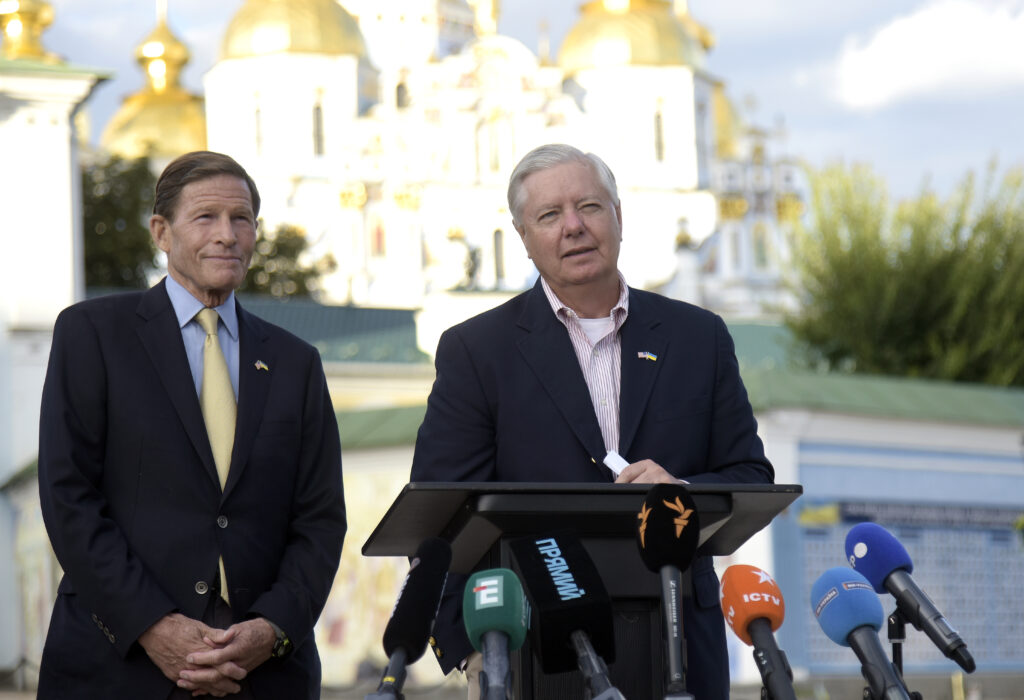Since February 2022, dozens of US senators and representatives, both Democrats and Republicans, have made the long journey to Kyiv to show support for Ukraine’s fight against Russia. It’s a challenging trip from Washington involving multiple flights, a sometimes-jammed border crossing, and a long train ride. But the chance to show US support and learn more about Ukraine’s struggle up close evidently makes the journey worthwhile.
Perhaps none have been as active, nor shown a greater commitment to bipartisanship, than Senators Richard Blumenthal (D-CT) and Lindsey Graham (R-SC), who made their sixth trip to Kyiv on August 12. This was no recess joyride down Kyiv’s Khreshchatyk Street. Most notably, the two senators met with Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy and then quickly announced what could be a blueprint for US policy toward Ukraine in the waning months of the current Congress.
In a joint press release, Blumenthal and Graham outlined four pillars for a strong US policy on Ukraine through 2024 and 2025. First, they called on NATO to “issue an invitation this year to Ukraine for membership,” an obvious but crucial next step to more formally bind the country into the Alliance.
Second, the two announced that Blumenthal would introduce the Stand with Ukraine Act when Congress returns to Capitol Hill in September to “codify the bilateral security agreement” that the Biden and Zelenskyy administrations reached in June. This, too, is a sensible and necessary move. While Ukraine has signed security pacts with a host of Western partners, nearly all of them have been non-binding, including the US-Ukraine agreement. An act of Congress would seal its implementation over the length of its ten-year lifespan.
The senators joined a growing chorus of US lawmakers and experts calling on the Biden administration to lift restrictions on Ukraine’s use of US weapons against military targets in Russia. After months of pressure, the administration assented in May to allow limited strikes inside Russia, but only under specific conditions. Blumenthal and Graham see the folly in limiting when and how Ukraine can use US weapons and vowed to “urge the Biden administration to lift restrictions on weapons provided by the United States so they can strike the Russian invaders more effectively.”
Finally, and perhaps most interestingly, the senators offered the prospect of a strategic economic partnership between the United States and Ukraine centered on metals and rare earth elements development. Their press release hinted that their suggestion was a welcome surprise for Zelenskyy, whose government has expressed hopes of leveraging Ukraine’s vast mineral wealth to become a major exporter of lithium and rare earths, raw materials key to new technologies and the energy transition. In a veiled reference to China’s dominant position in the rare earths market, the senators noted that “an agreement with Ukraine in this area would make the US less dependent on foreign adversaries for rare earth minerals.”
Stay updated
As the world watches the Russian invasion of Ukraine unfold, UkraineAlert delivers the best Atlantic Council expert insight and analysis on Ukraine twice a week directly to your inbox.
After the House of Representatives belatedly passed the national security supplemental package that unlocked further US aid to Ukraine in April, experts and lawmakers alike began to wonder how Washington might continue to support Ukraine throughout the rest of 2024. The Blumenthal-Graham priorities outline what could be an ambitious, re-energized US policy on Ukraine through the end of the current year.
US President Joe Biden has been skittish at the last two NATO summits about pushing for Ukraine’s membership in the Alliance, largely for fear of escalating tensions with Russia. But with Biden now out of the 2024 presidential race, he may be thinking more about his foreign policy legacy. Having already helped usher Finland and Sweden into the Alliance, opening Ukraine’s accession bid in earnest would be the third in a hat-trick of transatlantic security wins for Biden. Meanwhile, the Kremlin’s underwhelming response to Ukraine’s offensive into Russia’s Kursk Oblast should certainly tamp down any misplaced fears of escalation.
Eurasia Center events

Blumenthal’s Stand With Ukraine Act will likely run up against latent partisanship and electoral jitters when he introduces it in September. Much of Congress will be campaigning this fall, avoiding difficult votes while trying to score political points against the other party. Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer could very well bring the bill to a floor vote, both to support Ukraine and to force a vote from anti-Ukraine Republicans, but Speaker of the House Mike Johnson may be loath to spend political capital to do the same. Even so, the bill may get the ball rolling on further Ukraine legislation, especially as some pro-Ukraine Republicans indicate they want funding to continue uninterrupted, even under the prospect of a Donald Trump presidency.
As for dropping restrictions on the use of US weapons, only the Biden administration can reverse this policy, something it has repeatedly declined to do. It may take further public and private calls from Democrats such as Blumenthal before the White House agrees to a change. In the meantime, Russian rockets will continue to kill Ukrainian civilians using launch systems that could have been taken out by US-provided Army Tactical Missile Systems (ATACMS) and other Western-supplied weapons.
The senators’ proposal for a US-Ukraine economic partnership has all the ingredients for bipartisan consensus in Washington: Support for Ukraine without US taxpayer dollars, reduced dependence on China, and the potential for economic gain by importing one of the few materials the United States can’t make itself. A formal agreement would likely be highly technical and take many months to negotiate, but all the incentives are there for a new element in US-Ukraine relations.
Congressional delegations can sometimes be high on style and discussion but low on action and deliverables. This time, Blumenthal and Graham delivered on all counts and laid out a road map outlining US support for Ukraine through the end of 2024. Their list is as ambitious as it is sounds, both in its support for US interests and in helping Ukraine move toward victory on the battlefield. That combination of vision and vigor is exactly why their initiatives deserve bipartisan support.
Andrew D’Anieri is a resident fellow at the Atlantic Council’s Eurasia Center.
Further reading
The views expressed in UkraineAlert are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Atlantic Council, its staff, or its supporters.

The Eurasia Center’s mission is to enhance transatlantic cooperation in promoting stability, democratic values and prosperity in Eurasia, from Eastern Europe and Turkey in the West to the Caucasus, Russia and Central Asia in the East.
Follow us on social media
and support our work
Image: United States Senators Richard Blumenthal (L) and Lindsey Graham hold a briefing in Mykhailivska Square outside the St. Michael's Golden-Domed Monastery in Kyiv, Ukraine. August 12, 2024. (Photo by Ukrinform/NurPhoto)