economic statecraft strategy that is both sustainable and effective in limiting G7 policy choices toward China. This study aims to improve understanding of the uses and limits of China’s statecraft tools, as well as the potential costs of escalation, in order to make the commitments from both sides to deescalate in a crisis far more credible.
For the purposes of this report, we are limiting the measures discussed to explicitly economic tools and sources of economic power, even as we are aware that any crisis scenario would also include consideration of other nonmilitary options such as cybersecurity-related measures or disinformation campaigns, as well as military coercion below the threshold of war. Conventional wisdom assumes that China’s response would be coordinated and centralized, free from the democratic factors that constrain US and G7 action, including rule of law and separation of authorities across different branches of government and agencies. This study questions some of those assumptions, as Chinese bureaucratic interests are likely to clash on the question of the country’s need for US dollar inflows in the event of economic sanctions, as well as China’s economic interests in imposing restrictions on trade.
In chapter one, we build a framework to categorize the channels of economic interaction at risk from Chinese economic statecraft. In chapter two, we explore how each of these tools might be used at different levels of escalation, up to the level of retaliation against a major G7 sanctions program. In chapter three, we review China’s capacity to circumvent sanctions and statecraft using financial networks outside of the US dollar system.
This paper, and our prior work on sanctions options in a Taiwan crisis, focuses primarily on China and the G7. A forthcoming paper will explore the role of the G20 in a Taiwan contingency.
Chinese economic statecraft in a Taiwan crisis: Tools and applications
No country has ever tried to sanction an economy of China’s size and importance to the global economy. The use of economic statecraft against Russia following its invasion of Ukraine was exceptional in its breadth and its level of international coordination, but Russia was only the world’s eleventh-largest economy before the war began and had few economic countermeasures available aside from energy export denial.
As the world’s second-largest economy and premier manufacturing powerhouse, China has a far larger toolkit of economic policy instruments. It also has a history of using economic leverage assertively to achieve foreign policy objectives, though with mixed success. That experience means retaliatory efforts are nearly certain in ways the Western powers did not experience after imposing sanctions on Russia in 2014 and 2022 onward. In past work we took stock of economic statecraft tools available to the G7 and the costs and limitations of their use. In this chapter we catalogue China’s economic statecraft tools and applications, and assess the likeliness of their use in moderate or high Taiwan scenario escalations.
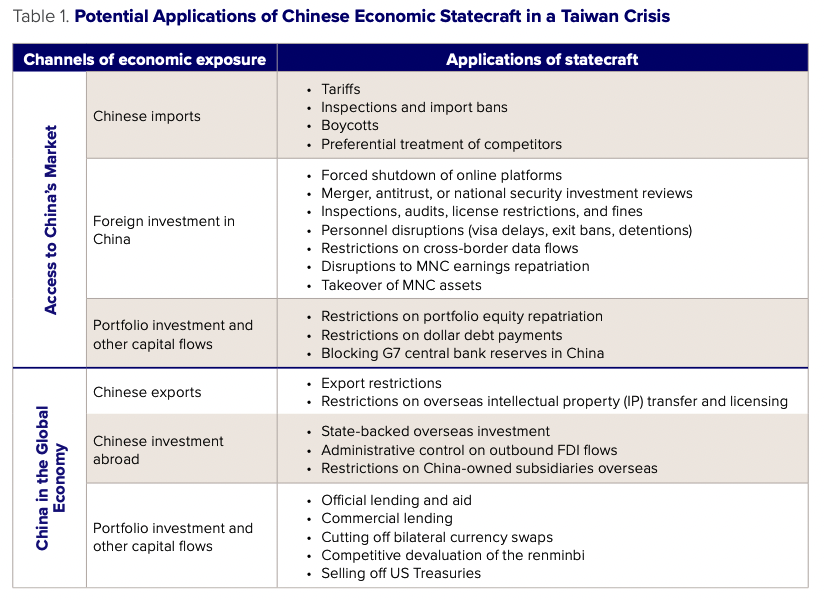
Drawing on past case studies and China’s growing legal and regulatory toolkit, we identify a range of economic statecraft actions that China could use in a Taiwan Strait escalation scenario. Scholars of economic statecraft typically subdivide statecraft tools into categories based on their direction (i.e., inbound or outbound flows) and on their channel (i.e., trade or capital flows).5David A. Baldwin, Economic Statecraft (Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1985); China Center, Understanding U.S.-China Decoupling: Macro Trends and Industry Impacts, U.S. Chamber of Commerce and Rhodium Group, 2021, https://www.uschamber.com/assets/archived/ images/024001_us_china_decoupling_report_fin.pdf. In the first section of this chapter, we look at access to China’s markets—i.e., the potential use of statecraft tools against economic flows into China, looking respectively at trade, foreign direct investment (FDI), and portfolio flows. In the second section, “China in the Global Economy,” we look at the use of statecraft tools aimed at these flows from an outbound perspective.
There is substantial debate within Chinese expert circles on the use of these tools. Academics and experts affiliated with China’s financial and economic bureaucracy often argue that defending against economic sanctions starts by building a strong financial system to improve domestic resilience and by deepening China’s global economic ties to increase the economic and diplomatic costs on the sanctioning economy. Zhang Bei, an economist at the People’s Bank of China’s (PBOC) Financial Research Institute, has argued that although China needs to strengthen countersanctions tools such as the Unreliable Entity List and Anti-Foreign Sanctions Law, it also needs to strengthen management of domestic financial risks and deepen global economic engagement through renminbi internationalization and international financial cooperation.6Zhang Bei, “Impact of Financial Sanctions on National Financial Security and Countermeasures,” China Security Studies (October 30, 2022), accessed via CSIS Interpret: China, https://interpret.csis.org/translations/impact-of-financial-sanctions-on-national-financial-security-and-countermeasures/. Chen Hongxiang, another PBOC-affiliated researcher, describes the anti-sanctions policy toolbox as a “last resort strategy.”7Chen Hongxiang, “Logical Analysis of U.S. Financial Sanctions and China’s Contingency Plans,” Contemporary Finance (October 10, 2022), accessed via CSIS Interpret: China, https://interpret.csis.org/translations/logical-analysis-of-u-s-financial-sanctions-and-chinas-contingency-plans/. Chen notes that the United States faces limitations in the use of financial sanctions given the risks to the attractiveness of the US dollar as a global currency and the diplomatic and economic costs of sanctions.
Other scholars have discussed China’s use of retaliatory measures and the legal foundations for responses in the future. For example, Yan Liang of Nankai University has described trade controls on strategic resources as having played an important role in China’s sanctions toolkit in the past, noting the 2010 export controls on rare earths.8Yan Liang, “China’s Economic Sanctions: Goals and Policy Objectives,” Foreign Affairs Review 6 (2012), China Foreign Affairs University. Cai Kaiming, a Chinese cross-border compliance lawyer, has written about the newly developed legal foundations of Chinese economic statecraft tools, including the Anti Foreign Sanctions Law, the 2021 blocking statute, the Unreliable Entity List, and the reciprocal measures of China’s Export Control Law, Data Security Law, and Personal Information Protection Law (see Appendix 1).9Cai Kaiming, “Research on American Legal Polices Against China and China’s Countermeasures,” Dentons China, 2022, http://dacheng.com/ file/upload/20230105/file/20230105164302_762feab8ea3a4756b88f12397470f0e5.pdf. “Blocking statute” refers to the Ministry of Commerce Order No. 1 of 2021 on Rules on Counteracting Unjustified Extraterritorial Application of Foreign Legislation and Other Measures. Throughout this paper, we consider the use of these new formal tools in a Taiwan crisis scenario, as well as the range of informal tools available, such as phytosanitary inspections and administrative orders, to China’s customs department. Given the range of both formal and informal tools available for the purpose of statecraft, the focus of this paper is on the ends, rather than the means. These tools span many different bureaucratic jurisdictions, but it is likely that, as in past instances of major statecraft actions where major costs to China’s economy are involved (such as China’s retaliatory tariffs against the United States in 2018), the decision to use these tools will come from China’s senior-most leadership.
Scenarios
While China’s past use of economic statecraft is instructive, Beijing may not necessarily respond to future escalations with the same old tools, or with the same intensity. In recent years, China showed a willingness to use economic statecraft more explicitly and intensely than in the past, albeit in a concentrated fashion (e.g., trade bans against Lithuania). China has also created new legal frameworks to justify future retaliatory or punitive actions.10Emily Kilcrease, No Winners in This Game Assessing the U.S. Playbook for Sanctioning China, Center for a New American Security, December 2023, https://www.cnas.org/publications/reports/no-winners-in-this-game. In short, we need to make predictions of future use cases beyond the range of China’s past actions.
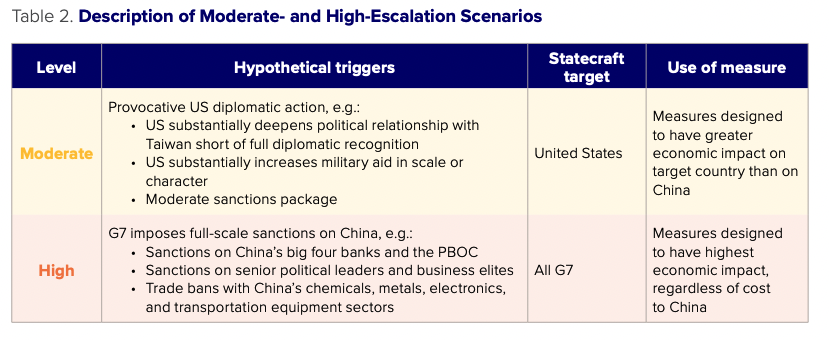
To explore how China might use economic statecraft tools in the future, we consider two scenarios:
Moderate-escalation scenario: China responds to the United States taking an escalatory diplomatic action in the Taiwan Strait, such as a substantial deepening of the political relationship with Taiwan, a step-change in military aid, or a limited sanctions package in response to Chinese aggression toward Taiwan. In this scenario, China reacts with economic statecraft measures targeting the United States designed to impose relatively higher costs on the United States than China. In this scenario, China’s willingness to use statecraft is constrained by the necessity to maintain a strong business environment amid high geopolitical tensions.
High-escalation scenario: China retaliates to a maximalist G7 sanctions package that includes full blocking sanctions on China’s major banks and the PBOC, sanctions on senior political figures and business elites, and trade bans with relevance for China’s military.11Vest and Kratz, Sanctioning China in a Taiwan Crisis China adopts a much stronger and broader set of economic statecraft measures against the entire G7, with an intent to impose costs as high as possible on the sanctioning economies.
Both scenarios stop short of war between China and the United States or other G7 countries, and are meant to provide a context to evaluate the potential use of China’s statecraft tools. We consider only economic statecraft responses in a Taiwan escalation scenario, although China is also likely to consider military and quasi-military actions that are outside the scope of this paper, such as undersea cable cuttings, cyberattacks, or blockades. Where we highlight costs in dollar terms, they should be understood as the assets and annualized economic flows at risk of disruption unless otherwise specified.
Access to Chinese markets
One of China’s primary methods of exercising economic statecraft in the past has been to restrict access to its markets, either through trade barriers or disruptions to the operations of foreign companies and investors in China. In this section we consider the use of these tools in the past and in moderate- and high-escalation future scenarios.
Chinese imports
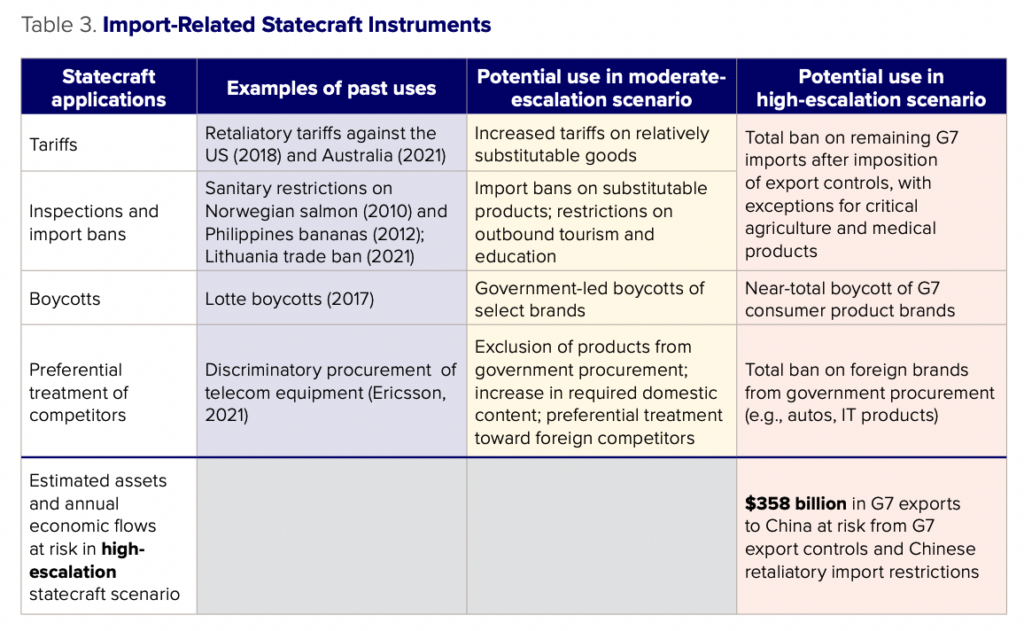
One of China’s primary methods of exercising economic statecraft in the past has been to restrict access to its markets through tariffs and nontariff barriers. In a moderate escalation with the United States over Taiwan, China could scale up these tools to restrict imports across a range of noncritical goods such as consumer products, easily substitutable goods, and goods where the United States is heavily dependent on China as an export market. In a higher-escalation scenario involving a maximalist G7 sanctions program, China could impose import bans on a broader range of goods, although the main initial disruptions to imports would likely come from sanctions against Chinese banks and importers. A total ban on G7 imports, with exceptions for critical agricultural and medical imports, would put $358 billion in exports to China at risk.
Past uses of statecraft
Restrictions on market access have been one of China’s most common forms of coercion in past geopolitical incidents. In most cases, these tools have been narrowly targeted—either against single companies or narrow product categories—to minimize the impacts on China’s economy and to act as a warning rather than full-blown punishment mechanism. Yet they have the potential to be scaled up in response to higher levels of escalation, especially as many G7 companies depend heavily on the Chinese market for revenue and growth.
- Tariffs – In numerous past cases, China has increased tariff rates on imported products in an apparent response to political actions taken by other countries. China retaliated against the Trump administration’s imposition of across-the-board tariffs on Chinese exports to the United States, resulting in a 21% average tariff rate on goods imported from the United States.12Chad P. Brown, “US-China Trade War Tariffs: An Up-to-Date Chart,” Peterson Institute for International Economics, April 6, 2023, https://www.piie.com/research/piie-charts/2019/us-china-trade-war-tariffs-date-chart. After members of Australia’s cabinet called for independentinvestigations into the origins of COVID-19 in April 2020, China imposed economic restrictions on a range of Australian products. China’s Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM) announced tariffs as high as 218 percent on Australian wine and 80.5 percent tariffs on barley.13Richard McGregor, “Chinese Coercion, Australian Resilience,” Lowy Institute, October 2022, https://www.lowyinstitute.org/publications/ chinese-coercion-australian-resilience; Ministry of Commerce of the People’s Republic of China, “Announcement on the Final Ruling on the Anti-dumping Investigation into Imported Wine Originating from Australia,” 2021, http://www.mofcom.gov.cn/article/zcfb/zcblgg/202103/20210303047613.shtml; Ministry of Commerce of the People’s Republic of China, “Announcement on the Final Ruling of the Anti-dumping Investigation into Imported Barley Originating from Australia,” 2020, http://gpj.mofcom.gov.cn/article/cs/202005/20200502965862.shtml. In these cases, China provided the justification for higher tariffs on the basis of anti-dumping action against Australian exporters, but the timing and character of the tariffs led to speculation that the tariffs were retaliatory action by the Chinese government.14McGregor, “Chinese Coercion. Notably, China targeted goods where the costs to China’s economy would be lower than products like natural gas and iron, for which Australia also depends on China as an export market. In the Australia case, MOFCOM was responsible for raising tariffs, but the State Council itself also has powers to increase tariffs, as it did in imposing retaliatory tariffs against the Trump administration’s June 15, 2018, Section 301 tariff announcement.15Chad P. Bown, Euijin Jung, and Zhiyao (Lucy) Lu, “China’s Retaliation to Trump’s Tariffs,” Trade and Investment Policy Watch, Peterson Institute for International Economics, June 22, 2018, https://www.piie.com/blogs/trade-and-investment-policy-watch/chinas-retaliation-trumps-tariffs; State Council of the People’s Republic of China, “Announcement of the Tariff Commission of the State Council on Imposing Additional Tariffs on $50 Billion of Imported Goods Originating in the United States,” June 2018, https://finance.sina.com.cn/roll/2018-06-16/doc-ihcyszsa0555207.shtml.
- Inspections and import bans – China also exerts economic pressure through inspections and informal bans on imported goods. In 2010, China effectively banned salmon imports from Norway on the pretense of a violation of sanitary regulations after the Norwegian Nobel Committee awarded the Nobel Peace Prize to dissident Liu Xiaobo.16Richard Milne, “Norway sees Liu Xiaobo’s Nobel Prize hurt salmon exports to China,” Financial Times, August 15, 2013, https://www.ft.com/content/ab456776-05b0-11e3-8ed5-00144feab7de. China banned banana imports from the Philippines on health grounds in 2012 amid tensions in the South China Sea.17Andrew Higgins, “In Philippines, banana growers feel effect of South China Sea dispute,” Washington Post, June 10, 2012, https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/asia_pacific/in-philippines-banana-growers-feel-effect-of-south-china-sea-dispute/2012/06/10/gJQA47WVTV_story.html The most recent major case followed the opening of a Taiwanese Representative Office in Lithuania in 2021.18Reuters, “Taiwan opens office in Lithuania, brushing aside China opposition,” November 18, 2021, https://www.reuters.com/world/china/taiwan-opens-office-lithuania-brushing-aside-china-opposition-2021-11-18/. China imposed a de facto ban on imports from Lithuania through a range of measures, including denials of trade finance, revocation of import permits, the removal of Lithuania from China’s customs system, and cancelation of freight shipping to Lithuania by a Chinese rail shipping operator. Given that Lithuania only accounts for 0.003 percent of Chinese imports and its goods are primarily agricultural, the immediate cost to the Chinese economy from the import bans was limited. However, the diplomatic blowback from targeting a European Union (EU) member state with a full trade ban was arguably quite high. Coercion against Lithuania led the EU to raise a trade case in the World Trade Organization against China, and it likely strengthened support for the creation of the Anti-Coercion Instrument. It is a matter of debate whether China took these actions against Lithuania accepting these costs, or whether it underestimated the harshness of the EU’s reaction.
- Boycotts – China uses its state media to foment and support boycotts of foreign brands during crises. In 2022, Chinese consumers boycotted H&M for its refusal to use cotton from Xinjiang with backing from state media and party organizations.19Tu Lei, “H&M boycotted for ‘suicidal’ remarks on Xinjiang affairs,” Global Times, March 24, 2021, https://www.globaltimes.cn/page/202103/1219362.shtml. In February 2017, the Lotte Group approved a land swap with the South Korean government to place a Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) missile defense system on its former property. In response, China forced the closure of 74 Lotte supermarkets for supposed fire safety violations and published news articles urging consumers to punish South Korea “through the power of the market.”20Darren J. Lim and Victor A. Ferguson, “Informal economic sanctions: the political economy of Chinese coercion during the THAAD dispute,” Review of International Political Economy 29 (5) (2002): 1525–1548, https://doi.org/10.1080/09692290.2021.1918746. In both cases, China focused on companies that had ample local competition and low import dependence to mitigate the costs to China’s economy. South Korean companies in petrochemicals and semiconductors, by contrast, saw limited or no effect on their performance during the THAAD incident.21Ibid.
- Preferential treatment of competitors – Beijing’s direct and indirect control of state-run procurement provides leverage over foreign firms hoping to capture a slice of China’s market. Companies fear that officials can manipulate the bidding process to hurt their sales and exert influence on their home countries. One example came in 2021 after Swedish authorities implemented a ban on Huawei and ZTE 5G technology in late 2020. In subsequent bidding for state-owned China Mobile in June 2021, Ericsson’s share of 5G equipment awards dropped by nearly 80 percent. Ericsson had previously lobbied against the ban in Sweden, fearing it would be targeted for retaliation in China,22Stu Woo, “Ericsson Warns China Backlash Threatens Its Market Share,” Wall Street Journal, July 16, 2021, https://www.wsj.com/articles/ericssonwarns-china-backlash-threatens-its-market-share-11626440735; Jonas Froberg and Linus Larsson, “Ericssons vd Börje Ekholm bekräftar påtryckningar från Kina” [Ericsson CEO Börje Ekholm Confirms Pressure from China], Dagens Nyheter, January 4, 2021, https://web.archive.org/web/20210106070006/https://www.dn.se/ekonomi/ericssons-vd-borje-ekholm-bekraftar-patryckningar-fran-kina/. and an editorial in the state-run Global Times later tied the bidding results to Sweden’s policy decision.23Li Qiaoyi and Shen Weiduo, “Ericsson’s setback in China linked to Sweden’s crackdown on Chinese firms: source,” Global Times, July 22, 2021, https://www.globaltimes.cn/page/202107/1229399.shtml.

Potential use in moderate-escalation scenario
How countries choose which imports to restrict is a central question of economic statecraft. In China’s retaliation against US tariffs in 2018, China’s tariffs tended to target US exports produced disproportionately in counties that leaned Republican and voted for then president Donald Trump in 2016, suggesting a political influence logic to China’s tariff targets.24Thiemo Fetzer and Carlo Schwarz, “Tariffs and Politics: Evidence from Trump’s Trade Wars,” Economic Journal 131 (636) (May 2021): 1717–1741, https://doi.org/10.1093/ej/ueaa122. More broadly, policymakers are likely to think about the effectiveness of tariffs: Is the sender country able to bear the cost of sanctions while imposing enough damage to compel the other side to make concessions?25Kerim Can Kavakli, J. Tyson Chatagnier, and Emre Hatipoğlu, “The Power to Hurt and the Effectiveness of International Sanctions,” Journal of Politics 82 (3) (July 2020), https://doi.org/10.1086/707398.
Past instances of China’s restrictions on imports have typically been targeted in ways that limit costs to China’s economy: single firms, narrow sectors, or smaller economies. In a scenario involving the United States in a moderate escalation over Taiwan, China might accept elevated costs if it felt that sanctions on the United States were necessary to signal resolve, punish US behavior, or deter further action. In such a circumstance, China could target a range of sectors where costs to the US economy are high and costs to the Chinese economy, though elevated, are still relatively low. The tools used are likely to be the same as in the past: some combination of higher tariffs and both formal and informal import restrictions. The key question facing Chinese policymakers would be which sectors and goods to target.
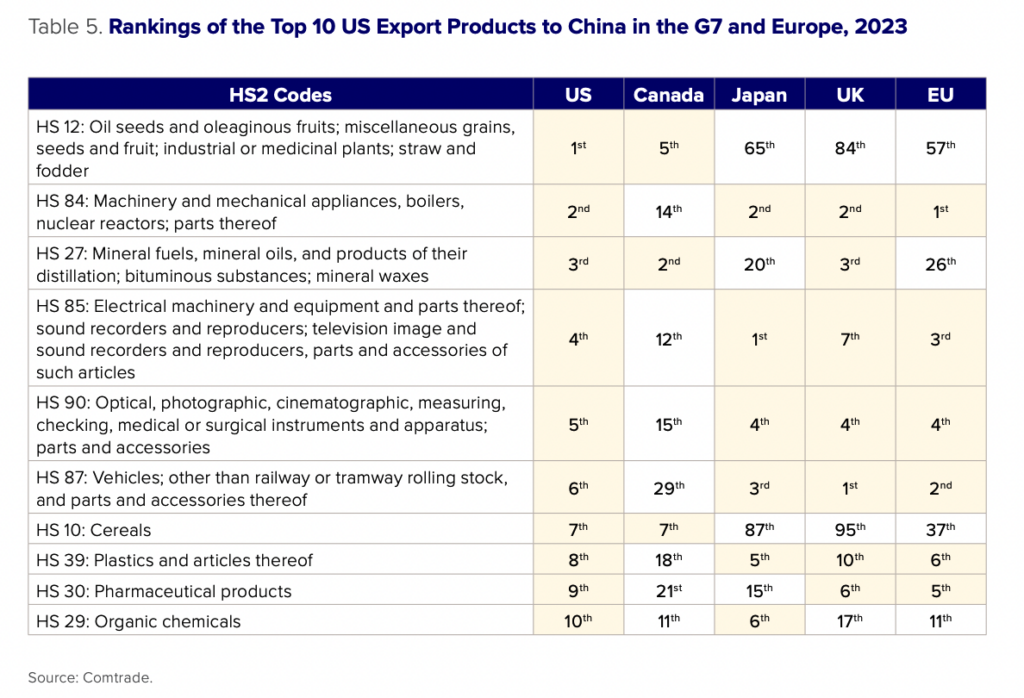
First, China could target consumer discretionary products such as imported cars and cosmetics. While consumers would face higher costs and fewer choices, a ban on these products would have a far lower impact on the Chinese economy than a ban on intermediate goods or capital goods that China depends on for industrial production. If restrictions were expanded to US-branded products made in China (Tesla cars made in Shanghai, for instance), China would face some employment impacts, but in general these would likely be the easiest goods to target.
Second, China could target products where it has diversified imports and the United States has limited market power. China imports commodities such as crude oil, coal, polyethylene, and copper ore from the United States, but in small quantities relative to other exporters. China could likely impose high tariffs or bans on such goods from the United States, and procure them from other countries (albeit at higher costs). While not included in the table below, China might also include products where import dependence is still high but where China is actively pursuing self-sufficiency and strong local players are emerging, such as medical devices. China would likely avoid targeting critical inputs to its supply chains that would be difficult or costly to replace quickly, such as integrated circuits.
Finally, China could target areas based on how much the United States depends on China as an export market. In 2022, over half of US exported soybeans went to China, as did 83 percent of its exported sorghum. US dependence on China for its agricultural goods informed China’s decision to target these goods in response to the Section 301 tariffs. Yet the costs to China for imposing tariffs on these products would also be high: the United States supplied 31 percent of China’s imported soybeans and 64 percent of its imported sorghum. China would likely tailor the strength of its import restrictions depending on global agricultural conditions and whether alternative supply could be found elsewhere.
Tariffs or bans on US imports could also provide China with an opportunity to drive wedges between the United States and other countries. Sustained demand from Chinese consumers amid higher restrictions on US imports would increase demand for imported goods elsewhere. As a group of advanced industrial economies, the G7’s exports overlap substantially with US exports that could be at risk from Chinese trade barriers. Table 5 shows the top ten exports from the United States to China by value, and the export rank of those products from other G7 countries and Europe to China. For every product that ranks among the United States’ top ten exports to China, at least one other G7 country (and often multiple countries) also have that product ranked in their top exports to China. While these products are often diverse and not completely substitutable, the overlap in the export baskets of G7 countries to China points to the potential for China to exploit competitive dynamics between the United States and other G7 countries.
Potential use in high-escalation scenario
In a maximalist-escalation scenario, the initial disruptions to foreign exports to China would stem from G7 sanctions themselves rather than Chinese retaliation. As we argued in our June 2023 study on G7 sanctions toward China in a Taiwan crisis, many goods such as chemicals, energy, and electrical equipment would likely fall under a strengthened G7 export control regime, putting hundreds of billions of dollars of trade at risk.26Vest and Kratz, Sanctioning China in a Taiwan Crisis Sanctions on China’s banking system would limit exporters’ ability to settle transactions with importers.
Over time, however, foreign businesses could shift their transactions to unsanctioned importers and banks. Despite sanctions on much of Russia’s economy, at least 101 multinational companies from G7 countries are continuing operations in Russia as of January 2024, according to Yale researchers.27Chief Executive Leadership Institute, “Yale CELI List of Companies Leaving and Staying in Russia,” Yale School of Management, accessed February 29, 2024, https://www.yalerussianbusinessretreat.com/. While some of these firms are operating in sectors that may be considered humanitarian exceptions— such as agriculture and healthcare—most are not.
G7 trade with Russia fell by more than half in 2022. One quarter of the remaining trade is in agricultural commodities, medicine, and medical devices, which are explicitly authorized under a general license from the US Office of Foreign Assets Control.28Office of Foreign Assets Control, “Russia-related General License 6C – Transactions Related to Agricultural Commodities, Medicine, Medical Devices, Replacement Parts and Components, or Software Updates, the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pandemic, or Clinical Trials (January 17, 2023),” US Department of the Treasury, accessed March 15, 2024, https://ofac.treasury.gov/sanctions-programs-and-country-information/russian-harmful-foreign-activities-sanctions. But despite sanctions on many major Russian firms and banks, G7 countries exported almost $25 billion in non-agriculture and non-medical products to Russia in 2022, regardless of the reputational and logistical challenges of exporting even permitted goods to Russia.
The resilience of G7 exports to Russia after sanctions suggests that trade with China, though diminished, could continue even in a maximalist sanctions regime. Broadly speaking, there are three groups of exports in a maximalist sanctions program: (1) goods at higher risk of G7 export restrictions, (2) goods at higher risk of Chinese import restrictions as retaliation, and (3) goods at lower risk of either G7 or Chinese restrictions.
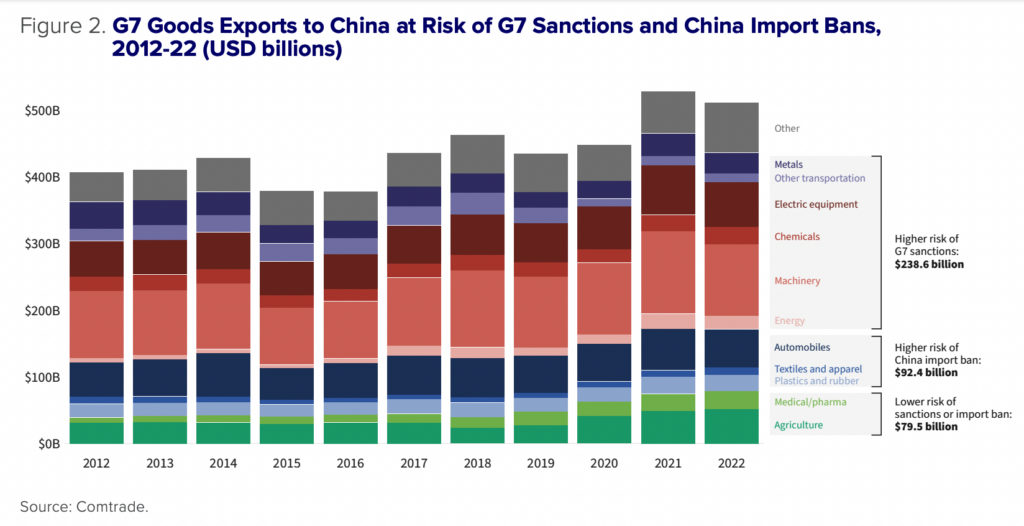
It is impossible to know a priori what sectors G7 countries would agree to impose strict export controls upon, given the substantial costs to their own economies from these sanctions. But for the sake of this analysis, we assume that energy, machinery, chemicals, electrical equipment, trains, planes, and metals are at higher risk of G7 sanctions, making Chinese import restrictions in these sectors less relevant.
What’s left? China imported $92.4 billion in automobiles, plastics, textiles, and rubber from G7 countries in 2022. Losing these imports would certainly be costly to the Chinese economy, but not fatal, making them possible candidates for Chinese retaliation in a maximalist scenario.
Finally, China imported $79.5 billion in agricultural goods, pharmaceuticals, and medical devices from G7 countries in 2022. Agricultural and medical goods were exempt from G7 sanctions in the Russia case as part of humanitarian carveouts present in all sanction regimes. It is likely they would be exempt from G7 sanctions against China as well. While China is likely to impose some restrictions on agricultural products (as it has in the past against French wine and US soybeans), a total ban on agricultural products from the G7 would be extremely costly to the Chinese economy, even if some of those imports could be backfilled by greater imports from non-G7 countries like Brazil. Medicine and pharmaceuticals would be even more so. In this instance, it seems likely that agricultural and medical goods would face lower risks of a total trade ban from either China or the G7.
Import-related statecraft tools have been a part of China’s economic statecraft toolkit in the past and would likely be featured in a moderate- and high-escalation scenario in the future. In a moderate-escalation scenario, the tools would remain more or less the same, but could target a broader range of sectors where Chinese dependence is low (consumer discretionary goods and substitutable goods) or where US dependence on China as an export market is high. Targeted import restrictions against the United States would also create opportunities for China to weaken G7 unity by importing more from other G7 countries.
In a high-escalation scenario, the initial disruption to foreign market access in China would stem primarily from G7 sanctions and market turbulence more broadly, rather than Chinese countersanctions. China is more likely to be judicious in imposing import bans on agricultural goods and pharmaceuticals against the full G7. Excluding those products, the full range of G7 exports to China at risk from G7 sanctions and Chinese countersanctions is around $358 billion.
Foreign direct investment in China
During past geopolitical crises, China has used investment-related tools such as audits, inspections, and antitrust rules, typically either to punish a specific firm for its own actions (such as perceived support for Taiwanese independence) or to pressure firms to lobby their home governments. In a Taiwan escalation scenario, these tools could be used more expansively, potentially affecting up to $460 billion in G7 investment in China and an estimated $470 billion in annual revenue, but at the cost of undermining investor sentiment and accelerating capital flight from China.
Past uses of statecraft
China’s past use of statecraft against foreign firms domiciled in China indicates the wide range of tools available:
- Forced shutdown of online platforms – China’s cyberspace regulator has in the past used its authorities to force companies to adhere to China’s conception of “One China” on their websites and branding materials. In 2018, the Cyberspace Administration of China (CAC) forced Marriott to temporarily shut down its website in China due to an email questionnaire that listed Hong Kong, Macau, Tibet, and Taiwan as separate countries.29Abha Bhattarai, “China asked Marriott to shut down its website. The company complied.” Washington Post, January 18, 2018, https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/business/wp/2018/01/18/china-demanded-marriott-change-its-website-the-company-complied/.
- Merger/antitrust reviews – China has used its antitrust authority, the State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR), as a powerful extraterritorial tool to block mergers between foreign companies during times of geopolitical tension. It is widely believed that China blocked the $44 billion merger of Qualcomm and NXP in 2018 in retaliation for US Section 301 tariffs on Chinese goods.30Don Clark, “Qualcomm Scraps $44 Billion NXP Deal After China Inaction,” New York Times, January 25, 2018, https://www.nytimes.com/2018/07/25/technology/qualcomm-nxp-china-deadline.html. The deal had been approved by eight other jurisdictions but was ultimately called off, as China’s refusal to approve the deal would have prevented the merged companies from operating in China. SAMR refused to approve the merger of Intel and Israeli firm Tower Semiconductor in 2023 amid escalating US tech controls on Chinese semiconductor firms.31Anirban Sen, “Intel scraps $5.4 bln Tower deal after China review delay,” Reuters, August 16, 2023, https://www.reuters.com/technology/intel-walk-away-54-bln-acquisition-tower-semiconductor-sources-2023-08-16/.
- Inspections, audits, fines, and permit delays – China has often used health, safety, environmental, and quality inspections, tax audits, and other routine regulatory actions to punish firms (or the firm’s home country) for their stances on crossstrait issues. In 2021, the Chinese subsidiaries of Taiwan-owned conglomerate Far Eastern Group were fined $13.9 million for a range of violations, including breaches of environmental protection rules. Far Eastern had been a major donor to Taiwan’s Democratic Progressive Party (DPP), a party that Beijing views as advocating for Taiwan’s independence. In the leadup to the 2024 Taiwan general election, Foxconn’s Chinese subsidies became the subject of tax audits and land-use investigations. The investigations were believed by some to be meant to force Foxconn’s founder, Terry Gou, out of the presidential race to avoid splitting votes away from Beijing’s favored party, the Kuomintang.32Reuters, “Foxconn faces tax audit, land use probe, Chinese state media reports,” October 22, 2023, https://www.reuters.com/technology/foxconn-faces-tax-audit-land-use-probe-chinese-state-media-2023-10-22/. And in 2017, China used fire safety and health code inspections to force the closure of Lotte supermarkets during the THAAD incident.33Cynthia Kim and Hyunjoo Jin, “With China dream shattered over missile land deal, Lotte faces costly overhaul,” Reuters, October 24, 2017, https://www.reuters.com/article/idUSKBN1CT35Y/.
- Personnel disruptions – In some cases, China has imposed restrictions on personnel traveling in or out of China for geopolitical reasons. 34Jennifer Creery, “Buzzfeed journalist denied new China visa following award-winning coverage of Xinjiang crackdown,” Hong Kong Free Press, March 31, 2020, https://hongkongfp.com/2018/08/22/buzzfeed-journalist-denied-new-china-visa-following-award-winning-coverage-xinjiang-crackdown/. China’s aviation regulator in 2019 ordered Hong Kong carrier Cathay Pacific to ban airline staff who supported the Hong Kong protests from traveling to China.35Blake Schmidt, “China Cracks Down on Cathay After Staff Join Hong Kong Protests,” Bloomberg, August 9, 2019, https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2019-08-09/china-bars-cathay-pacific-staff-who-took-part-in-protests. In March 2023, China detained five local staff of Mintz Group, a corporate due diligence firm.36Michael Martina and Yew Lun Tian, “China detains staff, raids office of US due diligence firm Mintz Group,” Reuters, March 24, 2023, https://www.reuters.com/world/us-due-diligence-firm-mintz-groups-beijing-office-raided-five-staff-detained-2023-03-24/. In October 2023, China detained and then arrested a Japanese employee of Astellas Pharma on suspicion of espionage.37Kiyoshi Takenaka and Kaori Kaneko, “China formally arrests Astellas employee suspected of spying, Japan urges release,” Reuters, October 19, 2023, https://www.reuters.com/world/china/china-formally-arrests-astellas-employee-suspected-spying-japan-urges-release-2023-10-19/.
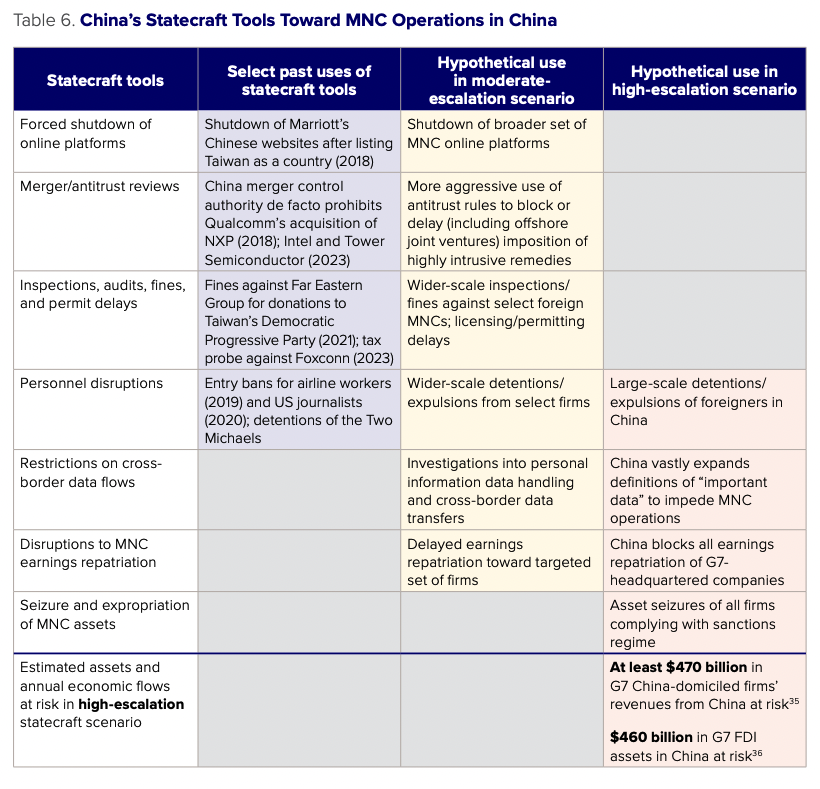
Table footnotes38International Monetary Fund, “Coordinated Direct Investment Survey,” accessed March 15, 2024, https://data.imf.org/?sk=40313609-f037-48c1- 84b1-e1f1ce54d6d5. 39Ministry of Commerce of the PRC, “中国外资统计公报2023年 [Statistical Bulletin of FDI in China 2023],” 2023, https://fdi.mofcom.gov.cn/resource/pdf/2023/12/19/7a6da9c9fb4b45d69c4dfde4236c3fd9.pdf.
Potential use in moderate-escalation scenario
Past methods of disrupting multinational corporation (MNC) activities in China could be scaled up in a moderate-escalation scenario, but the use of these tools runs the risk of accelerating MNC diversification away from China and impairing China’s economy. These tools are more effective when firms believe that, despite short-term tensions, China still holds promise for their business operations and sales.
The CAC could use its powers to shut down US companies’ websites in China, disable their apps, or close their app stores. China could impose these restrictions through a variety of legal and regulatory tools, including revoking a firm’s Internet Content Provider (ICP) filing license or by blocking their Internet Protocol (IP) address within China’s Great Firewall.40Tim Hardwick, “Apple Adopts Tighter Chinese App Store Rules, Closing Foreign App Loophole,” Mac Rumors, October 3, 2023, https://www.macrumors.com/2023/10/03/apple-adopts-tighter-china-app-store-rules/. Through merger reviews, authorities can force companies to choose between abandoning the Chinese market or what can be years-long, multibillion-dollar deals. Inspections, audits, and fines could be scaled up against US firms in a crisis. Personnel disruptions, including tacit hostage-taking as in the cases of Michael Kovrig and Michael Spavor, is extremely worrisome for firms. Put together, these instruments may create a strong incentive for businesses to lobby their home governments for more amicable relations that would allow a deal to go through, but they would also accelerate plans to move operations from China, particularly if it looks like relations will be tense for the long term. Previously unused tools could also be used at higher levels of escalation. China could initiate investigations into a firm’s handling of data or revoke certifications for cross-border data handling. Rules around data, personal information, and cybersecurity ranked second on the list of US companies’ top 10 challenges in China in 2023.41US-China Business Council, Member Survey, 2023, https://www.uschina.org/sites/default/files/en-2023_member_survey.pdf. Already many companies are working to minimize their regulatory risk by partially or completely localizing their data storage, information technology, human resources, and software solutions in China.42Ibid. Data issues are particularly acute in the automotive, healthcare, and financial services sectors, making retaliatory data audits and investigations a possibility in a moderate escalation scenario.43Antonio Douglas and Hannah Feldshuh, How American Companies are Approaching China’s Data, Privacy, and Cybersecurity Regimes, US-China Business Council, April 2022, https://www.uschina.org/sites/default/files/how_american_companies_are_approaching_chinas_data_ privacy_and_cybersecurity_regimes.pdf. Chinese authorities could also restrict how firms repatriate earnings. In past times of macroeconomic stress, China has restricted remittances for MNCs moving money abroad, although there is no evidence suggesting these restrictions were geopolitically motivated.44Erin Ennis and Jake Laband, “China’s Capital Controls Choke Cross-Border Payments,” US-China Business Council, n.d., https://www.uschina.org/china%E2%80%99s-capital-controls-choke-cross-border-payments. Foreign companies in China often repatriate income by issuing dividend payments to their overseas parent companies, which requires certain tax documents and processing by a Chinese bank. Chinese authorities could initiate tax audits targeting US companies to delay repatriation, or order banks to delay or reject processing requests. However, even in a moderate-escalation scenario, China would face macroeconomic pressures that would constrain how aggressively it targeted foreign companies. High geopolitical tensions would likely increase capital outflows and put depreciation pressure on the Chinese currency. Although China has substantial foreign reserves and strong capital controls, China’s reserves are finite and its capital controls are imperfect. Aggressive moves against foreign companies in China could exacerbate capital outflows in ways that Beijing would want to avoid.
Beijing would also seek to avoid moves that make it appear “uninvestable” to foreign firms more broadly. China’s long-term economic and financial stability depends in part on the willingness of foreign investors to continue investing in China, both to offset inherent outflow pressures and to drive productivity through partnerships with world-leading MNCs. Actions taken against MNCs, even if targeted against only one country, could undermine China’s narrative that it is a safe and attractive place for foreign investors to do business.
Potential use in high-escalation scenario
In a high-escalation scenario, China’s willingness to use aggressive economic statecraft actions against MNCs would likely be much higher. G7 sanctions on China’s major banks would immediately make China appear “uninvestable” for many investors, and many MNCs would be executing plans to exit the market even before considering Chinese retaliatory action. At this point, China would have little to gain from holding back on retaliatory actions on a pretense of maintaining “investability.”
Firms selling their assets in China would likely do so at a steep discount given a limited number of buyers and intense pressure to move quickly. Even once assets are sold, it would not be guaranteed that sellers could repatriate the proceeds of the sales to their home countries given strict capital controls on foreign reserves.
Tools used at lower levels of escalation could be used at greater scale. Local staff and visiting executives would likely face higher risks of travel delays and, potentially, exit bans or detentions amid heightened concerns over espionage. Restrictions on personal information protection and cross-border data transfers would likely be tightened considerably, adding to the logistical challenges of operating a Chinese subsidiary. Strict capital controls would likely prevent MNCs from repatriating any earnings in dollars whatsoever.
Companies would also be exposed to risks of asset seizure. G7 companies in strategic sectors such as chemicals and pharmaceuticals could face the risk of immediate expropriation. Within months of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, for instance, Russia took control of German and Finnish utility assets in Russia.45Bloomberg News, “Russia Seizes Foreign-Owned Utilities After EU Asset Moves,” Bloomberg, April 26, 2023, https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2023-04-26/russia-seizes-fortum-uniper-plants-in-response-to-asset-freezes?sref=H0KmZ7Wk. In China, companies that stayed, even in nonstrategic sectors, would face the risk of seizure as retribution in kind for G7 asset seizures or freezes or to ensure continued employment at firms that suspended their operations due to G7 sanctions.46Sarah Anne Aarup, “Russian roulette for Western companies that stayed,” Politico, August 8, 2023, https://www.politico.eu/article/western-companies-stayed-russia-war-face-consequences/; Andrew Osborn, “West stands to lose at least $288 bln in assets if Russian assets seized -RIA,” Reuters, January 21, 2024, https://www.reuters.com/business/west-stands-lose-least-288-bln-assets-if-russian-assets-seized-ria-2024-01-21/.
Estimating the FDI stock and revenues of G7 firms in China is hamstrung by a number of methodological challenges. China’s total inward FDI stock in 2022 was $3.6 trillion, according to the International Monetary Fund’s (IMF’s) Coordinated Direct Investment Survey.47International Monetary Fund, “Coordinated Direct Investment Survey.” However, because the IMF compiles data based on the immediate investing country, rather than the ultimate beneficial owner of the investing firm, it is difficult to identify what FDI ultimately comes from G7 countries. For instance, only $460 billion of China’s FDI stock comes directly from G7 countries, according to Chinese reporting to the IMF as of 2022, while $2.5 trillion (70 percent of the total) is attributed to Hong Kong, the Cayman Islands, and the British Virgin Islands, some of which is G7 investment channeled through these intermediaries. Complicating matters further, a substantial portion of China’s inward FDI stock is actually China-origin investment that is routed back through Hong Kong or other tax havens. Here we use the most conservative estimate of G7 FDI—that which is directly attributable to G7 countries. The full value of the G7 FDI stock in China is likely much larger.
Similarly, it is difficult to assess the total revenue and profit exposure from MNCs in China. Annual filings of listed companies do not systematically break out revenue by region. Data from China’s MOFCOM estimate that the total revenue of foreign-invested enterprises above designated size in China in 2022 was $3.9 trillion.48“Above designated size” refers to businesses with annual main business revenues of 20 million yuan or greater. “Foreign-invested enterprise” includes a range of entities, including wholly foreign-owned enterprises, Sino-foreign equity joint ventures, and other corporate structures. China does not individually report business revenues from foreign-invested enterprises by country, although MOFCOM does report the amount of realized inward FDI by country. Assuming that business revenues are proportional to overall business revenue, we estimate that G7 foreigninvested enterprises earned $470 billion in revenues in China in 2022 and $33 billion in profits—all of which would be put at risk from the combined impact of G7 sanctions and Chinese countersanctions in a high-escalation Taiwan crisis scenario.
Portfolio investment and other capital flows
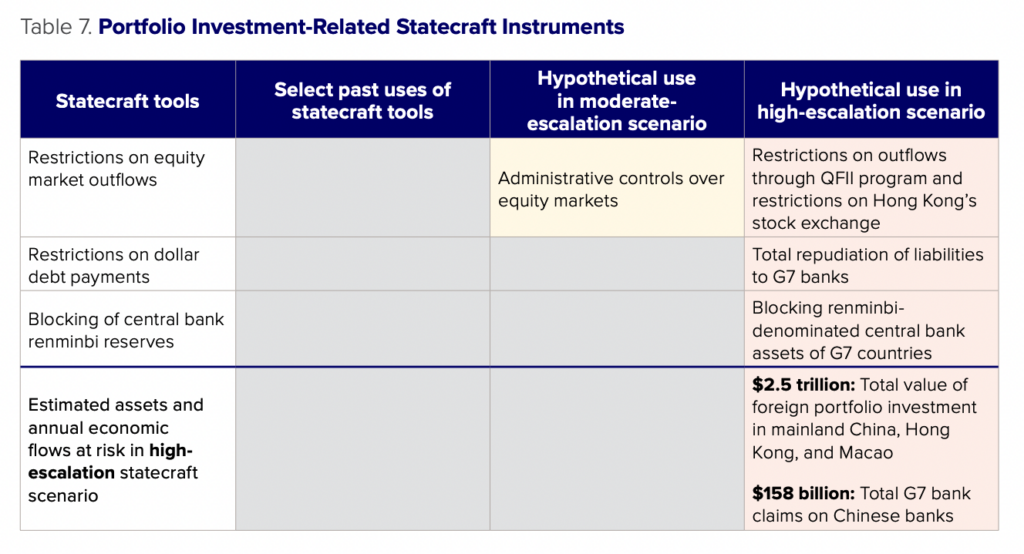
China could use restrictions on its equity markets to limit outflows of foreign portfolio capital from China. While these tools have not been used in the context of economic coercion in the past, China has restricted activity in its equity markets in an attempt to stabilize market conditions. In a moderate- or high-escalation scenario, China will likely consider imposing restrictions on market activity or outbound portfolio flows.
Past uses of statecraft
To our knowledge, China has not restricted trade orders or imposed capital controls in equity markets during disputes with other countries in an effort at coercion. However, China has intervened heavily in equity markets in the past in an attempt to steady markets during times of financial instability. In July 2015, a speculative bubble in China’s equity markets burst, with the Shanghai Composite Index falling by 32 percent from a peak the month prior. To stem the decline, China ordered brokerages not to process sell orders while using state funds to buy stocks.49Daniel H. Rosen and Logan Wright, “Credit and Credibility: Risks to China’s Economic Resilience,” Center for Strategic and International Studies, October 2018, https://www.csis.org/analysis/credit-and-credibility-risks-chinas-economic-resilience.
Potential use in moderate-escalation scenario
In a moderate-escalation scenario, it is probable that China would impose some capital controls and restrictions on equity markets to stanch capital flight stemming from a heightened sense of geopolitical risk among investors. Rather than a tool of economic statecraft per se, capital market controls should be seen as a likely response to financial instability during a crisis. In a more moderate scenario, where tensions with the United States and China trigger a stock market rout, for instance, China might turn to administrative controls on equity markets, as in 2015, that de facto restrict foreign investors selling Chinese stocks and repatriating funds. Given that the objective of such controls would be to ward off financial instability rather than impose costs on other countries, these restrictions would likely affect all financial investors in China rather than any one country.
Potential use in high-escalation scenario A higher-escalation scenario would likely see China impose capital controls across the board, including on capital flows through Hong Kong and Macao, to limit destabilizing outflows. Theoretically speaking, some of these tools could be targeted at G7 investors, but in practice, it would be difficult even for Chinese authorities to identify which portfolio assets belong to which investors. As with direct investment flows, portfolio investment is intermediated through tax havens, obfuscating the ultimate owners of capital. Efforts to estimate the holdings of Chinese securities on a nationality basis (rather than the typical residency basis) suggest that official data significantly understate holdings of Chinese securities.50Sergio Florez-Orrego et al., “Global Capital Allocation,” NBER Working Paper Series, Working Paper 31599, National Bureau of Economic Research, August 2023, https://www.nber.org/system/files/working_papers/w31599/w31599.pdf. Chinese authorities in a crisis would likely be hard-pressed to systematically identify G7 countries’ portfolio assets in China, let alone block them in a targeted fashion. If they did pursue this strategy, it is more likely that only a few high-profile investment firms would be targeted.
Instead, the more likely outcome is a comprehensive set of controls aimed at preventing a financial crisis. The IMF’s Coordinated Portfolio Investment Survey provides estimates of total portfolio assets and liabilities by economy.51International Monetary Fund, “Coordinated Portfolio Investment Survey,” https://data.imf.org/?sk=b981b4e34e58467e9b909de0c3367363. Based on this data, if full capital controls were put in place, an estimated $2.5 trillion worth of foreign equity assets in China, Hong Kong, and Macao would be at risk.
China in the global economy
China’s central place in global supply chains means that disruptions stemming from actions in a Taiwan escalation scenario would have far-reaching consequences. The previous section considers Chinese economic statecraft actions on flows and assets into China. This section considers the use of China’s statecraft toolbox on the global economy outside China: exports, outbound investment, and interactions with global financial markets.
Chinese exports
In an escalation over Taiwan, China could use its central position in global supply chains to exercise leverage against other countries. Because weaponizing supply chains may accelerate diversification away from China, these tools have been used sparingly in the past. However, new legal and regulatory tools have created a pathway for their use in a future scenario where China is more willing to bear the economic and reputational costs of disrupting supply chains.
Past examples of statecraft
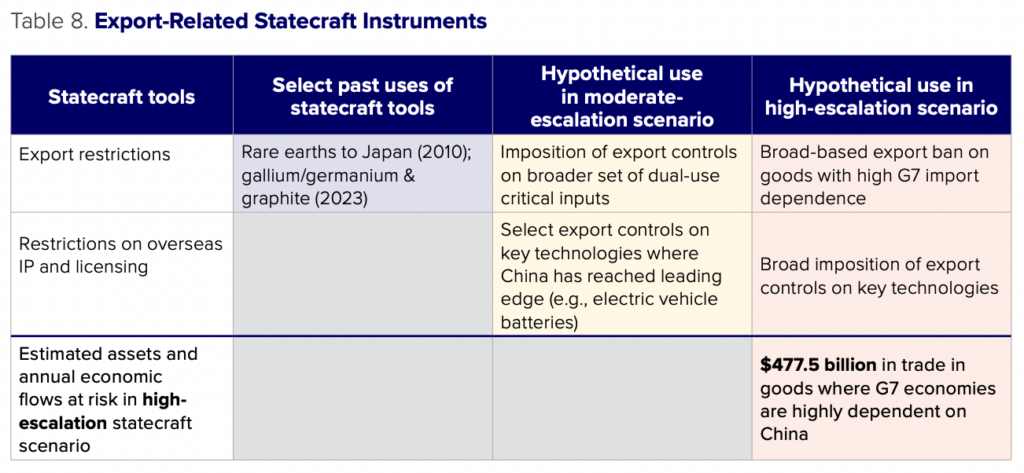
Export restrictions on critical goods – China has used export restrictions in past geopolitical incidents to exert leverage over other countries. In September 2010, after a collision between Japanese coast guard ships and a Chinese fishing vessel and Japan detained its captain, China imposed an informal export ban on rare earths to Japan.52Keith Bradsher, “Amid Tension, China Blocks Vital Exports to Japan,” New York Times, September 22, 2010, https://www.nytimes.com/2010/09/23/business/global/23rare.html. In October 2010, industry officials reported that China expanded the export restrictions to the United States and Europe amid a trade dispute. China resumed exports in November of that year.53Keith Bradsher, “China Restarts Rare Earth Shipments to Japan,” New York Times, November 19, 2010, https://www.nytimes.com/2010/11/20/business/global/20rare.html.
In July 2023, China announced it would require export permits for Chinese gallium and germanium, elements used in chip production and solar panels among other products.54Reuters, “China gallium, germanium export curbs kick in; wait for permits starts,” August 1, 2023, https://www.reuters.com/markets/commodities/chinas-controls-take-effect-wait-gallium-germanium-export-permits-begins-2023-08-01/ China’s announcement came as the United States imposed restrictions on high-end chip and chip equipment exports to China. China announced in October 2023 it would require licenses for export of graphite products used in electric vehicle batteries.55Ministry of Commerce and General Administration of Customs of the People’s Republic of China, “海关总署公告2023年第39号 关于优化调整石 墨物项临时出口管制措施的公告” [MOFCOM and GACC Announcement No. 39 of 2023 on Optimizing and Adjusting Temporary Export Control Measures for Graphite Items], October 2023, http://www.mofcom.gov.cn/article/zcfb/zcdwmy/202310/20231003447368.shtml. In both cases, demand for the products shot up immediately in advance of the license requirement, as importers stockpiled goods, and then fell, as the license regime was put in place. Gallium and germanium exports returned to pre-control levels by December. Rather than an export ban as in the past, the imposition of an export regime around gallium and germanium appeared to be an effort to formalize the legal foundation of export controls on a new set of critical goods. While Chinese authorities denied that the measures were retaliatory and aimed at any particular country, the announced measures did highlight China’s economic leverage in a period of heightened geopolitical tensions.
Potential use in moderate-escalation scenario
Export restrictions on critical goods – In a moderate-escalation scenario, China could limit exports to the United States across a range of products through export tariffs, informal restrictions, or full export bans. The United States is China’s largest export destination, with $583 billion in goods exported to the United States in 2022 (16 percent of China’s total exports).56United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, “UN Comtrade Database,” accessed March 4, 2023, https://comtradeplus.un.org/. Export trade to the United States is an important source of employment, with an estimated 21.6 million jobs in China supported by exports to the United States.57OECD, “Trade in Employment Database,” accessed March 4, 2023, https://www.oecd.org/industry/ind/trade-in-employment.htm. China’s dependence on the United States as an export market suggests that Chinese policymakers will be cautious when imposing export restrictions, aiming to reduce the impacts on the Chinese economy while still imposing meaningful costs on the United States.
For this reason, initial export restrictions would likely focus on select intermediate goods where trade volumes and Chinese export-dependent employment is low, but the lack of which would have compounding effects on US industry. Past supply chain analyses have identified some of the main dependencies on imports from China (see Table 9).
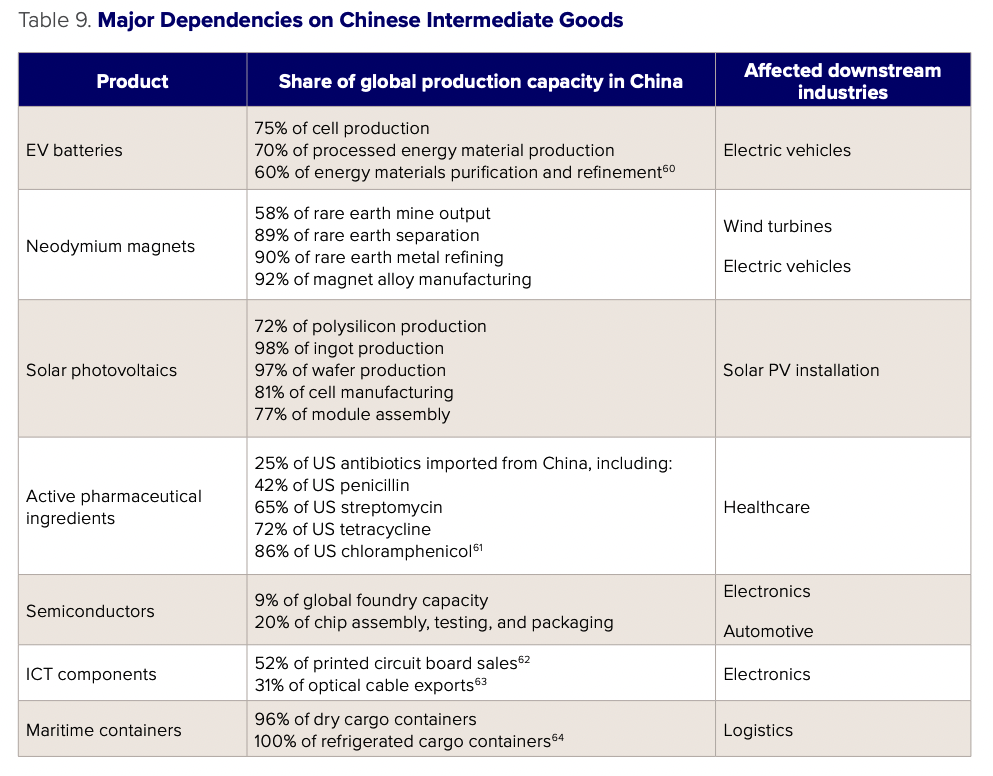
Table footnotes58Aakash Arora et. al., Building a Robust and Resilient U.S. Lithium Battery Supply Chain, Li-Bridge, February 2023, https://netl.doe.gov/sites/ default/files/2023-03/Li-Bridge%20-%20Building%20a%20Robust%20and%20Resilient%20U.S.%20Lithium%20Battery%20Supply%20Chain.pdf. 59U.S.-China Economic and Security Review Commission, “Section 4: U.S. Supply Chain Vulnerabilities and Resilience,” accessed March 3, 2024, https://www.uscc.gov/sites/default/files/2022-11/Chapter_2_Section_4–U.S._Supply_Chain_Vulnerabilities_and_Resilience.pdf. 60U.S. Department of Commerce and U.S. Department of Homeland Security, Assessment of the Critical Supply Chains Supporting the U.S. Information and Communications Technology Industry, February 24, 2022, https://www.commerce.gov/sites/default/files/2022-02/Assessment-Critical-Supply-Chains-Supporting-US-ICT-Industry.pdf. 61Ibid. 62U.S. Department of Transportation, Supply Chain Assessment of the Transportation Industrial Base: Freight and Logistics, February 2022, https://www.transportation.gov/sites/dot.gov/files/2022-02/EO%2014017%20-%20DOT%20Sectoral%20Supply%20Chain%20Assessment%20 -%20Freight%20and%20Logistics_FINAL.pdf.
Restrictions on overseas IP and licensing – In addition to restricting goods exports, China may also change its posture on technology exports to the United States. Since 2008, China has maintained a technology catalogue that regulates what technologies may be exported from China.63Hogan Lovells, “China updates technology catalogue for export control, targeting emerging and cutting-edge sectors,” January 31, 2024, https://www.engage.hoganlovells.com/knowledgeservices/insights-and-analysis/china-updates-technology-catalogue-for-export-controltargeting-emerging-and-cutting-edge-sectors. The technology catalogue contains twenty-four technologies prohibited for export and 111 technologies requiring an export license. The latest revision issued in December 2023 added LiDAR systems, used in autonomous driving applications, to the list of technologies requiring a license. Other technologies covered requiring licenses under China’s technology control regime include advanced materials processing (e.g., chemical vapor deposition) and underwater autonomous robot manufacturing and control technology, among others. As China reaches the cutting edge in some of these technologies, the ability to grant or revoke export licenses to companies in the United States and elsewhere represents an additional statecraft tool.
Potential use in high-escalation scenario
In a high-escalation scenario, Chinese policymakers may decide to impose as high costs as possible on the sanctioning G7 countries by imposing export restrictions on all goods where import dependence on China is high. Such an approach would cover a broad range of consumer and industrial goods, and would be aimed at disrupting the economies of the targeted countries and increasing costs for consumers. However, this would come at tremendous cost to the Chinese economy and its ability to withstand sanctions.
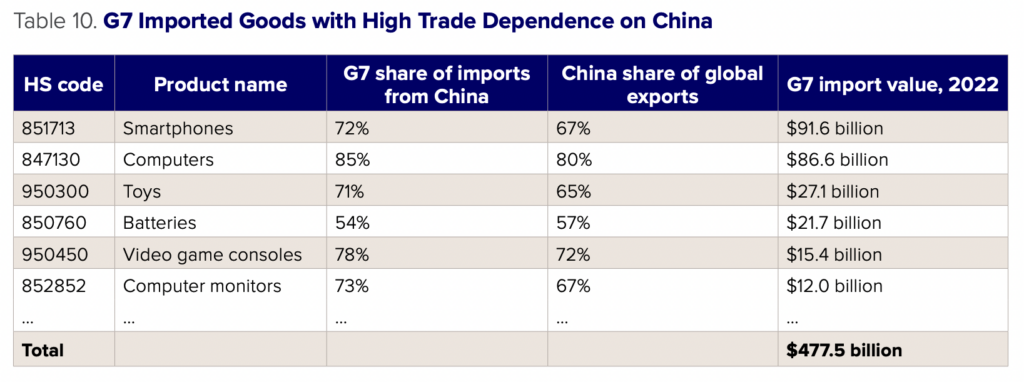
Import dependence is contingent on a range of factors, including not only how much a country depends on another for a particular good, but also how widely available that good is in the global market. While a true accounting of import dependence requires a sector-by-sector approach, we roughly estimate the value of goods where the G7 nations are highly dependent on China by summing up G7 imports at the HS 6-digit level where (1) over 50 percent of G7 imports come from China, and (2) China accounts for over 50 percent of global exports. This encompasses all products where both initial dependence on China is high and where substitutes from other countries may be expensive or hard to find given how dominant China is in that product category, at least in the short run. Based on this approach, the G7 is highly dependent on $477.5 billion in goods imported from China. This is a highly conservative measure, since losing access to intermediate goods would disrupt downstream manufacturing and incur costs much greater than their import value alone.
While export restrictions would be one of China’s most impactful economic statecraft tools, it would also be among the options costliest to China itself. First, an estimated 101.2 million jobs in China depend on foreign final demand, 44.8 million of which depend on final demand from G7 countries.64OECD, “Trade in Employment Database,” accessed March 4, 2023, https://www.oecd.org/industry/ind/trade-in-employment.htm. Any measures that disrupted these factories would exacerbate structural issues in employment and wages. Secondly, a major source of China’s resilience against sanctions is the fact that it runs a persistent trade surplus, which could be put at risk from export restrictions. Even under a full-scale G7 sanctions regime against Chinese banks, it would be very difficult to trigger a balance of payments crisis in China so long as the country continues to run a strong trade surplus. Trade restrictions from China that undermine its own trade surplus would work against China’s ultimate objective of maintaining macroeconomic stability in a moment of crisis. Finally, sanction regimes face the challenge of preventing transshipment of goods from third countries into the targeted economy. To effectively cut off the United States and other G7 economies from these products would require China’s non-sanctioned trading partners to agree not to transship controlled products to the G7, and for China to be willing to impose punishments on third countries that refuse to comply. China is unlikely to have the bureaucratic breadth even to monitor potential sanctions evasion on this scale, and may be loath to punish other countries in a moment where it is diplomatically isolated.
Chinese investment abroad
China has typically used overseas investment as a positive inducement rather than a coercive tool. In a moderate-escalation scenario, China could pair promises of outbound investment to friendlier countries with limitations on new outbound investment to other countries, although this would be likely driven less by a statecraft agenda and more by geopolitical realities in the host countries. In a highescalation scenario, China could potentially force the shutdown of Chinese-owned subsidiaries abroad, but this would be extremely costly and of limited effectiveness.
Past uses of statecraft
State-backed overseas investment – Overseas investment is a key part of China’s economic diplomacy.65Xinhua, “Full text of President Xi’s speech at opening of Belt and Road forum,” May 14, 2017, http://www.xinhuanet.com/english/2017-05/14/c_136282982.htm. Although it is debatable how much investment is driven by state versus commercial interests, major investment projects are often marked by both governments as opportunities to demonstrate a constructive relationship. In many cases these projects bring tangible economic benefits to the host country, making them an important part of China’s statecraft toolkit.66See, for example: Government of the Republic of Croatia, “Senj wind farm opened for trial run, the project will contribute to Croatia’s green transition,” December 7, 2021, https://vlada.gov.hr/news/senj-wind-farm-opened-for-trial-run-the-project-will-contribute-to-croatia-s-greentransition/33504; Wilhelmine Preussen, “Hungary’s Orbán courts China and wins a surge of clean car investments,” Politico, December 20, 2023, https://www.politico.eu/article/hungary-pm-viktor-oran-china-ties-ev-clean-car-investments-tensions-eu/.
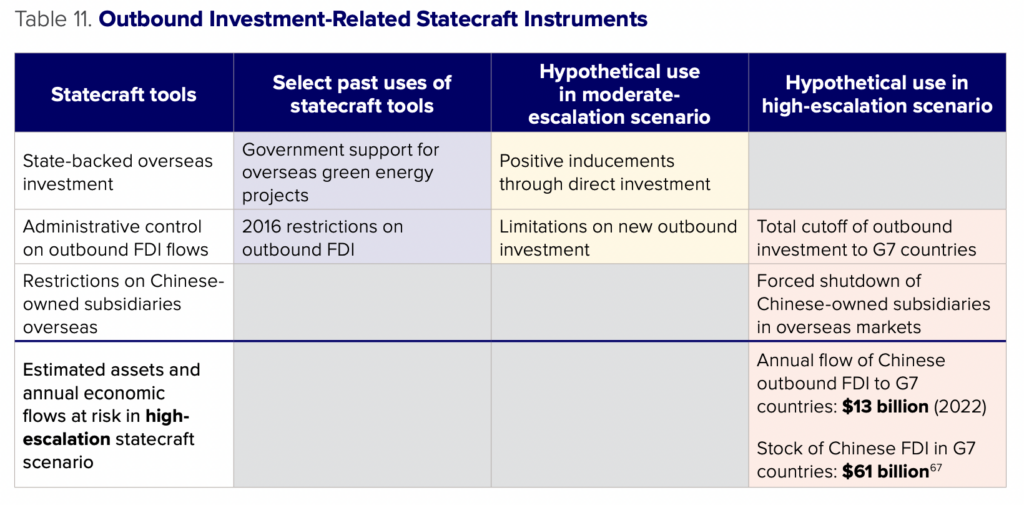
Table footnote67International Monetary Fund, “Coordinated Direct Investment Survey.”
Administrative control on outbound FDI flows – China maintains administrative controls on outbound investment, limiting or approving investment when it meets political and economic goals. In the early 2010s, China began liberalizing its strict controls on outbound FDI to encourage Chinese firms to invest abroad.68Thilo Hanemann, “Testimony before the U.S.-China Economic and Security Review Commission,” U.S.-China Economic and Security Review Commission, Hearing on Chinese Investment in the United States, January 26, 2017, https://www.uscc.gov/sites/default/files/Hanemann_USCC%20Hearing%20Testimony012617.pdf. In 2016, a surge in capital outflows led Beijing to reimpose restrictions on outbound FDI in an attempt to mitigate balance of payments pressures. While this is not a direct application of statecraft, the tools exist for China to selectively restrict outbound investment in a future escalation scenario.
Potential use in moderate-escalation scenario
In a moderate-escalation scenario, Beijing could use promises of investment as positive inducements to align with China diplomatically, or use threats to cut off ongoing or future investments as a form of coercion.
The perceptions of China and its role in a moderate-escalation scenario would matter significantly to the effectiveness of these tools. Where the escalation exacerbates national security concerns toward China, Chinese promises of outbound investment or threats to cut off ongoing or new projects will likely have little effect. Similarly, if the geopolitical environment contributes to capital outflow pressure, China will be less likely to greenlight much new outbound investment.
Potential use in high-escalation scenario
In an escalation over Taiwan, China could theoretically halt all outbound investment to G7 countries as a form of coercion, although geopolitical conditions would likely make the point moot. G7 countries would be unlikely to welcome new investment from China in a major Taiwan escalation. The wave of new and updated inbound investment screening regimes across the G7 over the past decade give G7 governments the capacity to block many types of investments on national security grounds.69OECD, “Investment policy developments in 61 economies between 16 October 2021 and 15 March 2023,” April 2023, https://www.oecd.org/daf/inv/investment-policy/Investment-policy-monitoring-April-2023.pdf; Gabriel Rinaldi and Peter Wilke, “Germany rethinks China’s Hamburg port deal as further doubts raised,” Politico, April 19, 2023, https://www.politico.eu/article/germany-to-revisit-chinas-hamburg-port-deal-over-inconsistencies-on-critical-infrastructure-classification/. China would likely limit outbound investment regardless to stem capital outflows, and Chinese project developers would likely struggle to find overseas lenders willing to finance their projects at the risk of getting caught up in G7 sanctions.
China could hypothetically impose restrictions on the activities of Chinese-owned businesses abroad, with the aim of disrupting the domestic economy of the sanctioning countries. Chinese authorities could theoretically pressure Chinese firms in the United States to slow down operations or lay off workers. Chinese ownership of critical infrastructure — including State Grid Corporation of China’s 40 percent stake in the Philippines’ national grid and COSCO’s proposed 24.99 percent stake purchase in a port terminal in Hamburg — has raised concerns among policymakers over the national security risks of Chinese ownership of critical infrastructure in a crisis.70James Griffiths, “China can shut off the Philippines’ power grid at any time, leaked report warns,” CNN, November 26, 2019, https://www.cnn.com/2019/11/25/asia/philippines-china-power-grid-intl-hnk/index.html. To our knowledge, there have been no documented cases of Chinese firms shutting down their operations in other countries amid a geopolitical dispute with the intent to disrupt the local economy.
In a moderate- or high-escalation scenario, it is unlikely that China would or could compel Chinese-owned firms in the United States or G7 countries to disrupt their operations as part of an economic statecraft campaign. First, except in the most extreme circumstances, China would avoid pressuring its firms abroad to disrupt their own operations for fear of reputational blowback that could undo years of efforts to expand the global footprint of Chinese companies. Second, a large share of Chinese direct investment abroad is held in minority stakes, and China-based board representation would be too small to unilaterally force a work disruption. Finally, in the event of a deliberate slowdown or disruption, it is likely that G7 governments would nationalize the assets of the Chinese firms, as Germany preemptively did when it nationalized Gazprom’s German subsidiary after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.71Deutsche Welle, “Germany nationalizes former Gazprom subsidiary,” November 14, 2022, https://www.dw.com/en/germany-nationalizes-former-gazprom-subsidiary/a-63754453
Altogether, China holds an estimated $61 billion in FDI assets in G7 countries that could be theoretically put at risk from disruption, although the likelihood of China turning to such tools—even in high-escalation scenarios—seems low. China invested $13 billion in G7 economies in 2022. The most substantial disruptions to Chinese outward investment to G7 economies would likely be China’s own capital controls and defensive investment restrictions from G7 countries toward China in a moment of high escalation over Taiwan.
Portfolio investment and other capital flows
In addition to restrictions on market access or manipulation of operating conditions for multinational companies in China, Beijing could potentially use some of its financial policy tools to achieve certain political signals in response to G7 economic statecraft. However, China would struggle to use these tools aggressively without creating corresponding costs for its own economy and financial institutions. Most of the tools of financial leverage that China can use, including currency swap lines, are likely to be directed against borrowers from Chinese institutions. That volume of lending or the terms of lending could be adjusted in response to political developments. Selling foreign assets in large volumes (particularly US Treasuries) has never been a particularly viable policy option for Beijing. Similarly, using a policy-led depreciation of China’s currency as a tool of statecraft to pressure other countries would have significant implications for China’s own financial stability.
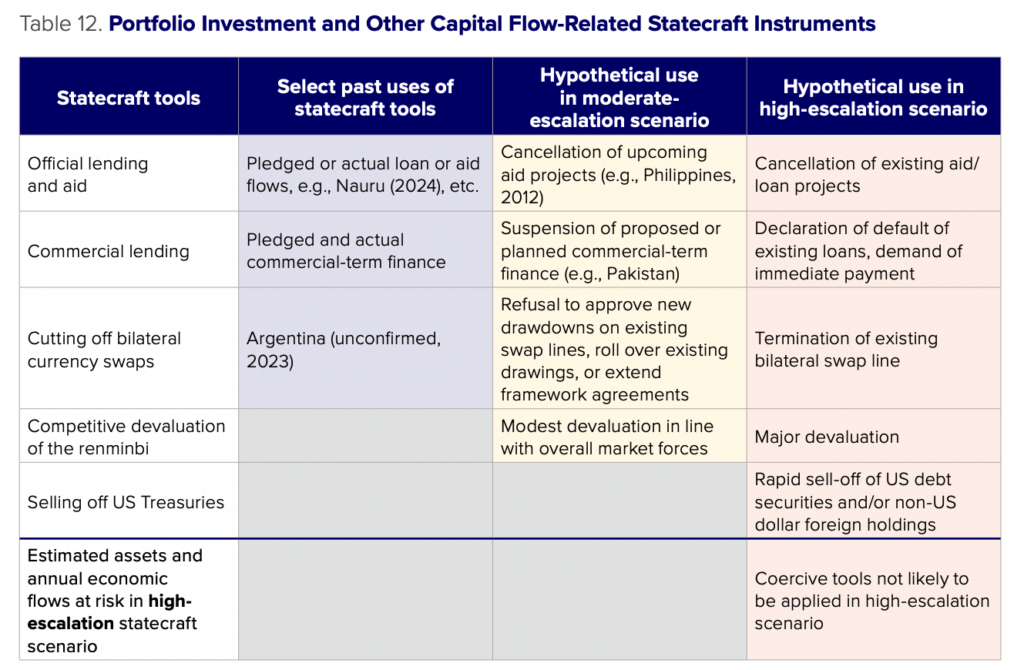
Past uses of statecraft
Official lending (in the form of subsidized concessional or preferential loans) and foreign aid are some of China’s primary economic diplomacy tools with developing and emerging market countries. These programs rarely take the form of explicit quid pro quos, but instead build long-term bilateral relationships that China can later activate to obtain political support on controversial Chinese “core issues,” including Taiwan, Hong Kong, and Xinjiang.
Aid and lending pledges are also key elements of the unofficial financial packages that China uses to induce diplomatic recognition switches from Taiwan to China. Recent examples include Nauru, the Solomon Islands, and Panama. Diplomatic relations with China (rather than Taiwan) are a prerequisite for the receipt of official aid (including concessional loans). Importantly, pledged lending may be just as important as the receipt of actual funds. Past cases suggest China can effect some control over the timing of these recognition switches to maximize their potential political impact on Taiwan, including Gambia (2016, after the DPP’s electoral victory in Taiwan), the Solomon Islands (2019, ahead of the People’s Republic of China’s 70th anniversary), and most recently Nauru (2024) (and likely Tuvalu), to coincide with adverse political events.
China has also offered bilateral swap lines to provide liquidity to developing countries. Although these are nominally intended to facilitate renminbi-denominated trade and investment, most swap agreements are never activated. Yet they are increasingly critical to a handful of countries, including Argentina, Pakistan, and Egypt, providing several billion dollars in emergency liquidity. Swap agreements typically last three years; countries may request the line be activated for a specific amount, and in practice that amount is simply rolled over at the end of a year. It is very rare for China to refuse to activate a swap line or to roll over any outstanding amounts, which would put pressure on any country relying on the swap line as a foreign exchange backstop. One (unconfirmed) counterexample came in December 2023, when China allegedly refused a request from Argentina to activate additional funds under the swap in response to Argentine President Javier Milei’s criticism of the China-Argentina relationship during the 2024 elections.72Igor Patrick, “China suspends US$6.5 billion currency swap agreement with Argentina, reports say,” South China Morning Post, December 21, 2023, https://www.scmp.com/news/china/diplomacy/article/3245805/china-reportedly-suspends-us65-billion-currency-swap-agreement-argentina. The implications of China’s bilateral swap agreements with G20 countries will be covered in our forthcoming paper on the role of the G20 in a Taiwan crisis.
Potential use in moderate-escalation scenario
None of the G7 countries receive foreign aid or (official) loans from China in any significant amounts. In a moderate-escalation scenario, China could be expected to approach major recipients of development finance to ask for statements of diplomatic support or voting support in international forums like the United Nations General Assembly. China could look to accept a recognition switch from a country where discussions were already underway, to ratchet up additional pressure on Taiwan’s incumbent administration.
Most likely, China’s financial statecraft would not immediately increase in scope in a scenario of escalating tension over Taiwan. Financial pressures on China during a moderate escalation would likely constrain China’s ability to rush additional development finance to woo new allies. Rather, China would likely leverage the results of past financial statecraft measures to constrain Taiwan’s diplomatic space.
China would also benefit from deep economic and financial relationships with emerging market and developing countries itself to prevent alignment with the United States. China would also be unlikely to immediately begin punitive measures by formally cancelling or conditioning financial flows with existing partners. We are not aware of any examples of negative statecraft involving official lending or aid, where China either outright canceled existing aid projects or called in outstanding loans in response to a diplomatic or policy dispute. Such moves would be not only diplomatically counterproductive, but would also be restricted by Chinese aid and lending agreements and contracts, and a desire to avoid harming Chinese contractors, exports, and financial institutions for relatively limited marginal diplomatic gains. Rather than cancel existing projects, there is evidence that China instead has delayed or cancelled upcoming aid projects in past disputes. One example came in the Philippines in 2012. During a flare-up around the Scarborough Shoal, China continued to execute on existing aid and loan contracts, but does not appear to have undertaken new work until the election of Rodrigo Duterte in 2016.
Similarly, even in a moderate-escalation scenario, it is unlikely that Chinese lenders would cancel or otherwise call in existing projects or loans. As most of China’s project finance is funded on commercial terms, governed by commercial legal contracts, there are few instances where Chinese lenders could accelerate payment outside of clear events of default. One potential channel that could be deployed would be escrow accounts. China’s loans often require the use of escrow or other special accounts in China (either funded directly or through commodity sales to Chinese purchasers), which must be funded at certain levels. In an escalation, China in theory could raid these existing escrow accounts and demand replenishment. One recent example is Suriname, where in 2023 China EXIM Bank tapped an escrow account for payment while Suriname had halted debt service during multilateral debt renegotiations, a major breach of international debt protocol. Additionally, China would be more likely to halt lending (not yet committed or disbursed) in specific countries, as recent reports indicate it has done in Pakistan and Kenya. In an escalation scenario, bilateral swap lines would likely serve as an implicitly threatened target where they have been activated. This could constrain diplomatic support for any G7 sanctions or additional action. However, as very few countries have drawn upon swaps in significant volumes, China may find this tool of leverage limited.
Although China is unlikely to impose punitive measures with loans and aid, it has other options available to gain leverage. China accounts for 6 percent of the IMF’s voting share. An 85 percent majority is required for major decisions at the IMF such as quota increases and allocations of Special Drawing Rights (SDR). In partnership with a small number of other countries, China could disrupt processes (or threaten to do so) at the IMF to gain negotiating leverage.
In a moderate-escalation scenario, China might consider turning to other financial statecraft tools such as competitive devaluation of the renminbi. Facing persistent capital outflows for much of the last decade, China’s central bank frequently intervenes in currency markets to maintain the value of the renminbi, by selling US dollars and buying domestic currency. China could slow down that intervention, allowing the renminbi to depreciate, which would also likely trigger competitive devaluations and capital outflows in other emerging markets, particularly if the depreciation was seen as a policy signal. While this tool benefits from plausible deniability, Beijing runs the risk of undermining confidence in domestic monetary policy, encouraging additional capital outflows from both domestic and foreign investors, and antagonizing other countries with whom Beijing competes for export share. For G7 countries, a weaker renminbi would result in lower demand for G7 goods due to the weaker purchasing power of Chinese consumers, and greater competitive price pressure from Chinese exports.
Potential use in high-escalation scenario
In a high-escalation scenario, China would have limited capacity to harass G7 economies through financial statecraft without drastically undermining its own financial stability. Instead, China’s financial statecraft would be more effectively deployed at developing and emerging market countries to prevent a cohesive response outside of the G7.
Ever since China began to accumulate foreign exchange reserves in the 2000s, analysts have questioned whether China would sell its holdings of foreign assets to retaliate against the United States for political reasons. China officially held $782 billion in Treasuries at the end of November 2023, and likely holds around twice that level including holdings by state banks. The implied threat of a selloff would be to raise US interest rates and tighten US financial conditions. However, this threat has been somewhat overstated, as China could not sell these assets all at once, and US officials could take measures to respond well before significant volumes of assets could be sold. For example, if the Federal Reserve were to issue a statement claiming that it was noticing politically motivated disruptions in financial markets and would purchase securities as necessary to maintain stability, it would likely counteract any aggressive selloff. In March 2020, amidst COVID-19- related disruptions in markets, several foreign reserve managers began aggressively selling Treasuries and other US assets to repatriate funds and manage financial risks, and the Federal Reserve was still able to purchase assets and steady financial markets.
Even if China were able to sell significant volumes of its holdings of Treasuries, at the end of the day Beijing would still be holding US dollars, and would need to invest them in something, which would likely indirectly result in additional Treasury purchases. The withdrawal of China from new Treasury market purchases is also likely to have a limited impact, as Beijing has not been a significant net buyer of Treasuries for many years now. Ultimately, Treasury sales are an unlikely vehicle for Chinese economic statecraft, even in the case of a significant escalation in tensions.
Rather, Beijing would be likely to focus financial statecraft on preventing emerging and developing economies from aligning with G7 sanctions. Under high-escalation conditions, those countries would already feel acute macroeconomic pressure in the form of increased global finance and debt servicing costs (brought on by a stronger dollar), fluctuating commodity prices, and disruptions to global trade. This would increase developing countries’ potential susceptibility.
Even under high-escalation conditions, certain channels would still have constraints. Official lending and aid offers relatively little direct leverage against the G7. China would also be unlikely to be able to convince G20 or developing countries to impose their punitive measures against the G7, beyond pariah states like Iran, Russia, or Venezuela. But other channels would provide more room for maneuver. China has far greater ability to deliberately sell non-US dollar foreign assets in specific markets, as these are more discretionary purchases, and not the result of China’s decision to manage its exchange rate against the US dollar. China does hold significant proportions of non-US dollar currencies in its foreign reserves, and could potentially liquidate those holdings rapidly in response to political events. This may have an outsized impact on currency valuations and interest rates in certain emerging markets that are heavily reliant upon foreign demand for government bonds, such as Indonesia or Malaysia.
Additionally, more aggressive steps could be taken with outstanding loan agreements with developing countries. Publicly disclosed lending contracts from China’s policy banks allow for the lender to declare default—and immediately demand repayment—in response to certain political events, including a switch in diplomatic recognition to Taiwan (or China severing relations with a foreign country). Similarly, under “illegality clauses” common to commercial loans, China’s policy banks could immediately cancel disbursements or call in outstanding amounts due to changes in law that impact their ability to perform their obligations. G7 financial measures (like currency or banking restrictions) could, at least under a theoretical expansive reading, qualify. Yet invoking these clauses would come with bureaucratic risks for China Export-Import (EXIM) Bank and China Development Bank, which would be hard-pressed to collect any outstanding amounts and would likely be reluctant to acknowledge any debt as unrecoverable, especially at a time when China is seeking diplomatic support among other borrowing countries.
China’s capacity to circumvent financial sanctions and G7 economic statecraft
The previous section was concerned with China’s capacity to retaliate against US and G7 economic statecraft, but this is not Beijing’s only option. There have been long-running efforts in Beijing to not only develop tools to respond to foreign economic restrictions, including sanctions and export controls, but to circumvent or bypass them as well. Primary among those tools has been the development of alternative national-level and international financial networks using China’s own currency, the renminbi, rather than the US dollar. These have included bilateral currency swap arrangements for trade settlement, the designation of specific clearing banks in third countries, and the gradual expansion of China’s own interbank payment networks, the Cross-border Interbank Payment System (CIPS). The development of China’s central bank digital currency (CBDC) can be viewed in the same context, although the current structure is focused far more on domestic retail transactions than cross-border interbank financing.
At the same time, China’s reliance upon the US dollar is a major source of friction between different camps in Beijing. Security-minded officials have always viewed the dollar as a source of risk and vulnerability for China, given the potential threats posed by sanctions and other restrictions. However, financial technocrats in China have led the charge to integrate China’s economy more closely with the global financial system, precisely to attract foreign capital inflows. China faces a significant problem with the world’s largest single-country money supply at $40 trillion, which generates new pressures for Chinese savers to actively diversify into foreign assets, as the money supply continues growing by around $3.5 trillion in new renminbi every year. This outflow can create financial instability inside China and weaken the exchange rate and the global influence of China’s economy, unless it is counterbalanced by capital inflows via foreign direct investment or flows into China’s bond and equity markets, meaning purchases of renminbi-denominated assets. While the outflows from China’s financial system are inevitable, the inflows to stabilize conditions are contingent upon the state of China’s economy, interest rates, and the reform of the financial system.
As a result, throughout the past decade, even though the political climate in China has turned more hostile to foreign influence and interests, China has persistently attempted to attract foreign investment and capital inflows, denominated in foreign currency. This has also meant prioritizing policy choices and reforms favored by foreign investors and governments. Maintaining access to US dollar inflows has required deepening China’s access to the global financial system, and therefore exposing China’s financial institutions to potential restrictions on those dollar inflows. China has consistently made compromises when necessary to maintain foreign inflows, most recently including permitting audits conducted under the imprimatur of the US Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB) in order to prevent the delisting of Chinese companies on US stock exchanges.
Beijing will continue to prioritize maintaining access to foreign capital and inbound investment, despite concerns about the vulnerability of Chinese institutions to US sanctions. Should China lose access to US dollar inflows, the renminbi’s value globally would depreciate over time, and China’s influence and throw weight in the global economy would similarly diminish. Any credible claim that China could catch the United States in economic prowess would evaporate. As a result, even as China’s overall policy environment has become obsessed with security, this has not fully extended to the financial system, where technocrats have been able to push back against the concerns of security-oriented officials.
At the same time, it is not a credible threat that outside of a wartime or similar scenario, the United States would completely cut off China’s access to US dollars, or take actions against China’s financial system as comprehensive as those against Russia. First and foremost, China remains a sizable exporter and global manufacturing center, at an estimated 14 percent of global exports. While there are alternative sources of exports, disrupting China’s capacity to use US dollars would necessarily interrupt China’s $5.9 trillion in annual trade flows as well. Other more extreme options, such as freezing significant proportions of China’s $3.22 trillion in foreign exchange reserves, as was done to Russia’s central bank following the invasion of Ukraine, would similarly not be credible because the primary impact would be on China’s capacity to defend its currency, producing a sharp depreciation of the renminbi and ironically making China’s exports even more competitive in the global economy. The disruptions of global supply chains during the COVID-19 era created significant economic dislocations, which only moderately eased after China’s rapid return to production and exports in April and May 2020. Suspending China’s overall access to US dollar financing and its impact on trade would generate immediate political opposition in the United States and other allied and like-minded democratic states.
Moreover, Beijing is very aware that wholesale restrictions on financing channels for all of its banks are improbable and difficult to maintain. As a result, China’s methods for avoiding broader sanctions have focused on channeling transactions through individual banks that typically have limited cross-border business. Therefore, when these smaller banks are inevitably sanctioned themselves, the net impact on the rest of the financial system is minimal. This was the playbook that China used in designating the Bank of Kunlun as a preferred vehicle for transactions with Iran after sanctions were imposed in 2012, even though the sanctions did force the bank to shift its behavior as well. Banks in Hong Kong have similarly been forced to juggle overlapping sanctions threats from the United States and China in recent years, but no bank in Hong Kong has completely lost access to US dollar clearing facilities because of secondary sanctions imposed by the United States. And as long as some banks within the Chinese system maintain access to dollar clearing facilities, then it is probable that Beijing and Chinese firms will be able to channel transactions through these institutions. It remains highly unlikely that all Chinese banks will suddenly find themselves unable to access or trade in US dollars in a situation similar to some Russian financial institutions, given China’s importance in the global trading system. Beijing’s awareness of these limits similarly conditions China’s attempts to develop alternative financial networks that do not involve the US dollar. These can serve as alternative channels to be expanded in case of temporary need and limited purposes, rather than alternatives for everyday usage.
Using international Renminbi networks to circumvent sanctions
Obviously, one method China can use to avoid economic sanctions on US dollar-denominated transactions is to conduct business in China’s own currency, the renminbi. (Here, we are assuming that China’s efforts would be designed to avoid or circumvent an explicit secondary sanctions package from the United States or the G7.) Over time, China has sought to both encourage the development of offshore pools of the Chinese currency as well as denominate trade transactions in renminbi. At first, this was primarily a mechanism to avoid the disruptions to US dollar-denominated trade transactions caused during the global financial crisis in 2008. Later, and particularly following the Russian invasion of Ukraine, China’s efforts to promote the international use of its currency carried greater geopolitical significance, as a potential tool of sanctions avoidance, and to reduce the scope of Chinese financial transactions potentially exposed to US economic statecraft. Former Chinese officials such as Yu Yongding, who served on the PBOC’s Monetary Policy Committee, has pointed to the G7’s freezing of Russian foreign exchange reserves as proof of US “willingness to stop playing by the rules” and have suggested sitting Chinese officials are exploring new alternatives to safeguard its foreign assets.7473Liu, “China’s Attempts to Reduce Its Strategic Vulnerabilities to Financial Sanctions.”
Russia itself started invoicing a far higher proportion of its own imports in renminbi in 2022 and using renminbi as a “vehicle currency” for transactions with third countries as well.74Maia Nikoladze, Phillip Meng, and Jessie Yin, “How is China mitigating the effects of sanctions on Russia?” Econographics, Atlantic Council, June 14, 2023, https://www.atlanticcouncil.org/blogs/econographics/how-is-china-mitigating-the-effects-of-sanctions-on-russia/. Overall, however, the potential for renminbi-denominated transactions to bypass or circumvent economic sanctions depends upon:
- The liquidity and availability of renminbi to conduct economic transactions
- The capacity of Chinese international interbank payments systems to accommodate these transactions
- The ability of financial institutions to conceal those transactions from Western regulators, who could still impose secondary sanctions upon Chinese institutions should the transactions circumventing sanctions be discovered
Among these three requirements, the first one is likely the most difficult for Chinese authorities to control. It is always easy enough to provide financing in renminbi, but it is difficult to find counterparties willing to accept renminbi as payment or in borrowing, unless they have no other alternatives (as in Russia’s case). Setting up the institutional infrastructure to accommodate renminbi-denominated interbank transactions can occur largely within China’s borders, although it does require approvals of several international banks to facilitate these transactions. Beijing’s difficulty in avoiding detection of sanctions-busting financial transactions stems from the fact that China’s banks are also likely to maintain large volumes of dollar-denominated business, particularly for trade settlement. Beijing can always play a game of chicken regarding the imposition of secondary sanctions on China’s larger banks if certain sanctions-busting transactions are discovered, but it still runs the risk of retaliation from the United States and its allies.
Current scope of Renminbi internationalization
The term “renminbi internationalization” is often used to describe multiple phenomena, not all of which are relevant for China’s avoidance of Western economic statecraft. The most conventional definition involves the holdings and usage of renminbi outside of China’s borders, including for trade settlement. Other definitions include foreign holdings of renminbi-denominated assets within Chinese markets, which are less important in the context of sanctions avoidance. Sometimes “renminbi internationalization” incorporates the use of bilateral currency swaps extended by China’s central bank, or the usage of renminbi in outbound lending. But in terms of sanctions avoidance using renminbi-denominated transactions, the primary threat is the usage of Chinese financial networks by third parties to bypass US financial and regulatory surveillance. The most important consideration in that context is the liquidity and availability of renminbi itself, and trade and financial activity involving China’s currency, particularly wholesale transactions between banks.
One of the methods Beijing attempted to use to improve the attractiveness of renminbi-denominated assets was to have China’s currency included in the IMF’s SDR basket of currencies, which would provide an official designation that the renminbi was a currency that the IMF agreed was acceptable for holding within foreign exchange reserves. In addition, any transaction with the IMF would need to include renminbi, so this designation would produce a certain volume of purchases of renminbi. In addition, it would reduce a perceived obstacle to other investors, including central banks, acquiring renminbi-denominated assets. Beijing was required to demonstrate that the currency was “freely usable” in international financial markets. Because the renminbi was not fully convertible, and there were still capital controls in place on the currency, attesting to the currency’s usability was difficult. Instead, Beijing argued that the offshore currency, or the international renminbi (the Chinese yuan traded in the offshore market, or CNH) traded primarily in Hong Kong, fulfilled those criteria, since these transactions were subject to more limited capital controls. The IMF ultimately accepted the argument when it admitted the renminbi into the SDR currency basket in 2015, which helped to expand the range of investors who could readily invest in renminbi-denominated assets.
However, the accumulation of offshore renminbi and improving liquidity in financial markets for China’s currency is far from a straightforward process. Because China runs a global trade surplus, even if 100 percent of China’s trade was denominated in renminbi, no Chinese currency would necessarily accumulate outside the country’s borders, while foreign currency would come into the country. A portion of China’s trade could be denominated in renminbi—primarily China’s imports—which would result in third countries accumulating renminbi payments from Chinese companies. Then they would be forced with the choice of what to do with the Chinese currency: trade it for dollars or domestic currency, invest in renminbi-denominated assets, or deposit it in an overseas or Chinese bank. Chinese consumers could carry renminbi outside the country, but would need to find merchants to accept it. Capital outflows, including overseas investment and lending, could hypothetically increase the pools of available renminbi outside the country, assuming there were third parties willing to hold the currency or invest it in Chinese assets. This is one reason China’s central bank has encouraged currency swap deals to expand liquidity in offshore renminbi markets, but the actual utilization of these swap lines has been very limited. Simply put, there is no easy mechanism for Beijing to encourage foreign investors and central banks to hold the Chinese currency, as this depends upon public perceptions of the currency’s utility, liquidity, safety, and long-term value.
China’s currency is generally considered the fifth-most commonly used currency in the world, and is used for 3.6 percent of global transactions by value, according to SWIFT data. It still falls behind not only the US dollar and the euro, but the Japanese yen and pound sterling. Excluding payments within the eurozone, according to SWIFT’s data, the renminbi is sixth, falling behind the Canadian dollar. (And this may be low, given that SWIFT’s data will more heavily sample transactions in Western financial markets.) In terms of offshore holdings of renminbi, the PBOC’s own data shows that foreign holdings of renminbi-denominated assets totaled 9.76 trillion yuan ($1.36 trillion) as of June 2023, down from a peak of 10.8 trillion yuan in 2021. Naturally, the change in US interest rates starting in 2022 reduced the attractiveness of renminbi-denominated assets to foreign investors, along with geopolitical risks tied to China’s alignment with Russia.
Most relevant for sanctions avoidance is the liquidity of renminbi-denominated trading, or the ability of third parties to use renminbi in transactions outside of US and Western surveillance. However, the vast majority of renminbi-denominated financial transactions still take place in Hong Kong (79 percent), followed distantly by the United Kingdom (5 percent) and Singapore (3 percent). While this is logical given Hong Kong’s role as the gateway between China and international financial markets, the importance of Hong Kong within the offshore renminbi market raises the question of how “international” offshore renminbi trading really is. Most likely transactions involving offshore renminbi that are used to avoid sanctions would transact via Hong Kong, using institutions that would also maintain business in the US dollar, and would therefore also be subject to US sanctions or other economic statecraft.
As of 2023, the renminbi share of allocated global foreign currency reserves stood at around 2.4 percent, a decline from 2022 (2.6 percent) and 2021 (2.8 percent).75Rhodium Group analysis of IMF Currency Composition of Official Foreign Exchange Reserves (COFER) data. According to the PBOC, more than 80 foreign central banks or monetary authorities have held renminbi in their foreign currency reserves.76People’s Bank of China, 2023 RMB Internationalization Report, 2023, http://www.pbc.gov.cn/en/3688241/3688636/3828468/4756463/5163932/2023120819545781941.pdf. Many of the countries publicly committed to holding renminbi in their foreign currency reserves have a significant trade relationship with China (Table 13). China is the top trading partner of Russia, Australia, Brazil, Bangladesh, and Kazakhstan. At 13.1 percent, Russia holds the largest disclosed share of renminbi reserves (although the effective share of Russian reserves may be higher given the impact of sanctions). US sanctions on the use of US dollar assets have added pressure on Russia to diversify into other currencies, and Russia’s share of trade invoiced in renminbi increased from 3 percent in 2021 to 20 percent by the end of 2022.77Maxim Chupilkin et al., “Exorbitant privilege and economic sanctions,” EBRD Working Paper No. 281, European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, September 2023, https://www.ebrd.com/publications/working-papers/exorbitant-privilege-and-economic-sanctions. Around 2018, several European countries, including France, Belgium, Germany, Slovakia, and Spain, as well as the European Central Bank, began announcing the inclusion of renminbi in their reserves, likely a result of the renmimbi’s inclusion in the IMF’s SDR currency basket. However, these countries do not publicly disclose the current composition of reserves, and more recent reporting on the quantity of renminbi reserves is sparse. African countries such as Rwanda and South Africa primarily mention trade settlement and investment promotion as motives for diversifying assets with renminbi holdings.
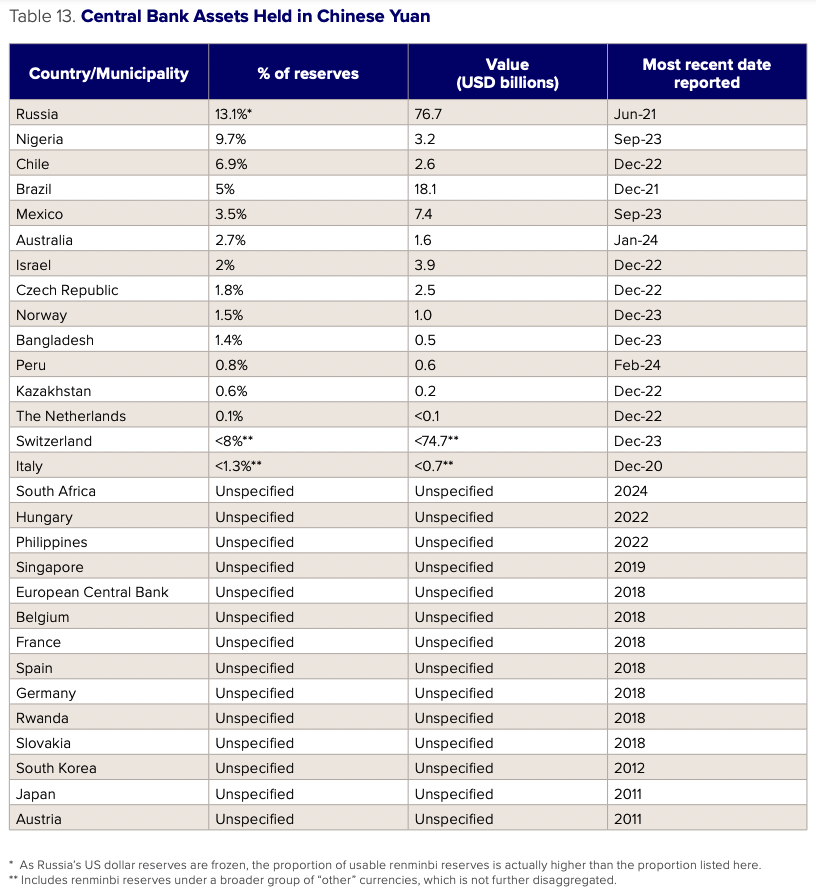
Because the currency remains subject to capital controls and is not fully convertible, choosing to hold foreign exchange reserves in renminbi is not necessarily as straightforward as holding other currencies. But during periods when interest rates on US Treasuries and other traditional reserve currencies are low, higher return on Chinese government bonds may offer an attractive alternative to diversify reserve holdings.
Trade settlement in China is also increasingly denominated in renminbi. Naturally, it is easier for China to impose payment terms upon its own imports from foreign companies, as the customer. As a result, along with foreign exchange reserves, countries that tend to denominate more trade in renminbi tend to be significant exporters to China, and run trade surpluses with China, primarily in raw materials or commodities. The overall volume or proportion of trade settlement in renminbi is a far less significant gauge of renminbi internationalization than other metrics such as the accumulation of renminbi assets or the volume of cross-border financial transactions in renminbi. Nonetheless, the proportion of trade denominated in renminbi has increased notably since the Russian invasion of Ukraine, and has hit all-time highs above 35 percent in recent months.
In the past, when renminbi-denominated trade settlement surged from 2013 to 2015, this reflected strong demand for renminbi in offshore markets, because the Chinese currency was appreciating against others, and against the US dollar. As a result, exporters to China were more likely to be willing to hold renminbi if Chinese importers paid in the currency. The recent surge also corresponds with a change in the currency’s value, but the renminbi has depreciated against the dollar since early 2022. The rise in renminbi-denominated trade settlement in recent years has occurred alongside the rise in US and global interest rates relative to Chinese interest rates. The lower Chinese rates can make trade credit denominated in renminbi more attractive to firms, relative to more expensive US dollar-denominated trade finance. The renminbi’s share of global trade finance increased to 5.12 percent in November 2023, from only 2 percent in December 2020, according to SWIFT data, and it is probable that lower Chinese interest rates can explain the recent rise in overall trade settlement.
Financial infrastructure: CIPS
Central to Beijing’s efforts to build resilience and circumvent potential G7 sanctions is CIPS. Launched by the PBOC in 2015, CIPS is a large-value renminbi payments system designed to facilitate and settle domestic and cross-border renminbi transactions.78People’s Bank of China, “人民币跨境支付系统(CIPS) 主要功能及业务管理” [Overview of the Main Functions and Business Management of the Cross-Border Payment System (CIPS) for Renminbi], July 2018. https://res.cocolian.cn/pbc/人民币跨境支付系统CIPS业务管理制度介绍-201807.pdf. Built to resolve the inefficiencies of China’s legacy payments system, including the China National Advanced Payment System (CNAPS), CIPS promises to integrate its participants into the existing global financial architecture, while allowing for onshore renminbi clearance and settlement services.79Josh Lipsky and Ananya Kumar, “The dollar has some would-be rivals. Meet the challengers,” New Atlanticist, Atlantic Council, September 22, 2022, https://www.atlanticcouncil.org/blogs/new-atlanticist/the-dollar-has-some-would-be-rivals-meet-the-challengers.
Structured like the Clearing House Interbank Payments System (CHIPS), the US-led interbank payments system, financial institutions are either direct participants, which maintain an account within CIPS, or indirect participants, which engage with the system through relationships with a direct participant. As of December 2023, CIPS boasts 139 direct participants, with foreign participants concentrated within China’s trading partners, and 1,345 indirect participants.80Cross-Border Interbank Payment System, “CIPS Participants Announcement No. 92,” accessed March 15, 2024, https://www.cips.com.cn/en/participants/participants_announcement/60849/index.html. Direct participants have to be incorporated in China. However, direct participants can be located abroad if they are a subsidiary of a Chinese financial institution In total, CIPS participants span across 113 countries and regions around the world.81Cross-Border Interbank Payment System, “CIPS Participants Announcement No. 93,” accessed March 15, 2024, https://www.cips.com.cn/en/participants/participants_announcement/60945/index.html.
CIPS’ stated goal is to improve efficiency and reduce costs associated with international renminbi settlements. Beijing aspires to make it an integral part of the world’s existing financial infrastructure. Unlike CNAPS, CIPS is directly interoperable with SWIFT and uses the ISO 20022 international payments messaging standard. However, CIPS’ potential as a replacement to the US-led global financial plumbing has not gone unnoticed. Experts in China noticed US efforts to disconnect Iran from SWIFT in 2012 and threats to take similar action against Russia in 2014. Fearful that the United States may eventually consider similar actions against China, some have argued CIPS may be more important as a tool to protect Beijing’s national and economic security.82Xu Wenhong, “SWIFT系统:美俄金融战的博弈点” [SWIFT System: The Game of Financial Warfare Between the United States and Russia], Regional Studies of Russia, Eastern Europe, and Central Asia 6 (9) (2019): 17–32, http://www.oyyj-oys.org/Magazine/Show?id=70963. Recent actions by the G7 against Russia to follow through and disconnect ten Russian banks from SWIFT have amplified these fears.83Vincent Ni, “Beijing orders ‘stress test’ as fears of Russia-style sanctions mount,” Guardian, May 4, 2022, https://www.theguardian.com/world/2022/may/04/beijing-orders-stress-test-as-fears-of-russia-style-sanctions-mount. As a result, while CIPS does reportedly utilize SWIFT for around 80 percent of the transactions it processes,84Reuters, “Russian central bank, sovereign fund may hold $140 bln in Chinese bonds – ANZ,” March 2, 2022, https://www.reuters.com/markets/europe/russian-central-bank-sovereign-fund-may-hold-140-bln-chinese-bonds-anz-2022-03-03/. among CIPS’ direct participants, it does maintain an alternate communications channel.
Due to its capacity to operate independently with its direct participants, even in a maximalist-sanctions scenario similar to G7 actions against Russia or US sanctions against Iran, CIPS can continue to function and process bank-to-bank transfers. CIPS provides meaningful insulation for the Chinese financial system as well as means to easily engage with willing partners abroad either through CIPS’ current roster of direct participants or by onboarding new ones.
There is also little question CIPS can scale to meet China’s needs in the face of Western sanctions. When looking at CIPS’ support for renminbi internationalization efforts, especially in the context of sanctions, it’s critical to disaggregate Chinese goals to encourage international use of the renminbi from building resilience against potential G7 sanctions. At the end of 2023, CIPS processed around 3 percent of the total value that passes through CHIPS.85“About Us,” Cross-Border Interbank Payment System, accessed March 15, 2024, https://www.cips.com.cn/en/index/index.html; “About CHIPS,” Clearing House, accessed March 15, 2024, https://www.theclearinghouse.org/payment-systems/CHIPS. This transaction volume is well short of what Beijing would need to legitimately challenge the dollar as the dominant currency of international commerce. However, taken along the far narrower goal of building a payments network that remains operational for trade and basic financial transactions in the face of economic sanctions, Beijing has succeeded.86Peter E. Harrell, “How to China-Proof the Global Economy,” Foreign Affairs, December 12, 2023, https://www.foreignaffairs.com/china/how-china-proof-global-economy-america. CIPS has the capacity and resilience to manage and onboard China’s global economic relationships in the event of maximalist G7 sanctions. While CIPS processes a fraction of the total value that passes through CHIPS, this is already adequate capacity to cover China’s total goods trade in the event Beijing is removed from SWIFT. In Q3 2023, CIPS processed, on average, $51 billion in transactions a day. Chinese total imports and exports over the same period amounted to an average of around $17 billion a day. Restrictions and transitional pain points will primarily stem from Chinese trading partners’ willingness to engage with the system.
Digital currency and e-CNY
In 2017, China established the digital yuan project, a CBDC, with the stated goal of facilitating cross-border transactions and reducing reliance on traditional payment systems. Mu Changchun, the director of the Digital Currency Research Institute at the PBOC, discussed expanding the scope of Project mBridge to eventually “formulating a road map to develop an influential cross-border payment infrastructure.”87Matt Haldane, “Head of China’s digital yuan addresses blockchain’s role in mBridge, pushing digital currencies beyond their borders,” South China Morning Post, November 2, 2022, https://www.scmp.com/tech/policy/article/3198094/head-chinas-digital-yuan-addresses-blockchains-role-mbridge-pushing-digital-currencies-beyond-their. In the context of a Taiwan crisis, policymakers should consider China’s advancements and ambitions in both retail and wholesale CBDCs and how these platforms could be leveraged to mitigate the effect of potential Western sanctions.
China’s retail CBDC project focuses on enabling Chinese individuals and businesses to use the digital currency for everyday domestic transactions and creating a network of state-enabled payments.88People’s Bank of China, Progress of Research & Development of E-CNY in China, Working Group on E-CNY Research & Development of the People’s Bank of China, July 2021, http://www.pbc.gov.cn/en/3688110/3688172/4157443/4293696/2021071614584691871.pdf Common use-cases of the retail e-CNY include public transportation, integrated identification cards, school tuition payments, tax payments, and refunds.89People’s Bank of China, “Notice from the General Office of the People’s Bank of China on Further Enhancing the Work of ‘Digital Renminbi,’” January 1, 2023, http://www.pbc.gov.cn/goutongjiaoliu/113456/113469/4761016/index.html. Currently, the domestic pilot project has 13.61 billion renminbi in circulation with 260 million digital wallets.90Ibid. However, this project has limited ability to help internationalize the yuan and serve as a means of sanctions evasion given its domestic focus.
China’s wholesale CBDC projects are different. Phase 1 of Project mBridge started in 2021 as a joint experiment with the central banks of China, Thailand, the United Arab Emirates, and the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA), and select commercial banks within these jurisdictions, as well as the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) Innovation Hub.91Bank for International Settlements, “Project mBridge: experimenting with a multi-CBDC platform for cross-border payments,” updated October 31, 2023, https://www.bis.org/about/bisih/topics/cbdc/mcbdc_bridge.htm.The project was initially designed to create a common infrastructure that enables real-time crossborder transactions using CBDCs. In the current version, the project connects over twenty banks across the four jurisdictions, reducing the reliance on the correspondent networks utilizing the dollar.92BIS Innovation Hub, Project mBridge: Connecting economies through CBDC, October 2022, https://www.bis.org/publ/othp59.pdf. mBridge can be understood as an upgrade to the current cross-border payments technology, and if implemented at scale could deliver efficiency, speed, and security to international payments outside of dollar-based networks. In October 2022, the project successfully conducted 164 transactions, settling a total valued at $22 million, with almost half of all transactions in e-CNY.9493Ibid. This was the first successful test of a wholesale CBDC with actual funds and concluded Phase 1 of the project.94Ibid.
In Phase 2 of the project, China and the BIS will expand the mBridge participants. As of January 2024, twenty-five central banks have joined the project as observing members and additional countries are interested in joining this expanding network.95Observing members: Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas; Bank Indonesia; Bank of France; Bank of Israel; Bank of Italy; Bank of Korea; Bank of Namibia; Central Bank of Bahrain; Central Bank of Chile; Central Bank of Egypt; Central Bank of Jordan; Central Bank of Malaysia; Central Bank of Nepal; Central Bank of Norway; Central Bank of the Republic of Türkiye; European Central Bank; International Monetary Fund; Magyar Nemzeti Bank; National Bank of Georgia; National Bank of Kazakhstan; New York Innovation Centre, Federal Reserve Bank of New York; Reserve Bank of Australia; Saudi Central Bank; South African Reserve Bank; and the World Bank. mBridge is organized in a three-tier participation structure.96BIS Innovation Hub, Project mBridge Update: Experimenting with a multi-CBDC platform for cross-border payments, October 2023, https://www.bis.org/innovation_hub/projects/mbridge_brochure_2311.pdf. The first level is the project’s founding members: China, Thailand, Hong Kong, and the UAE. The second level consists of eleven anonymous central banks engaged in mBridge’s sandbox testing; notably, the Central Bank of Türkiye has announced its involvement in testing. mBridge’s sandbox offers a secure environment for central banks to experiment with simulated nodes and transactions. The third tier consists of observing members, which includes the IMF, the World Bank, and fourteen additional central banks. The value of a payments infrastructure lies in the network effects it generates for participants. As more central banks join, this infrastructure becomes increasingly efficient.97Ibid. China has also announced plans to integrate traditional payment systems like real-time gross settlement systems or fast payment systems with mBridge, so that central banks can issue their own CBDC on mBridge without creating their own CBDC infrastructure.98Mike Orcutt, “What’s next for China’s digital currency?” MIT Technology Review, August 3, 2023, https://www.technologyreview.com/2023/08/03/1077181/whats-next-for-chinas-digital-currency/.
Transactions on this payment infrastructure are conducted outside of the US dollar and therefore outside of US sanctions influence. As a result, mBridge can offer an alternative cross-border settlement system to jurisdictions looking to bypass US sanctions or compliance with US anti-money laundering/countering the financing of terrorism regulations. Therefore, mBridge could serve as an alternative financial channel that could be leveraged in the event of a Taiwan crisis—especially as an option for jurisdictions that may be reluctant to join Western sanctions and/or “fence-sitting” economies that rely significantly on Chinese import and export markets. In a crisis scenario, China could also evade secondary sanctions and still maintain access to critical commodity markets and energy products.
There have been changes in technology that also reflect Beijing’s influence on the cross-border project. Until recently, mBridge was running on a proprietary blockchain based on Ethereum’s Solidity language and developed by “central banks for central banks,” unlike other CBDC initiatives that run on blockchains built by third parties.99BIS Innovation Hub, Project mBridge: Connecting economies. However, in November 2023, Chinese media reported that mBridge will be transitioning to the Dashing protocol, which was developed by the PBOC’s Digital Currency Research Institute and Tsinghua University.100Wang Huirong, “已在央行数字货币桥等落地应用!中国自主设计研发的大圣协议是什么[“It’s in use with mBridge! What is China’s indigenously developed Dashing protocol?”] ThePaper.cn, October 17, 2023, https://m.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_24964633. The specific program language has not been announced, but the protocol could achieve higher scalability and lower latency. This shift underscores how much China remains the center of mBridge as the project designer, manager, and main trading partner.
There is also a lack of US- or dollar-based alternatives to mBridge. Despite the dollar comprising more than 70 percent of SWIFT messages worldwide in 2023, there is currently no equivalent Western or G7 digital currency or platform to counterbalance the advantages presented by mBridge, including faster settlement and reduced transaction costs. This is a significant gap in the emerging digital financial ecosystem, which provides China with an opportunity to use this infrastructure to encourage more countries to opt for faster and more cost-effective transactions, and then turn to this system during a sanctions scenario.
While mBridge has significant potential to serve as a cross-border payments alternative for China, it is currently in the experimental stage—its scalability and wider adoption in real-world scenarios remains uncertain. Experts have projected that mBridge’s current capabilities are limited to facilitating roughly $190 million in transactions annually, which limits Beijing’s ability to shift flows in the event of a crisis in the short term.101Private conversations with experts associated with the project. In the medium term (three to five years), the project can potentially be leveraged to shield China’s financial system. In 2022, the total trade volume between the four founding mBridge members was $540 billion—if China moves just 5 percent of these flows to mBridge it could facilitate trade up to $27 billion.102UN Comtrade data (2022). Moving the mBridge consensus protocol to Dashing would also improve the efficiency of the project by increasing the number of transactions per second. However, liquidity remains a major concern for the scalability of mBridge. To facilitate large-scale cross-border transactions daily without dollars or euros would require a change in the current currency settlement system. However, at least for a shortterm crisis and for specific transactions that would fall under sanctions, mBridge can help the Chinese financial system and its commercial banks maintain liquidity.
mBridge, along with CIPS (see below), can potentially augment China’s ability to respond in a Taiwan crisis scenario. Despite its growth over the last two years, CIPS’ capability is limited by its reliance on SWIFT. Participants can message each other through the CIPS messaging system, but 80 percent of transactions on CIPS rely on the SWIFT infrastructure for translation.103Barry Eichengreen, Sanctions, SWIFT, and China’s Cross-Border Interbank Payments System, Center for Strategic and International Studies, May 20, 2022, https://www.csis.org/analysis/sanctions-swift-and-chinas-cross-border-interbank-payments-system. As a result, China might pivot toward strengthening the role of digital yuan and mBridge in its international payment networks, hoping to maintain transactional flows and mitigate the impacts of any restrictions on CIPS. Ultimately, China is likely to rely on both networks in a crisis to mitigate sanctions through multiple avenues.
One way to understand China’s goal with CIPS and its linkages with SWIFT is that by adding more banks to both networks China is making it more difficult to sanction the Chinese banking system without enormous repercussions to trading partners all over the world. Instead of a sanctions shield, like mBridge, CIPS expansion can be thought of as a leverage point to discourage sanctions.
There is growing interest around the world in finding alternatives to the dollar-based messaging and settlement systems. China is meeting this demand while also serving its own goals of internationalizing its currency and providing a hedge against sanctions. The development of the e-CNY and mBridge project provide Beijing with new options to circumvent a potential international sanctions regime in a Taiwan crisis. This makes the timing of a crisis critical. Without a change in current dynamics, the impact of sanctions today on China’s economy could be far more significant than the impact in three to five years when mBridge has become fully operational with additional countries as partners.
Prospects for future expansion of international Renminbi
While China has struggled to increase the attractiveness of the renminbi in overseas markets, there are certain political initiatives Beijing can take to increase the currency’s utility to third parties, and to expand participants in mBridge and CIPS. One of these is the use of currency swap arrangements to administratively offer pools of liquidity in renminbi for trade settlement or financial transactions in other countries. Another would be to offer concessionary lending to third countries in renminbi, for overseas infrastructure or Belt and Road Initiative-related projects, which can improve liquidity in overseas markets but may also require the borrower to spend or convert many of the proceeds back in China or with Chinese firms who can accept the renminbi.
Other options for Beijing include more ambitious concepts such as the use of a BRICS currency, which emerged as a topic of discussion during the last BRICS summit in South Africa in August 2023 and will continue to be a key area of policy exploration under the Russian BRICS presidency in 2024.104“BRICS Dedollarization: Rhetoric Versus Reality,” Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, January 23, 2024, https://carnegieendowment.org/2024/01/23/brics-dedollarization-rhetoric-versus-reality-event-8227 Any creation of a BRICS currency would necessarily require China’s participation, and given China’s economic weight within the group of countries, a BRICS currency would be almost equivalent to an offshore renminbi. The basic challenge persists, though, in that a BRICS currency could not provide any meaningful insulation from Western economic statecraft. Most of the BRICS countries, including China, run trade surpluses, so unless China dramatically increased imports from these countries, these countries would continue to export to Western economies, most likely using US dollars, and accumulating US dollars that would need to be cleared via US-domiciled accounts.
Beijing is also using the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) to advance non-dollar-denominated financial systems by promoting the use of local currencies like the renminbi in international trade and finance. Chinese leaders have supported the creation of an SCO development bank and have advocated for measures to increase local currency settlements including through improving local-currency cross-border payment and settlement systems as well as bilateral currency swaps arrangements.105Xinhua News Agency, “习近平在上海合作组织成员国元首理事会第二十二次会议上的讲话(全文)[Xi Jinping’s speech at the 22nd meeting of the Council of Heads of State of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (full text),” September 16, 2022, https://web.archive.org/web/20240213211131/https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2022- 09/16/content_5710294.htm.
The problem with the BRICS currency and Chinese efforts at the SCO speak to the larger limitations on the accumulation of offshore renminbi. As long as China runs a trade surplus, globally, then renminbi remains scarce, and remains inside China itself. Only by running a persistent trade deficit would renminbi end up circulating more regularly outside of China, and therefore create incentives for other market participants to hold renminbi-denominated assets. Otherwise, renminbi must spread through outbound investment, outbound lending, or currency swap arrangements, all of which must be negotiated with Chinese commercial banks or the central bank, rather than proceeding entirely via market transactions. The conundrum for Beijing is that should China run a persistent trade deficit or face persistent capital outflows, China’s currency would remain less attractive than other alternatives, because these forces may reduce the value of the currency over time. But those are also the only channels through which renminbi can significantly increase its circulation outside China.
Policy constraints on expansion of renminbi financial networks
China could meaningfully expand the international use of its currency by opening its capital account more rapidly to both capital inflows and outflows. The fact that the currency is not fully convertible meaningfully limits its usage, because market participants cannot exchange the currency freely for others, nor participate freely in Chinese financial markets. Beijing has significantly liberalized its own financial markets and allowed more foreign participation, but this has primarily been focused on maintaining inflows, rather than permitting outflows. There are still considerable restrictions on daily transaction volumes through China’s Bond Connect and Stock Connect programs, which permit two-way flows via Hong Kong.
However, fully liberalizing China’s capital account would bring a slew of additional financial risks, which explains Beijing’s reluctance to commit to greater opening. China has maintained a closed capital account for years, while the world-leading money supply has expanded to over $40 trillion, even though 98 percent of China’s monetary assets are denominated in renminbi. Currently, Chinese citizens are limited by the $50,000 annual quota on per capita foreign exchange conversions, and corporates are limited by a series of restrictions on outbound investments and rules limiting access to foreign exchange. These capital controls do not completely prevent conversions into foreign assets, but they slow down these flows considerably. Liberalization of the capital account would likely permit more inflows, but at the cost of much faster potential outflows, which may trigger significant liquidity problems within China’s financial institutions and significant pressure on the renminbi to depreciate. And such depreciation pressure would meaningfully reduce the attractiveness of the currency to overseas investors.
Implicit within these limitations is a broader problem of trust and credibility in Chinese policymaking. To hold an asset denominated in renminbi implicitly involves some degree of confidence in the longerterm value of the currency, the stability of China’s regulatory environment, and the credibility of China’s policymaking process. That policy credibility takes years to accumulate, but can be disrupted rapidly, through actions such as the crackdowns on IT firms or education and tutoring firms in 2021, or the botched efforts to bail out the equity markets, both in 2015 and earlier this year.106Tom Westbrook and Summer Zhen, “Why China’s national team won’t save spiralling markets,” Reuters, February 5, 2024, https://www.reuters.com/markets/asia/why-chinas-national-team-wont-save-spiralling-markets-2024-02-05/. These campaigns and crackdowns were highly adverse to foreign investors’ interests and raised questions about the ultimate intentions of China’s leadership to maintain economic growth and preserve an attractive climate for foreign investment. The same concerns among investors can emerge over geopolitical issues, such as China’s alignment with Russia after the invasion of Ukraine, which has cost China considerable credibility as an attractive economic partner or investment destination. As China’s political system has become more centralized, and campaign-style governance has become more common, it is more difficult for economic technocrats to send countervailing signals that campaigns have ended and normalcy has returned.
All of these constraints limit Beijing’s capacity to develop highly liquid and credible markets for its currency outside of China itself. As a result, China’s financial institutions remain dependent upon the US dollar at the same time as Beijing attempts to expand alternative financial networks in renminbi. Even while many states may seek an alternative to the US dollar system, Beijing faces meaningful limits in its capacity to provide that alternative, without jeopardizing financial stability in China itself.
Responding to G7 economic statecraft in a crisis
The concerns outlined above are longer-term in nature. The immediate question looming for Beijing is what China can plausibly do now if G7 countries initiated some of the economic sanctions and other statecraft measures discussed in the scenarios above. And Beijing does have some meaningful options, simply because most of the renminbi-denominated financial networks can still be used on a limited basis, even if they are unattractive for large volumes of conventional economic transactions.
The first and most obvious step would likely be to route trade transactions involving energy sources and critical commodities imports via countries that were unlikely to cooperate with G7 sanctions or export controls. This would also likely involve the use of the renminbi as a payment currency, which is plausible since many of the commodity exporters to China are likely already receiving renminbi from their Chinese customers. The third-party exporters to China could then be subject to secondary sanctions in some cases, but this would likely involve a significant escalation in targets from G7 countries. Most of this trade activity is likely to continue in spite of Western sanctions on China.
The second measure includes currency intervention, openly selling US dollars in order to shore up the value of China’s currency and reduce near-term pressures for capital outflows that would likely intensify as sanctions were imposed. Currency stability would likely be necessary to maintain Beijing’s capacity to use alternative financial networks in a crisis scenario, to prevent third countries from facing pressure to sell their renminbi and avoid the currency because of sanctions risks. This may appear in Western financial markets as China “dumping” US Treasuries or other US dollar-denominated assets, but the nature of this operation would be to maintain ammunition to stabilize China’s currency.
Third, Beijing can reallocate critical trade and financial transactions with the rest of the world through very large or very small financial institutions. Small financial institutions may be sanctioned, and lose access to US dollar clearing facilities, but these limits are unlikely to have significant implications for financial stability in China, and can shift to other institutions as necessary. Larger financial institutions are more difficult to sanction because of the potential for significant disruptions in regular trade activity with Western markets, and the potential for sudden dislocations in global supply chains. Shifting more critical transactions to larger state-owned banks such as the Bank of China or Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, for example, would be a more difficult secondary sanctions target for Washington.
In terms of rapidly accelerating the development of renminbi-denominated financial networks, Beijing may struggle to react quickly and effectively. More participants from third countries can certainly be admitted into CIPS, more central banks can be linked to mBridge, and more CBDC can be issued, of course. Beijing can suspend cooperation with SWIFT altogether, including within CIPS. But these are not the primary limits on the utilization of these networks, which remain the liquidity and attractiveness of renminbi financial assets, and the limits Beijing places on convertibility of the renminbi. The imposition of G7 sanctions would likely intensify these problems for Beijing, given the rising political costs of third countries in economic engagement with China, rather than catalyzing faster growth of renminbi-denominated financial networks.
Beijing’s responses to different types of crises
As discussed previously, the level of escalation and the mechanics of the scenarios involved will also influence the level of Beijing’s response and attempts to circumvent sanctions. Moderate escalation as defined in this report would suggest that Beijing will attempt to maintain the perception of normalcy in its international financial engagement, leaving channels open for capital inflows into China’s equity and bond markets. The exchange rate would likely be under pressure but within the capacity of the central bank to stabilize conditions, and under most circumstances, it would be in Beijing’s benefit to project financial stability. China would likely try to shift sensitive trade and financial transactions to smaller banks at less risk of international sanctions or restrictions.
Renminbi-denominated international financial networks could become more active in a moderate-escalation scenario, precisely because Beijing would not be facing widespread restrictions on trade, and would be attempting to portray Western sanctions as unreasonable and overreactions, demonstrating the lack of credibility in US and G7 economic policy. Beijing would likely attempt to sign up additional countries’ financial institutions to networks such as CIPS and mBridge, and channel trade and wholesale financial transactions through those networks. Renminbi-denominated central bank swap lines to friendly countries could also be expanded under these circumstances to improve liquidity conditions for renminbi-denominated trade transactions.
In a high-escalation scenario, the renminbi would presumably already be under considerable pressure and would be weaker against the US dollar, and the PBOC would not be as interested in maintaining a certain level of the currency (while also trying to prevent an outright currency collapse). Since this scenario assumes widespread restrictions on China’s financial institutions, it is probable that third countries would be cautious about engaging with China’s renminbi-denominated financial networks for fear of potential secondary sanctions. Furthermore, it is more likely that the pressure on the renminbi would reduce the attractiveness of engaging in trade transactions via China’s international financial networks. More probably, these transactions would be limited to those conducted with Beijing’s explicit political guidance.
Supply and demand of alternatives to the dollar-based financial system
Demand for alternatives to the dollar-denominated financial system are shaped by a desire to mitigate the impact of possible Western sanctions and reduce transaction costs associated with utilizing dollardenominated cross-border payments systems. The G7 and its partners levied unprecedented coordinated sanctions against Russia in response to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. However, several governments maintain economic and political relationships with Russia. These “fence-sitter” governments, which include BRICS and Gulf countries, have not joined the sanctions campaign and are exploring alternatives to the dollar and euro in order to continue their economic relationships with Russia.107New Atlanticist, “Transcript: US Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen on the Next Steps for Russia Sanctions and ‘Friend-shoring’ Supply Chains,” Atlantic Council, April 13, 2022, https://www.atlanticcouncil.org/news/transcripts/transcript-us-treasury-secretary-janet-yellen-on-the-next-steps-for-russia-sanctions-and-friend-shoring-supply-chains/.
The United States and its allies’ perceived willingness to use tools of economic statecraft in the event of any conflict shapes the urgency with which countries are pursuing these alternatives.108Daniel McDowell, “Overview” in Bucking the Buck: US Financial Sanctions and the International Backlash against the Dollar (Oxford University Press, March 2023). Similar to G7 economic initiatives to de-risk or pursue China+1 goods supply chain initiatives, nonaligned capitals around the world are also interested in analogous financial hedges.109Gerard DiPippo and Andrea Leonard Palazzi, “It’s All about Networking: The Limits of Renminbi Internationalization,” Center for Strategic and International Studies, April 18, 2023, https://www.csis.org/analysis/its-all-about-networking-limits-renminbi-internationalization. Their efforts are not necessarily meant to supplant the dollar as the dominant international currency but are designed to safeguard their economies in a crisis scenario. It is important to recognize that different countries within the BRICS, for example, have varying motivations and levels of interest in de-dollarization. It is therefore more useful to evaluate de-dollarization efforts on a country-by-country basis as the Atlantic Council has done in its Dollar Dominance Monitor.110“Dollar Dominance Monitor,” Atlantic Council, accessed March 15, 2024, https://www.atlanticcouncil.org/programs/geoeconomics-center/dollar-dominance-monitor/.
Countries are also striving to reduce dollar usage in cross-border payments because of potential efficiency gains brought about from local currency settlement, or, in the case of China’s trading partners, renminbi trade settlement. This is particularly prominent in Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) member states whose central bankers have long taken issue with the inefficiencies and risks incurred by their reliance on the dollar for regional trade and finance.111Association of Southeast Asian Nations, “Summary of Summaries of Topic1 ‘Ways to promote foreign trade settlements denominated in local currencies in East Asia,’” accessed March 15, 2024, https://www.asean.org/wp-content/uploads/images/archive/documents/ASEAN+3RG/0910/Sum/16.pdf. Currently, most high-value crossborder dollar payments are settled through the US-led CHIPS system. However, because only one ASEAN member state’s bank—Thailand’s Bangkok Bank Public Company Limited—is a direct participant in CHIPS,112“CHIPS Participants,” Clearing House, accessed March 15, 2024, https://www.theclearinghouse.org/-/media/new/tch/documents/payment-systems/chips_participants_revised_01-25-2021.pdf most dollar-denominated financial flows have to rely on correspondent banking relationships where local institutions maintain accounts with institutions that are members of CHIPS. This financial intermediation incurs costs on traders and financial institutions generating financial motivations to advance dollar alternatives.113Congressional Research Service, “Overview of Correspondent Banking and ‘De-Risking’ Issues,” April 8, 2022, https://crsreports.congress.gov/product/pdf/IF/IF10873/3. Still, the network effects associated with dollar dominance are considerable, and dollar alternatives may not be readily available or cost effective.114Gita Gopinath and Jeremy C. Stein, “Banking, Trade, and the Making of a Dominant Currency,” Working Paper 24485, NBER Working Paper Series, National Bureau of Economic Research, https://www.nber.org/system/files/working_papers/w24485/w24485.pdf. So while ASEAN countries, for example, are exploring new systems to directly link national payments systems as an alternative to correspondent banking,115Kominfo, “The Development of Cross-Border Payment Cooperation in ASEAN,” ASEAN, September 22, 2023, https://asean2023.id/en/news/the-development-of-cross-border-payment-cooperation-in-asean. policymakers in the region face considerable headwinds to develop an alternative that is cheaper than established US dollardenominated financial networks.
Foreign exchange markets are one such example. Countries interested in local currency settlement still must utilize foreign exchange markets to convert their domestic currency to their partner’s. However, G7 currencies, led by the dollar, make up nearly 85 percent of all foreign exchange transactions globally.116“OTC foreign exchange turnover in April 2022,” Triennial Central Bank Survey, Bank for International Settlements, October 27, 2022, https://www.bis.org/statistics/rpfx22_fx.htm#graph4. With emerging market currencies comprising just 8.9 percent of all foreign exchange transactions, markets for non-dollar currency pairs are mostly underdeveloped. Low volumes for local currency settlement increase the gap between buying and selling rates (the bid-ask spread). For example, in Asia, where ASEAN governments have made a concerted effort to close this gap and increase cross-border local currency use, the bid-ask spread can still be more than double what traders pay for a transaction involving the local currency against the dollar.117Robert Greene, “Southeast Asia’s Growing Interest in Non-dollar Financial Channels—and the Renminbi’s Potential Role,” Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, August 22, 2022, https://carnegieendowment.org/2022/08/22/southeast-asia-s-growing-interest-in-non-dollar-financialchannels-and-renminbi-s-potential-role-pub-87731. This can counteract the dollar transaction costs incurred by financial intermediation, reinforcing the role of the dollar.
To decrease local currency transaction costs between China and its trading partners, Beijing is actively providing additional pools of renminbi offshore to improve liquidity. During the summer of 2022, the PBOC and the HKMA upgraded their currency swap line to a standing arrangement, providing offshore renminbi markets with stable, long-term liquidity support. The PBOC has also encouraged other regional central banks, namely the Monetary Authority of Singapore, to utilize its renminbi swap funds to enhance the liquidity of their own renminbi markets. The PBOC has suggested it will continue to improve offshore renminbi liquidity through additional supply arrangements.118People’s Bank of China, 2023 RMB Internationalization.
Geoeconomics and transactional efficiency gains must reinforce each other for meaningful supplies of dollar alternatives to emerge. The immense network effects of the dollar mean that governments must foot some of the bill, as Beijing and its financial system is doing to develop renminbi foreign exchange markets. These costs can be more easily justified when there is a legitimate national security concern. While the Russia sanctions have accelerated interest in efforts to find dollar alternatives, many of these initiatives are still years away from having enough demand from China’s partners to be useful and effective at scale. However, in the aftermath of a Taiwan crisis, and a sanctions package from the G7, it is likely countries would increase efforts to build these systems both between each other and with China. However, if G7 use of financial statecraft instruments becomes more infrequent or guidelines are adopted to constrain them, there will be less incentive and momentum to develop and adopt alternatives.
Assessing China’s capacity to respond to G7 statecraft
The costs of any Taiwan crisis scenario that threatens to spiral into broader conflict between China and the United States are so large that it may seem trivial to draw finite distinctions between these scenarios, or break down where costs are likely to be most severe. But understanding how China is likely to respond to G7 economic statecraft can help policymakers prepare to minimize those costs, while also outlining alternative paths to avoid conflict by emphasizing that the G7 understands the scope and range of China’s economic second-strike capability. Respect for the damage that both G7 and Chinese economic statecraft can impose can help both sides walk back from the brink of a Taiwan crisis.
The timing of any scenario is also critically important, given how policy is currently evolving in both Western democracies and in Beijing to improve the range of choices in the event of a crisis. The process of de-risking and diversification of supply chains is likely to marginally reduce China’s capacity to practice critical elements of economic statecraft via trade and export restrictions over time. But in finance, policy is trending in the opposite direction, with China’s renminbi-denominated financial networks likely to continue to expand in scope and liquidity, providing more alternative options for China to potentially circumvent US or G7 statecraft tools. A Taiwan crisis in a year’s time will present both sides with far different options and concerns about costs relative to a scenario in five years’ time.
The impact on trade and FDI
One of the principal arguments of this study is that China is armed with powerful statecraft options relating to trade (both imports and exports) and foreign investment (particularly inbound FDI), but that the expansive use of these tools in a moderate- or high-escalation scenario comes with steep economic and reputational costs. Prior geopolitical incidents have shown China to have a wide array of formal and informal tools available, but it has generally used these tools in a targeted fashion: on single firms or industries, or smaller trading partners. China is expanding the legal foundations for these tools. China’s Anti-Foreign Sanctions Law, anti-blocking statute, and expanding export control regime serve to highlight Beijing’s leverage in trade and direct investment with G7 countries.
In an escalation over Taiwan, China has the capability to expand the use of these coercive tools. Trade-related tools would likely focus first on restricting access to China’s market in goods where the costs to China are lower (consumer discretionary goods, easily substitutable goods) and where the relative costs to adversaries are high. Export-related restrictions would likely focus on critical raw materials and key industrial inputs that account for a relatively small share of China’s overall output and employment, but which are difficult for other countries to replace or do without. Investment-related tools would likely begin with disrupting MNC operations through investigations, audits, and interfering with data and financial flows. In a higher escalation scenario, all of these tools could be scaled up further, up to near-total trade restrictions and seizure of MNCs assets in China.
But using these tools, even in limited ways, comes with immediate costs to China. China’s economy depends in large part on the contributions of foreign firms and export-oriented manufacturing. It also carries longer-term costs from frightening off global investors worried about China’s “investability” due to macroeconomic and geopolitical risks. In short, though these coercive tools exist, their use comes at a cost that Chinese policymakers will be loath to bear.
More germane in a moderate-escalation scenario will be China’s usage of positive trade and investment inducements to create cracks in G7 unity on economic sanctions or restrictions, in combination with other restrictions on market access. Beijing may combine measures to restrict market access for one country while offering preferential access to another. In conditions where countries adopt unilateral sanctions against China, China is likely to seek opportunities to undercut alignment by focusing countersanctions solely on that country and offering positive inducements to other G7 countries or the broader G20.
Beijing’s response will also ultimately depend on China’s central position within global supply chains, and as a node in $5.9 trillion in annual global trade activity. Gradual de-risking and diversification of global investment will shift this position, even if the outright volume of China’s trade with the rest of the world remains at a high level and China continues to provide intermediate goods to newer manufacturing centers.
Financial statecraft and consequences
Beijing’s capacity to retaliate against G7 economic statecraft using financial tools alone is limited, and far less consequential for the global economy than Chinese statecraft’s impact on trade and FDI activity. More important are Beijing’s efforts develop alternatives to the dollar-based system financial infrastructure to withstand Western sanctions in the future.
Certainly, Beijing has the ability to impose financial sanctions on Western banks and firms. In a crisis, Beijing is likely to impose stricter capital controls in ways that disrupt financial investments in China, although the primary purpose of these tools would be to prevent destabilizing capital outflows rather than punish foreign investors. Beijing also exerts considerable influence over countries that have borrowed from state-owned banks or received other preferential credit terms for infrastructure construction in cooperation with Chinese companies. These loans could be withdrawn or renegotiated quickly, imposing immediate financial concerns for the borrowing country. This is far less relevant a tool in retaliation against the G7 specifically, but could help Beijing to shape the global political environment in the course of an escalating Taiwan crisis.
The greater focus of policy efforts in Beijing is to expand the scope and capacity of renminbi-denominated international financial networks to offset or circumvent some of the impact of G7 financial sanctions or other economic restrictions. These renminbi-denominated networks are unlikely to challenge the US dollar-dominated financial system at any point in the future, in terms of liquidity, global reach, or reducing transaction costs. But Beijing does not need a comparable or fully competitive system in order to preserve alternatives for critical transactions that can bypass US or G7 controls in the event of broader financial sanctions. Beijing is likely to make further progress in expanding the technical reach of these networks via its digital currency pilot programs such as mBridge and adding more banks in multiple countries to CIPS. This can occur even if offshore renminbi liquidity conditions continue to weaken, as China’s currency remains under pressure to depreciate from capital outflows, which would likely intensify considerably in the event of a Taiwan crisis. Ultimately, it is easiest to understand the internationalization of the renminbi as a safety valve for Beijing in the event of a crisis rather than a full-fledged alternative to the US dollar system.
Preventing escalation in economic warfare
In contemplating the use of economic statecraft in a Taiwan crisis scenario, the challenge for policymakers in G7 capitals and in Beijing will be managing escalation, limiting economic costs, and preventing a spillover into broader kinetic conflict. Understanding how Beijing is likely to respond to G7 statecraft tools can thus help to communicate the potential costs of responsive or retaliatory spirals, and assist both sides in stepping back from the brink before ruinous economic costs result. Escalation is a particular concern for financial markets, which are likely to draw simple parallels between any Taiwan-related crisis and the Russian invasion of Ukraine, along with the past G7 sanctions response. The potential costs of escalation will be presented clearly in the very early stages of any crisis scenario.
Beijing’s initial responses to G7 statecraft measures are likely to fall upon predictable ground, in line with the past actions that China has taken in more limited scenarios. The range of those actions detailed in the previous sections is unlikely to surprise G7 policymakers. But there will still be uncertainty about China’s escalatory responses from those initial steps. The revealed capacity of Beijing to respond with policy agility on unfamiliar ground appears limited, based on the current state of economic policymaking. In addition, past episodes of retaliation against economic statecraft seem to value the perception of reciprocity rather than a technocratic skill in targeting a response toward G7 weaknesses. However, there are some notable counterexamples, such as the restrictions impacting specific foreign firms in the semiconductor industry.
As a result, the chances of escalation and rising economic, political, and potentially humanitarian costs will be higher if in addition to Beijing, G7 actions are also seen as unpredictable, rather than following a logic that global policymakers, financial markets, and Beijing can understand. The case for transparency about the enormous costs of even economic restrictions short of military conflict is strong, particularly as tensions over Taiwan have already risen over the past several years.
Similarly, the more frequent usage of economic sanctions and G7 statecraft targeting US dollar-denominated transactions that are central to the global trading system will help to create further global demand for alternative networks, including those managed by Chinese institutions (even as Beijing maintains similar threats of controlling access to these alternative financial architectures). Explicit restraint in deploying the most aggressive restrictions on economic activity can therefore help to reduce the attractiveness of alternative renminbi-denominated financial networks to third countries, and can also weaken China’s potential leverage over global supply chains and trade activity.
As the lines between economic statecraft and military conflict blur, mapping the paths and consequences of escalatory dynamics can help to prevent initial actions that risk policymakers finding justifications to unveil newer economic statecraft tools. But analyzing the steps China has taken in the recent past and anticipating steps Beijing may take in the future can only go so far. China’s economic second-strike capability is considerable, extending into a large proportion of global trade activity. Credible commitments to restraint in the usage of the most aggressive G7 economic statecraft tools can be just as effective as actively threatening their deployment in limiting escalation in a crisis.
Appendix 1: China’s formal economic statecraft toolkit
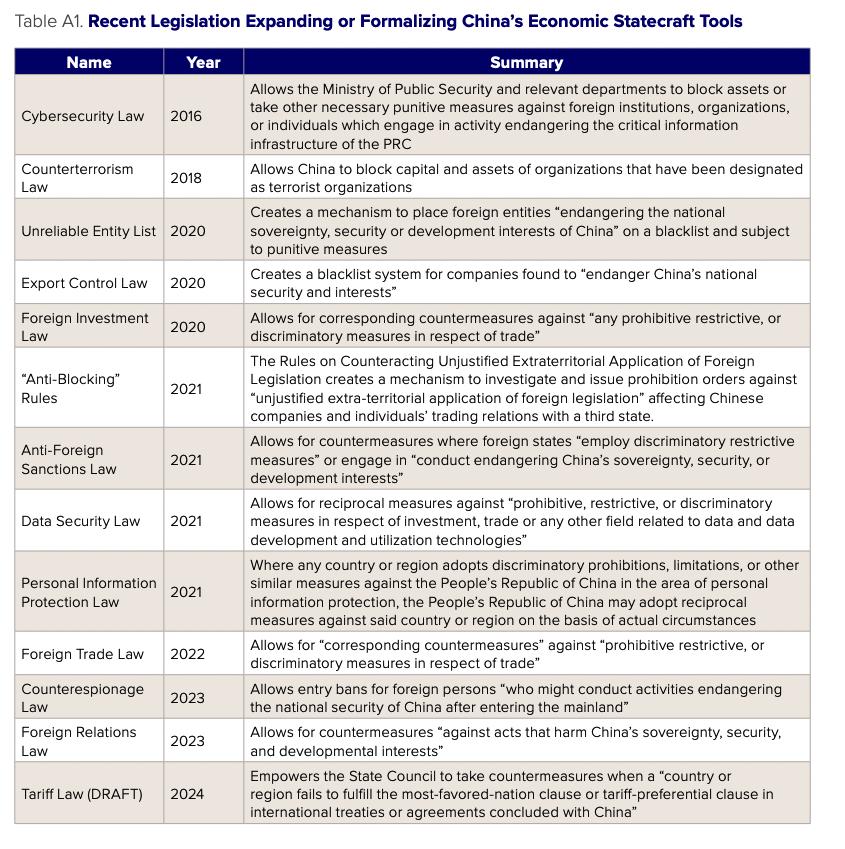
About the authors
Logan Wright is a partner at Rhodium Group and leads the firm’s China Markets Research work. He is also a Senior Associate of the Trustee Chair in Chinese Business and Economics at the Center for Strategic and International Studies. Previously, Logan was head of China research for Medley Global Advisors and a China analyst with Stone & McCarthy Research Associates, both in Beijing. Logan holds a Ph.D. from the George Washington University, where his dissertation concerned the political factors shaping the reform of China’s exchange rate regime. He graduated with a Master’s degree in Security Studies and a Bachelor’s degree in Foreign Service from Georgetown University. He is based in Washington, DC, after living and working in Beijing and Hong Kong for over two decades.
Agatha Kratz is a director at Rhodium Group. She heads Rhodium’s China corporate advisory team, as well as Rhodium’s research on European Union-China relations and China’s economic statecraft. Agatha also contributes to Rhodium work on China’s global investment, industrial policy and technology aspirations. Agatha holds a Ph.D. from King’s College London, having studied China’s railway diplomacy. Her previous positions include associate policy fellow at the European Council on Foreign Relations and editor-in-chief of its quarterly journal China Analysis, assistant editor for Gavekal-Dragonomics’ China Economic Quarterly, and junior fellow at the Asia Centre in Paris.
Charlie Vest is an associate director on Rhodium Group’s corporate advisory team. He manages research and advisory work for Rhodium clients and contributes to the firm’s research on US economic policy toward China. Charlie holds a master’s degree in Chinese economic and political affairs from UC San Diego and a bachelor’s degree in international affairs from Colorado State University. Prior to joining Rhodium, he worked in Beijing as research manager for the China Energy Storage Alliance, a clean energy trade association.
Matthew Mingey is an associate director with Rhodium Group, focusing on China’s economic diplomacy and outward investment, including development finance. Matthew is based in Washington, DC. Previously, he worked on global governance issues at the World Bank. Matthew received a Master’s degree in Global Business and Finance from Georgetown University’s Walsh School of Foreign Service and a Bachelor’s degree from the University of Pennsylvania.
Acknowledgments
This report was written by Logan Wright, Agatha Kratz, Charlie Vest, and Matthew Mingey in collaboration with the Atlantic Council GeoEconomics Center. The principal contributors from the Atlantic Council GeoEconomics Center were Josh Lipsky, Kimberly Donovan, Charles Lichfield, Ananya Kumar, Alisha Chhangani, and Niels Graham.
The GeoEconomics Center and Rhodium Group wish to acknowledge a superb set of colleagues, fellow analysts, and current and former officials who shared their ideas and perspectives with us during the roundtables and helped us strengthen the study in review sessions and individual consultations. These individuals took the time, in their private capacity, to critique the analysis in draft form; offer s uggestions, w arnings, a nd a dvice; and help us to ensure that this report makes a meaningful contribution to public debate. Our gratitude goes to Sarah Bauerle Danzman, Gerard DiPippo, Matthew Goodman, Peter Harrell, Annie Froehlich, Emily Kilcrease, Daniel McDowell, William J. Norris, Daniel Rosen, Dave Shullman, and Hung Tran.
This report is written and published in accordance with the Atlantic Council Policy on Intellectual Independence. The authors are solely responsible for its analysis and recommendations.

At the intersection of economics, finance, and foreign policy, the GeoEconomics Center is a translation hub with the goal of helping shape a better global economic future.
Related content
Image: View of Shanghai Lujiazui Financial District, October 30, 2017, ISTOCK/owngarden.


