Go behind the scenes as financial leaders gather in Marrakesh for the IMF-World Bank meetings
Recovery from this decade’s economic shocks—from a pandemic to the war in Ukraine—is slow and uneven, International Monetary Fund (IMF) Managing Director Kristalina Georgieva warned last week, raising the urgency of the global fight against poverty.
This week, leaders are meeting at IMF-World Bank Week in Marrakesh, Morocco, to get the world’s economic engine back on track. But with so many global crises putting countries (especially emerging markets) in a bind, audiences worldwide will be watching to see whether the IMF and World Bank can help countries respond to debt distress, climate change, and the economic impact of conflict.
With so much happening behind closed doors, we’ve dispatched our experts to Marrakesh; on the ground and in conversation with finance ministers, central bank governors, and other top leaders, they are evaluating the IMF and World Bank’s response to today’s biggest financial challenges. Below are their takeaways and insights from behind the scenes as the week unfolds.
THE LATEST FROM MARRAKESH
Watch all our conversations with central bank governors and finance ministers
OCTOBER 17, 2023 | 4:00 PM GMT+1
As the meetings wrap, macroeconomic and gender equality agendas remain tightly linked
A month ago, on the margins of the United Nations General Assembly in New York, I discussed top risks and opportunities in the year and near years ahead with foresight experts from the Atlantic Council. On the risk side, I talked about debt and geopolitical fragmentation—and the resulting drop in investment (especially in the Global South) that undermines productivity and growth. On the opportunity side, I talked about women’s economic and labor force participation driven in part by policy reforms and investments taking root that enable women to work, start, or grow businesses; including through care.
These risks and opportunities appear to be bearing out—at least if the conversations and reports this week at the World Bank-IMF Annual Meetings are to be believed.
The World Economic Outlook (WEO) projects that global growth will slow to historically low levels—from 3.5 percent in 2022 to 3 percent this year and 2.9 percent next year—driven down by risks associated with weakened Chinese growth, persistent inflation and debt distress, and the geopolitical fragmentation of commodity markets. These factors are also contributing to a widening divergence in growth across countries; and though not routinely discussed in the WEO, we are also seeing widening inequality, worsening food insecurity, and increasing poverty as a result—including higher numbers of poor people in wealthy countries—as macroeconomic challenges bear disproportionate impacts for already marginalized or disadvantaged economic groups, youth, women, and rural communities.
At the same time, the dialogue this week put women’s economic participation front and center as a solution to challenges, including those that are macroeconomic in nature, such as debt: More women in the labor force increases the tax base. In a conversation on mobilizing domestic resources to boost growth, Canadian Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Finance Chrystia Freeland touted investing in early learning and childcare as her government’s “best bang for the buck” for increasing prime age women’s labor force participation to record highs of over 85 percent (and 8 percent higher than the US record high) and increasing productivity, tax revenues, and household consumption in return. It’s a theme echoed across campus this week, including in my conversation with Hana Brixi, global gender director at the World Bank. At the same time, discussions of increasing women’s economic activity through improved financial inclusion and digital access were widespread—including in my Brixi conversation and in a conversation on digital financial inclusion with Josh Lipsky, Jesse McWaters, and Raj Kumar. In these risks and opportunities, we see the impact of the choices that policymakers make—and, increasingly, the impact of the choices that private sector leaders make.
OCTOBER 14, 2023 | 7:26 PM GMT+1
The final verdict: The IMF and World Bank are struggling to see how geopolitics and economics intertwine
The IMF-World Bank Annual Meetings in Marrakesh actually delivered concrete outcomes—and more than many expected going into the week. But the dark clouds of war loomed over the Meetings, and all the quota deals and debt agreements in the world couldn’t hide the fact the biggest risk to the global economy was staring the ministers right in the face—and they weren’t sure what to do or say about it.
The IMFC couldn’t agree to a joint communique, likely because of debates over how to characterize the ongoing war in Ukraine. And the Group of Twenty finance ministers’ statement surprisingly avoided mentioning anything about the Israel-Hamas war directly.
But the IMF’s steering committee did broker an agreement on quotas—the money all members pay to the IMF, and in return, they receive a share of voting power at the Fund. The United States got what it wanted: an “equi-proportional” increase, which means more money from everyone but no change in how the votes are allocated. China, India, and Brazil stay with their current percentages. When I interviewed Indian Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman yesterday, she told me this was going to happen: “This solution that came from the US has been accepted.” But she also said next time around, things will have to be different.
For the agreement on this solution, credit is due to the range of emerging countries that put the stability of the IMF ahead of the understandable desire to have the size of their economies more accurately reflected in voting share. And credit is also due to the United States for brokering an agreement that many thought wasn’t possible.
That success would have been enough for everyone to hang their hats on. But the Zambia debt memorandum of understanding was the “will they, won’t they” question of the meetings. Early in the week, when I spoke to Zambian Finance Minister Situmbeko Musokotwane, he confirmed it was happening. Then IMF Managing Director Kristalina Georgieva announced it was a done deal. And then, it wasn’t. After a few days of carefully crafted press releases and hedging, the deal was officially done. The question is whether doing debt restructuring with China is going to be like developing a new pharmaceutical drug—it takes years to do the first one but then easily replicated—or if each process is going to be as torturous as Zambia’s was.
Looking at the Marrakesh meetings by themselves, they were a success. The problem for the finance ministers and central bank governors is that the world around them is on fire. Brune Le Maire, France’s finance minister, probably said it best when he said geopolitics is the biggest risk to global growth.
For peace and stability, the world needs geoeconomics, Spain’s Nadia Calviño said earlier today. But the best the IMF and World Bank could offer was that it was too early to tell when it comes to the economic fallout from the war in Israel. It’s an understandable but insufficient position from the world’s leading financial institutions. How many crises can the world handle at once? It seems we are at the tipping point. That was the sense of urgency that was missing in some of the language and events during the Meetings.
So the final verdict? There was strong progress on the economics, but a missed moment on geopolitics. Geoeconomics is ultimately the lesson—hard-learned during World War II when the IMF and World Bank were created—that the two can actually never truly be separated.
OCTOBER 14, 2023 | 6:49 PM GMT+1
As IMF-World Bank Week wraps, we wonder: Is that all there is to say?
Amid the (welcome) fundraising and quota-raising progress reports, today’s IMFC Chair Statement missed an opportunity to reassure a concerned public by providing a strong response to the extraordinary uncertainty around the global economic outlook.
The IMF’s flagship reports released this week were already in need of an update, given that their timing did not allow for a full analysis of the rise in long-term interest rates, appreciation of the US dollar, and increase in oil prices following the attack on Israel. With the Global Financial Stability Report warning particularly about the risks in the global banking system, it would have been important to emphasize a willingness to closely collaborate on economic policies to avoid further increases in volatility.
This is not to downplay the agreement to increase IMF quotas, an important step to strengthen the global safety net, but especially with a rudderless US Congress and a sharp slowing of the Chinese economy, a better understanding of how global policymakers intend to preserve global stability would have been welcome.
The lack of a policy message from the IMF-World Bank meetings further adds to the policy vacuum left after the Group of Twenty (G20) communique similarly avoided specific policy commitments. Both documents echoed the language agreed upon at the Delhi summit, leaving the impression that ministers and central bank governors were too distracted by the need to negotiate geopolitical language and secure agreement on fundraising and quota issues to focus on their most important task at hand.
Moreover, the failure to change the relative voting shares at the IMF has been criticized by the Group of Twenty-four (G24) (comprised of developing countries) as setting a bad precedent in perpetuating an unequal governance structure, which in their view continues to undermine the IMF’s legitimacy and effectiveness. This will remain a bone of contention between developing and developed member countries going forward, even if tempered by the permanent inclusion of the African Union in the G20 and the creation of a twenty-fifth seat at the IMF Executive Board, to be allocated to Sub-Saharan Africa.
DAY FIVE
OCTOBER 13, 2023 | 5:29 PM GMT+1
A G20 communique is turning heads in Morocco
This morning, the IMF-World Bank Annual Meetings Plenary took place, with thousands of participants filling up the biggest hall on campus to watch remarks from Ukraine’s finance minister, the World Bank president, and the IMF managing director.
But don’t count me among those thousands: I was also hurriedly scrolling through the Group of Twenty (G20) communique that had just been released following yesterday’s meeting of G20 ministers and governors. While the group isn’t organizationally related to the IMF and World Bank, its member countries account for 85 percent of global gross domestic product and most of the votes at the Bretton Woods institutions. Thus, their decisions will translate into the IMF and World Bank’s new actions and policies.
So, where is the “new”? The communique released today basically repeats the one from the New Delhi Summit in September. It encourages the World Bank and all the multilateral development banks to implement the recommendations in the G20’s capital advocacy framework (over a year old now) to optimize their balance sheets and free up more lending power. However, the communique fails to mourn the tragic loss of life in Israel and Gaza—or even acknowledge the unfolding Israel-Hamas war at all.
In addition, the communique doesn’t say anything about the proposed equi-proportional IMF quota increase—indicating that the increase is less likely to come to fruition than we, on the ground, originally thought. However today, we spoke with Indian Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman who told us that the equi-proportional quota increase has, in fact, been approved. However, we may not know for certain until the International Monetary and Financial Committee meeting tomorrow—or even until the end of the IMF’s sixteenth quota review (to determine whether it is necessary to increase the quota and revise the distribution formula), scheduled to wrap in December this year.
OCTOBER 13, 2023 | 4:45 PM GMT+1
Equi-proportional IMF quota increase has been accepted—for now, says Indian finance minister
The equi-proportional IMF quota increase proposed by the United States “has been accepted,” Indian Minister of Finance Nirmala Sitharaman said at Atlantic Council studios in Marrakesh.
She said that it is a “temporary” solution, in that it is “a solution for now,” but during the next IMF four-year review cycle, “some discussions will happen” to map out how IMF stakeholder countries address the issue moving forward.
“The equi-proportional quota seems to be the less contentious way… for now” to address the IMF’s capital needs, Sitharaman argued, “because it doesn’t alter the… proportions and therefore it’s at least some more money without upsetting the balance.” However, the concerns of the countries “who are otherwise not adequately represented” still remain, she noted.
Sitharaman spoke with GeoEconomics Center Senior Director Josh Lipsky on the ground at IMF-World Bank Week. The IMF World Economic Outlook forecast India’s 2023-2024 growth at 6.3 percent. Sitharaman chalked up that strong growth projection to the country’s agricultural industry, services sector, and manufacturing—among other aspects. But, she said, global challenges present risks to India’s growth.
The finance minister reflected on India’s presidency of the G20, noting that New Delhi originally set out to highlight voices of the Global South throughout the year. The African Union’s joining the group “gives us immense satisfaction, Sitharaman said.
Focusing on the Global South is important because, while they are a varied bunch of countries, “the problems which they face are fundamentally the same,” the finance minister said.
OCTOBER 13, 2023 | 3:58 PM GMT+1
Your guide to IMF Special Drawing Rights
OCTOBER 13, 2023 | 3:47 PM GMT+1
The EU’s plans to bolster its resilience against climate change, trade dependency, and an array of other crises
European Commission Vice President Valdis Dombrovskis is keeping a closer eye on the EU’s relationship with China since Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine.
“We need to engage with China in areas like climate change” (with China being the biggest emitter of carbon dioxide) and “on current geopolitical challenges” including the war in Ukraine. But “at the same time,” he cautioned at an Atlantic Council event at IMF-World Bank Week, the EU should be careful not to establish “strategic dependencies” on China as it had on Russia for its fossil fuel supplies. “We need diversified and resilient supply chains, and we cannot be dependent on a single supplier [for] a number of critical inputs.”
The EU recently initiated an anti-subsidy investigation into imports of electric vehicles from China, which will determine whether electric vehicle supply chains in China benefit from subsidies in a way that breaches World Trade Organization rules—and whether those subsidies inflict injury on the European electric vehicle industry. “WTO members have a right to use these tools,” Dombrovskis said. “We are going to conduct this investigation in a facts-based manner, fully in line with applicable EU and WTO rules and principles.”
He added that as the investigation proceeds, it’ll be “important that also Chinese companies… are cooperating.”
On trade, the EU and its biggest trade partner, the United States, are approaching a deadline for negotiating an agreement on steel and aluminum trade that (if the EU gets its way) would address global steel overcapacity, encourage a “greening” of the industry, and put an end to tariffs imposed during the Trump administration. “We are making progress,” he said, adding that he is “optimistic” any remaining gaps will be filled soon.
In responding to this decade’s polycrisis, the EU is employing the Recovery and Resilience Facility to ensure that the bloc emerges stronger. The fund has thus far disbursed 153 million euros to eighteen member countries.
While it was originally aimed at mitigating the economic impacts of the pandemic—through investments such as digitizing public services and boosting sustainable transport—“Russia’s aggression has brought some corrections,” Dombrovskis said. One such correction is the creation of REPowerEU Plan to roll back Europe’s dependency on Russian fossil fuels—and roll out more renewable energy sources.
Dombrovskis also discussed EU macro-financial assistance to Ukraine, saying that the bloc is “committed to [supporting] Ukraine for as long as it’s necessary.” He explained that once this assistance program wraps (there are still about 4.5 billion euros left to be paid this year) the EU will unleash a fifty-billion-euro package of assistance to Ukraine, to last from 2024 to 2027, through the EU Multiannual Financial Framework. The “EU is definitely doing its part,” he said. “It’s important that also other major players, including [the] United States, are playing their part.”
OCTOBER 13, 2023 | 12:56 PM GMT+1
Regional multilateral banks are having their moment in Marrakesh
In October 2020, at the peak of the pandemic, I wrote about why and how regional development banks play a critical role in COVID-19 response and recovery, arguing that the banks and the nature of their lending and operational practices have been, and remain, especially important for the agility, complementarity, and continuity of pandemic response.
It’s clear from conversations this week—on stage, in studio, and off the record—that this is perhaps even truer today than it was then as we grapple with how to respond to polycrises: COVID-19, conflict, and climate, and the inflation, debt, food insecurity, and rising inequality and poverty that result.
The European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, with its long history in Ukraine, is at the forefront of responding to Russia’s 2022 invasion—leading from the onset in investment, advisory, and technical assistance, as well as research, planning, and coordination. Among its response measures, it has been leveraging its distinct expertise and experience working with and through the private sector. While the Asian Development Bank, with large numbers of small island developing states as well as fragile and geopolitically tense areas, is leading on climate and resilience finance and innovation, stretching its balance sheet by adjusting its disposition toward risk and expanding lending by nearly 40 percent to about $36 billion annually. To that end, the Inter-American Development Bank and World Bank are collaborating to catalyze green finance across Latin America and the Caribbean. Given the dynamics of debt and demographics on the African continent—which have been a prominent theme this week no matter the subject—the African Development Bank is uniquely positioned to lend in a way that can support policy reform and advance inclusive growth and reduce inequality with its investments. At the same time, given the scale of what’s required, more than ever it’s about coordination and leverage between regional development banks and with the World Bank and IMF.
Given this, the importance and value of regional development banks is arguably missing from the (somewhat overlooked) “Marrakech Principles for Global Cooperation” released this week, which call for enhanced collaboration between the IMF and the World Bank “and with partners.” It is a miss to skip explicitly referencing these key international financial institutions which are clearly ready to meet the moment.
OCTOBER 13, 2023 | 12:24 PM GMT+1
Decoding the Marrakesh G20 communique: Progress, but no inspiration
The last Group of Twenty (G20) communique under India’s leadership did not break any new ground. Notwithstanding the recognition that “the G20 is not the platform to resolve geopolitical and security issues,” most of the energy spent during the negotiations seemed to have been focused on the categorization of recent geopolitical tensions.
On that front, a general expression of deep concern for “the immense human suffering and the adverse impact of wars and conflicts around the world” seemed to be an attempt to compensate for the fact that one or several participants remained opposed to condemning the Hamas attack on Israel. The communique also rehashed previously used language on the war in Ukraine and expressed concerns about attacks on food and energy infrastructure given the potentially global consequences.
On the global economy, one paragraph of the communique repeated the IMF’s World Economic Outlook and referred to the macroeconomic policy section of September’s G20 New Delhi Leaders’ Declaration. The onus is now on the IMFC’s communique, which is due tomorrow, to react to a weakening medium-term economic outlook, as well as the rise in long-term interest rates and the strong dollar. The G20 also did not use the opportunity to push for an IMF quota increase, which could indicate that important issues have yet to be resolved behind closed doors.
The remainder of the document was similarly underwhelming. One full page on the topic of strengthening multilateral development banks mostly dealt with process issues, with words like “remain,” “reiterate,” or “reemphasize” abounding. The IMF and World Bank were asked to provide a report on domestic revenue mobilization (i.e., tax measures), most likely a concession to those G20 members that emphasize the need for responsible economic management from developing countries themselves.
Reflecting the political attention paid to individual debt restructuring cases, the communique provided a cautious welcome of progress in the cases of Zambia and Ghana, and called for a swift debt treatment for Ethiopia as well as Sri Lanka (the latter being outside the G20 Common Framework).
There is no doubt that the G20 process will be reenergized by the start of Brazil’s G20 presidency on December 1, but it is hard to escape the impression that the G20 has been diminished by the political divergences within its membership. While it still appears possible to reach consensus in some important areas, the G20 is clearly no longer the dynamic forum it was several years ago.
OCTOBER 13, 2023 | 12:17 PM GMT+1
How are IMF stakeholder countries working to mitigate climate change? The case of Morocco and renewable energy
OCTOBER 13, 2023 | 12:15 PM GMT+1
Inside Turkey’s plans to bounce back from economic shocks and policy challenges
After a string of “policy distortions” and economic shocks, “Turkey is back,” Turkish Finance Minister Mehmet Şimşek said.
Şimşek’s gave his remarks at Atlantic Council studios in Marrakesh, on-site at the IMF-World Bank Annual Meetings. There, he outlined the three new Turkish economic programs to help the country bounce back, which included measures on disinflation, fiscal discipline, and structural reforms.
The finance minister explained that he wants to see inflation down to single digits over the next three years—inflation was still at 61 percent year-on-year this September. “It’s a challenging global backdrop, but we believe it is doable.”
As for the structural reforms: Şimşek pointed to several policies meant to improve the business climate, boost savings, deepen capital markets, and enhance labor market flexibility and human capital stock. He also said that Turkey is focusing on the green transition and investing in digital infrastructure.
Throughout these reforms, Şimşek said that it’ll be important to communicate with citizens so that they understand that “there are no quick fixes [and] that there are no shortcuts,” and that the reforms are designed for the medium term. “There will be trade offs,” he cautioned, adding that “for the sake of the country, sometimes you have to take harsh measures.”
At the Annual Meetings, Şimşek said that his delegation is meeting with various counterparts to boost Turkey’s economic relations. In meetings with European counterparts, he said that the discussions tend to focus on how to retighten EU-Turkey ties. “We would like to be re-anchored to [the] EU,” he said. “Europe is a source of inspiration for us… but we want Europeans also to treat Turkey with respect and as an equal partner.”
According to Şimşek, one way for the EU to show Turkey that it is an equal partner is by upgrading the EU-Turkey Customs Union, which was put into place in 1996. “The world was very different at that time,” he said, adding that “today’s enhanced free trade agreements are ahead of [the] Customs Union.” Şimşek explained that he’d like to see the customs union “expanded” to include services, agriculture, and more. “We’re not asking for any favor from our European friends; we’re asking [for]… mutually beneficial dialogue.”
Şimşek argued that the EU and Turkey should cooperate in another way: on reconstruction in Ukraine. “Peace and stability in our region is the most important global public good,” he said, so “we would like to play a constructive role, a significant role in helping rebuild the country.” He explained that combining European long-term funding with Turkish contractors could “create a great synergy.”
Regarding global governance, Şimşek said that he has been encouraged this week by discussions at the Group of Twenty about reforming multilateral development banks and equipping them with more resources to assist the Global South. And as for the IMF quota, Şimşek said that emerging markets are increasingly playing a bigger role on the world stage and their economies are increasing in size. “I think it’s important that there is better representation, better voice for everyone… We should not ignore the Global South.”
OCTOBER 13, 2023 | 11:57 AM GMT+1
Staring into the gap between Africa as a global leader and a development challenge
Governance remains the trend line in my meetings here in Morocco. It has made an appearance in everything from my senior-level conversations with the Cameroonian delegation to discussions about the World Bank’s new president and his mandate, to more technical discussions about central bank digital currencies and new payments systems.
Thinking through these issues, I’m struck that on one hand, Africa is on the leading edge of emerging fintech like virtual currencies including CBDCs and stablecoins, while on the other, the continent is still struggling with basic representation in global institutions like the World Bank. If you’re a pessimist, you could say that many countries are still only on the lonely and winding path to the long and bumpy road of development.
But it is important to see the hope for change as I did yesterday. I sat for a conversation between one of Africa’s biggest philanthropists, Mo Ibrahim, and World Bank President Ajay Banga. Ibrahim seemed to take pleasure in pointing out the contradictions in the governance and actions of the World Bank in Africa, often comparing the Bank’s solutions for low-income countries’ problems to the better, faster, and more robust solutions deployed for Western and European countries. The crowd seemed to laugh anxiously—but it is this upfront calling to attention of the World Bank’s shortcomings that will push the Bank to change tack.
Looking forward, African countries must build a strong coalition of reform minded countries to maximize their power and voice. This coalition could more effectively push for badly needed updates to governance structures of the global economic and financial architecture—even as many Group of Seven countries seem to prefer the status quo. Africa needs these changes urgently to meet its current and future challenges.
OCTOBER 13, 2023 | 9:32 AM GMT+1
Georgieva’s emphasis on the positive is a reminder of the power of global collaboration
There is reason for gloom at the Annual Meetings, with war still raging in Ukraine, the Israel-Hamas war newly under way, and the effects of natural disasters still reeling in countries like Morocco and Turkey. Against that backdrop, the economists meeting here are focusing on finding solutions to crises involving interest rates, equity, and slow economic growth—providing reason to have some optimism for the future.
Yesterday, IMF Managing Director Kristalina Georgieva focused on the positive of the World Economic Outlook—even though the forecast, to the dismay of many participants, forecasted slow recovery from the crises of the last few years. The positive: There is still time to bolster global resilience and tackle collective action problems like climate change. However, to do that, the world has to work together, build bridges, and invest in multilateral institutions and frameworks. And while time is running out to keep the global average temperature rise below 1.5 degrees Celsius, Georgieva stressed that doing so may be feasible if the world adopts some form of carbon pricing—which is something the IMF is working on with the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
Georgieva’s second point of positivity: Low-income countries, especially those in Africa, have great potential to foster a more prosperous, inclusive future. With her characteristic “we all have a role to play” remarks, Georgieva made clear that the IMF sees itself as a steward for attracting more sustainable investment to low-income countries to create that future. The type of lending and investment the Bretton Woods institutions have in mind, however, will require more capital and increased quota investments in the institutions. This would align with new World Bank President Ajay Banga’s calls for a bigger and better bank, but also requires resolutions of debates and disagreements over quota shares held by high-, middle-, and low-income economies.
And while Georgieva was more serious on the topic of high bond yields and above-average yield spread across countries, she pointed out that this market response is due to rising interest rates, which are a sign that central banks are waking up to the necessity to respond to inflationary pressures.
In these positive points lie the solutions that will empower countries as they look to recover more quickly from the last few years’ economic shocks.
DAY FOUR
OCTOBER 12, 2023 | 7:37 PM GMT+1
There’s still time to show that global collaboration is possible
From hallway conversations to heated debates in closed-door meetings, the inescapable topic this week in Marrakesh has been global governance.
The power structure of Bretton Woods institutions—despite the fact that they function reasonably well, even in the midst of growing geopolitical tension—is under increasing scrutiny.
The United States has been pushing for an increase in the capital that countries contribute to the IMF (their quotas) without proposing an increase in votes for China and other emerging markets who feel undervalued with their growing economies and stagnant vote shares. As I wrote in a new issue brief this week, the governance arrangements of the Bretton Woods institutions are fundamentally out of touch with economic reality.
Despite that, there are signs on the ground that the quota increase may be approved, which would provide an important boost for the world’s official lender of last resort—and show that global collaboration is still possible.
Across the IMF-World Bank Meeting campus, I’m also seeing global collaboration in another form: Widespread support for Ukraine among many of the IMF’s major shareholders. The IMF’s Ukraine program is largely successful because it is focused and because the Fund’s shareholders are stepping up to ensure that the program reaches its intended objectives—putting Ukraine’s war economy on a more solid footing and making further progress on improving economic governance. Today, we also sat down with Ukrainian Finance Minister Serhiy Marchenko to map out the next steps for coordinated international support for Kyiv, including its war-risk insurance needs.
OCTOBER 12, 2023 | 7:00 PM GMT+1
Ukraine’s finance minister on Russia’s blocked assets and why he’s reaching out to the Middle East
“A gear is shifting” among Group of Seven (G7) countries, said Ukrainian Finance Minister Serhiy Marchenko in conversation with the Atlantic Council’s Charles Lichfield.
On the ground in Marrakesh, Marchenko is noticing that G7 countries are ready to discuss seizing Russian assets and repurposing them to fund Ukraine’s reconstruction efforts. But if the G7 can’t come together on the Russian assets, he said he hopes that they can quickly agree on deploying the interest earned on these blocked assets for reconstruction efforts.
Marchenko gave his remarks at an Atlantic Council event at IMF-World Bank Week. Marchenko told Lichfield, the deputy director of the GeoEconomics Center, that Ukraine’s economic situation has improved—with lower inflation rates—”due to the resilience of [the] Ukrainian people as well as support from our partners.”
The IMF’s World Economic Outlook—released earlier this week—forecasts Ukrainian gross domestic product growth at 4 to 5 percent through 2024. Marchenko noted that the section on Ukraine was drafted at the beginning of the year, but now, Kyiv is fighting “a totally different war.” That means “it’s a modern war: We’re using drones, using a high level of munition.” Marchenko said the IMF was pessimistic about the Ukrainian forecast to account for uncertainty about the course of the war. “That’s why they predicted that Ukraine’s economy will be in… slow growth for [a] longer period of time,” he explained.
This week, Marchenko said the Ukrainian delegation has been having bilateral discussions not only with European countries to try to preserve their support but also with other countries, such as those in the Middle East, to “try to convince them to be more supportive of Ukraine.” In those discussions, he said that Ukraine also tried to “show [a] good example” of how to govern a country during war and invasion.
But “it’s quite necessary to preserve… support for [the] next year,” he warned, because the next year will be “much [more] stressful,” with much more “uncertainty.” So while Ukraine’s economy is more stable, he said, international partners can’t “forget about Ukraine” now.
OCTOBER 12, 2023 | 11:28 AM GMT+1
How the MENA region is facing up to today’s biggest economic crises
As the crowds of IMF-World Bank Week participants get larger in Marrakesh, the Atlantic Council empowerME Initiative’s Racha Helwa got together with Moroccan Economy and Finance Minister Nadia Fettah Alaoui and Citi Head of Middle East and Africa Ebru Pakcan to talk about how the MENA region is facing up to today’s biggest economic crises.
Morocco is focusing on building a strong macroeconomic foundation and on its resilience, the finance minister said, explaining that the Moroccan government launched a reform program recently to diversify the economy and create a strong social state. But it won’t be a “peaceful” journey to implement these reforms, she argued, because at the same time, “we have also to deal with multiple crises that we have been going through.”
Pakcan said that private-public relationships may help MENA countries manage the risks they face. With these partnerships, there are “a lot more creative solutions that can be… devised,” she argued. Those solutions, she added, are needed to help MENA countries “actually ride the storm” of today’s crises so that it can “focus on what really matters in the future,” like climate change and digitalization.
OCTOBER 12, 2023 | 11:04 AM GMT+1
The numbers aren’t adding up on financing investment for climate change mitigation projects
Here in Marrakesh, many speakers have emphasized the urgent need to mobilize substantial amounts of money to finance climate change mitigation and green transition projects. Reportedly, to achieve net zero emissions by 2050 and to prevent world average temperatures from rising by more than 1.5 degrees Celsius this century, global investment in such climate-related projects will need to total $2.7 trillion a year. Developing and low-income countries in particular would need to receive significant financial assistance from the international community to be able to cope with the challenges.
At the same time, both the IMF and World Bank have pointed out that in many countries, fiscal deficits are high, with government debt rising to record levels—faster than the pre-pandemic pace. Both of these institutions have emphasized that fiscal restraints are much needed to safeguard sustainability and rebuild fiscal buffers to be able to deal with future shocks. The IMF’s “Fiscal Monitor” has also recognized that citizens in many countries are averse to increased taxes by their governments.
Consequently, it should be clear that governments, including those of developed countries, will not be in a position to raise huge sums of money for climate-related investments, especially in support of developing and low-income countries.
That has led the World Bank and IMF to push for using public money to catalyze private sector climate investments in developing and low-income countries by offering various risk-sharing schemes to improve the risk-return profiles of those investment projects. However, officials looking to use public money to catalyze significant private sector investment—often at a rate of five times or more—are likely to see their hopes dashed: According to GlobalMarkets magazine, $1 of public sector lending can generate only $0.7 of private investment.
In short, while climate investment needs are huge, the numbers in terms of plausible financing sources from the public and private sectors simply don’t add up. Anyone concerned about climate change would have to be more realistic about to how to get the needed funding.
OCTOBER 12, 2023 | 8:53 AM GMT+1
Where will the coalition of African countries take its message for reform next?
Kristalina Georgieva said it best: “A prosperous twenty-first century is only possible with a prosperous Africa.”
Here in Marrakesh, the IMF-World Bank Annual Meetings are clearly underscoring African priorities, the urgency of climate action, and the need for increasing global coordination for policy solutions. Africa is front and center—fitting considering these are the first Annual Meetings to take place on the African continent since the Nairobi Meetings in 1973.
On the ground—just as they did in 1973—policymakers, central bankers, and international economists are looking for ways to alleviate global poverty, boost economic activity, and reinforce programs that can support sustainable development solutions. As decision makers hopping from pavilion to pavilion debate how to address growing public debt, elevated interest rates, and rising geopolitical tensions between the world’s largest economies, it is important to look at the changing trends across the African continent.
It is becoming clearer how African countries are a part of the solution to global issues, whether it is on matters of war and peace, economic development, or global governance. In regard to governance, African countries are asserting their agency in multilateral fora. A great example of this effort is the posture African countries present on Bretton Woods reform, consistently driving their message at global convenings such as recent Group of Twenty meetings in India, the UN General Assembly in New York, and here at the IMF-World Bank Meetings in Marrakesh. Against this backdrop, African countries are facing new and emerging challenges from the shocks of the COVID-19 pandemic; the spike in food, fuel, and fertilizer products due to the Russian invasion of Ukraine; and natural disasters aggravated by a changing global climate, among others.
Despite the growing impetus for pan-African positions on things like World Bank reform, more needs to be done. Changing the political calculus of traditional powers such as the United States, France, Germany, and other Group of Seven countries (and beyond) will be important to bring reform efforts into reality. African leaders should continue to look for ways to highlight the urgent need for reforming these institutions, specifically with audiences that may be unfamiliar with the need for reforms, while continuing to drive a coalition for change. The challenges facing African countries are no longer theoretical or in the future, and the Bretton Woods institutions and multilateral development banks must take steps to meet the changing, complex, and interconnected development needs of African countries without delay.
DAY THREE
OCTOBER 11, 2023 | 5:57 PM GMT+1
Signs of inspiration in dark times
As day three wraps at the World Bank-IMF Annual Meetings, the buzz is building as all quarters of campus kick into high gear—and seats are becoming harder to find in the “town square” where I’m enjoying local musicians giving melody and voice to the storied history, warmth, and resilience of the Moroccan people, who are hosting this event just weeks after a devastating earthquake.
Though the hot sun continues to shine, the mood has been darkened for some following the release of the IMF’s flagship World Economic Outlook, which forecast a more subdued recovery, and following reality checks about the extent of global debt distress. For those in the World Bank conversations, me included, talk of resilience and growth felt more uplifting.
Still there’s a sense of urgency on the ground, as participants quickly realize there is too much work to be done and plenty of opportunity at hand.
On that note, there was extra pep in my step today as it’s October 11, which means it’s International Day of the Girl—a chance to recognize the rights, celebrate the achievements, and amplify the opportunity of the world’s one billion girls and young women. And where better to mark the occasion than in Africa—the youngest continent where, if empowered and enabled, girls can help communities and countries realize a double demographic dividend through increased youth economic participation and closing gender gaps. I was reminded of this in a conversation I had with the World Bank’s Global Director for Gender and in my behind-the-scenes conversations with the inspirational generational leaders comprising the IMF youth fellows.
So heading into the remaining days of deliberation and debate, I’m hoping for meaningful movements and commitments to accelerate development, address debt, and accentuate inclusive growth on a livable planet.
OCTOBER 11, 2023 | 4:37 PM GMT+1
What’s next for monetary policy and Europe’s fiscal rules, according to Spain’s Nadia Calviño
Just a day after the IMF released its World Economic Outlook—which forecast that Spain, among other countries, would have strong growth in 2023 and 2024—Spanish Economy Minister Nadia Calviño joined GeoEconomics Senior Director Josh Lipsky for a conversation on the ground at IMF-World Bank Week.
Calviño chalked up Spain’s good forecast in part to its “diversified energy mix.” “A high penetration of renewables and a very diversified energy mix… has enabled Spain to withstand better than others the blow coming from Russia’s war against Ukraine.”
Seeing Spain’s growth, Calviño said it would be “quite wise” for the European Central Bank to pause interest rate hikes. “You have countries such as Spain with strong growth [and] low inflation. Other countries are very close to a recession and have higher inflation,” she explained. “So we better get it right because we need to ensure that we manage… inflationary expectations.”
Currently, the EU is undergoing a review of its fiscal rules on government spending and taxes to avoid a debt crisis. She signaled the need for commitment to a new framework—one that enables growth, job creation, and the green transition—by the end of this year.
Calviño looked back to the IMF-World Bank Spring Meetings, saying that while “the global economy has shown to be more resilient than many expected,” that “the world has become even more complicated” with conflict on the rise. “That makes it even more important that we gather here” at the Annual Meetings, to “find solutions.”
But Calviño’s stance on China hasn’t changed since the Spring Meetings, where she said that the EU cannot turn its back to China or ignore it. “The EU is a global trade powerhouse, and we need to keep our relations with all the main trading partners,” she said. “At the same time, we need to ensure that the global framework and our trade policies ensure that there is a level playing field and [a] fair trading framework.”
OCTOBER 11, 2023 | 4:28 PM GMT+1
The finance world braces for impact from the Israel-Hamas war
The shockwaves of the Israel-Hamas war have finally reached Marrakesh. It took several days—as it often does in the technocratic world of international economics—for financial leaders gathered here at the Meetings to grasp that the conflict could affect everyone.
Here on the ground, the full scale of the devastating human tragedy and military conflict unleashed by Hamas’s assault on Israel last Saturday is coming into focus—and with it a focus on the war’s economic ramifications. Several conversations are happening at once.
First and foremost, there is growing horror as reports about the terrorist attacks and fallout in Israel and Gaza play on TV screens and phones inside and outside the official venue for the Meetings.
There is also discussion of the global economic fallout. Energy prices have understandably been a big focus, with memories of the 1973 Yom Kippur War and ensuing oil embargo front of mind for ministers. But as many of the economists milling about the pavilions have noted, the global energy market has shifted dramatically in the fifty years since that war. The world doesn’t solely rely on the Middle East for energy. And—for now—the conflict hasn’t spread through the region.
Then there’s the shekel and Israel’s economy. Israel’s central bank intervened to prop up the currency by selling thirty billion dollars in foreign reserves, but the shekel’s slump continues. There is wider concern that foreign investment in Israel will dry up and create a recession in the Israeli economy.
With regard to Gaza, the question is about reconstruction—whenever that time comes. Will the World Bank and other development banks play a role and step in with aid? A European commissioner initially signaled that the Commission would stop sending some aid to Palestinians, but that decision was quickly reversed by the European Union. There are open questions in Marrakesh right now about 1) what kind of aid will flow to Gaza in the near term and 2) what kind of money will be requested in the long term. Because these are questions for the development banks, the IMF has, so far, been able to sidestep the questions.
But don’t expect avoidance of these issues to continue. By the end of the week, the ministers and governors in Marrakesh will realize what many around the world already see clearly: What is unfolding in Israel and Gaza will have global political and economic impacts.
OCTOBER 11, 2023 | 10:21 AM GMT+1
Africa’s demographics matter—but they’re not the only ones that do
The Moroccan government has been keen to shine a light on its identity as a North African, growing economy. The resilience of Morocco and the Moroccan people, who are hosting a great Annual Meetings week despite a devastating earthquake and previous cancelations due to COVID-19, has also been spotlighted. Africa—a diverse, growing, and bustling continent that is often overlooked at conferences of international organizations—is finally getting the attention and press it deserves.
Demographic challenges and the threat aging societies pose to the world economy are being brought up at these Annual Meetings almost as frequently as the climate crisis. Demography is the critical area where Africa has the advantage over other regions. While European countries rapidly age, fertility is slowing down in the United States, and even China is entering an era of demographic aging. Africa’s high birthrate and young labor market have the potential to massively boost the continent’s emerging market economies. This will, however, require inclusive political stability, equity investment, and the prioritization of educational and labor market skills funding. For the time being, many African ministers and officials are reveling in the chance to directly pitch for more investment in their region, and IMF and World Bank officials appear interested in highlighting newer funds (like the IMF’s Resilience and Sustainability Trust) that have benefited sustainable investments in the region.
OCTOBER 11, 2023 | 10:11 AM GMT+1
With the Bank abuzz, Banga begins…
On day 2 of the World Bank-IMF Annual Meetings in Marrakesh, the Bank’s activity got underway in earnest with a number of flagship and civil society events. The mood was arguably more upbeat than “across campus” as the IMF released its latest World Economic Outlook portraying a dim macro picture with slowing growth and widening divergence worldwide.
On-the-ground conversations—which touched upon everything from resilience to jobs-driven growth to digital inclusion—recognized the compound crises facing the world (although disproportionately impacting the Global South) while recognizing, if not celebrating, the opportunity. Across the conversations between officials and civil society, inclusion, especially of women and youth, was a repeated priority. There were other big themes, too, across these conversations: interconnectedness; jobs and livelihoods, and how they are critical for resilience, climate adaptation, and climate change mitigation; and improved and diffuse digital foundations, which can fuel economic dynamism and increase transparency while also strengthening systems and the provision of public services necessary for responding to shocks.
Capping the day, Ajay Banga—who took the helm as president of the Bank in June—made his formal Meetings debut with a much-anticipated town hall with civil society, where he locked in his newest mission for the Bank: “Ending poverty on a livable planet.” It’s a reflection of the fact that the number of poor people has increased after decades of decline as significant pre-pandemic gains have been lost; it also reflects how responding to climate change goes hand-in-hand with efforts to advance development and end all forms of poverty. Alongside the evolution roadmap, Banga (or Ajay, as he prefers) believes it can be done by “doing what’s right, not convenient” to “first build a better Bank, then build a bigger Bank”: a better Bank that stretches every dollar and leaves no one behind; a bigger bank that “allows what works to scale.” Over the next few days, the Bank and its partners will need to get specific on how this “knowledge and money” Bank will come to fruition.
OCTOBER 11, 2023 | 8:44 AM GMT+1
A tale of two sovereign debt restructuring processes: Why Zambia and Sri Lanka differ
Different developments in the Zambian and Sri Lankan sovereign debt restructuring processes have commanded the attention of participants in the IMF-World Bank Annual Meetings in Marrakesh, highlighting the difficulties still remaining in the international effort to improve the restructuring framework.
Zambia, having defaulted on its external debt of over $32 billion in 2020, reached agreement with its official bilateral creditor committee (including China) in June 2023 on terms to restructure the debt, giving the country a 40 percent reduction in the present value of its bilateral debt of $6.3 billion. However, the country has had to wait until now for the bilateral creditors to develop language on the comparability of treatment in the memorandum of understanding that satisfied China—so that it could be signed, reportedly by the end of the Meetings this week. This has raised the hope that China could participate in the official bilateral creditor committee; the committee could eventually agree on a deal despite delays.
By contrast, Sri Lanka defaulted on its fifty-billion-dollar external debt in April 2022; with the country not being viewed as low-income, it is not eligible for the Common Framework for Debt Treatment. As a result, Sri Lanka has had to negotiate separately with various creditor groups, including the Paris Club, Japan, and India (on $4.8 billion of debt), as well as China’s Export-Import Bank (on $4.3 billion of debt)—but not the China Development Bank (which it owes $3 billion of debt, but the bank is considered to be a commercial creditor). This process has increased the complexity of coordination problems for the restructuring negotiations—leading to delays in the first review of the Sri Lankan program with the IMF needed for additional disbursement to the country. Further complicating the comparability of treatment problem, China has announced that its Export-Import Bank has agreed to restructuring terms with Sri Lanka ahead of scheduled meetings between the Sri Lanka and Paris Club creditors this week in Marrakesh.
This unwieldy process should be improved, basically by extending the Common Framework to include vulnerable, middle-income countries so that official bilateral creditors have to form a committee to negotiate jointly with the debtor country.
DAY TWO
OCTOBER 10, 2023 | 7:04 PM GMT+1
EBRD president: Supporting Ukraine’s reconstruction must happen now
As Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy continues to meet with Western leaders in a search for support and military assistance, the Atlantic Council GeoEconomics Center’s Charles Lichfield sat down with Odile Renaud-Basso, president of the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, to talk about the bank’s support to Kyiv.
“We are focusing a lot on the private sector… and infrastructure in particular,” she said, explaining that the EBRD is paying particular attention to gas and electricity companies to keep the economy running.
When asked whether it is time to begin focusing on reconstruction assistance, Renaud-Basso said that there isn’t “a clear sort of separation” between supporting Ukraine in war and in reconstruction. “What is already needed now is to reconstruct what has been destroyed and we don’t know whether there will be further destruction—there probably will be.”
Recently, EBRD shareholders granted the bank the ability to invest in six Sub-Saharan African countries, expanding its mandate after determining that its approach to investing in the private sector—specifically in small and medium-sized enterprises and green projects—“would add value” and would “bring something different [to] the table.”
The EBRD currently works in over thirty countries. Renaud-Basso explained that when a country’s democratic values aren’t in line with the EBRD’s, the bank does as much as it can to “ensure progress in this area.” “Helping to develop the private sector independent from government… will help develop a middle class that will help contribute to democratization,” she argued. Currently, with the Israel-Hamas war, the EBRD—which invests in the West Bank—is reviewing its project.
OCTOBER 10, 2023 | 6:14 PM GMT+1
Why everyone—from participants to officials—should keep in mind Africa’s demographics
Demographics matter—and they matter a lot. IMF Managing Director Kristalina Georgieva also seems to agree; here at the Annual Meetings in Marrakesh, she has repeatedly emphasized that the only region in the world where long-term growth has the potential to accelerate is Africa because of its young population.
But how young is Africa’s population compared to elsewhere? The answer: very young. More than two-thirds of Africa’s population is under the age of thirty, and 40 percent are under the age of fourteen. Only 3 percent of African residents are sixty-five and above. Moreover, within thirty years, Africa’s population is expected to double from 1.4 billion to 2.8 billion. In other words, by the early 2050s more than a quarter of the world’s projected population of 10 billion will be on the continent.
Age breakdown of population
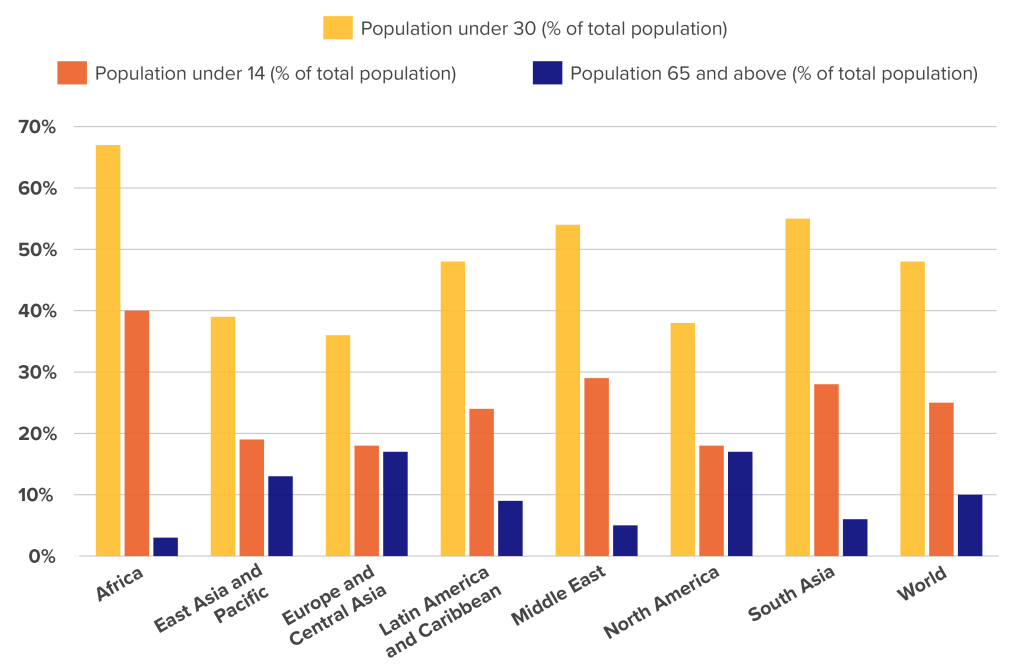
Source: World Bank, author’s calculations. Data as of 2021.
What does this mean for the African economy and the global economy? First, while the rest of the world will be aging at varying rates, Africa is going to be blessed with a young and vibrant labor force for many decades to come. If African countries can get the necessary capital, institutional reforms, and job creation policies, that young labor force can lead to robust growth rates for the continent. This will in turn increase the average African household’s income, leading to higher aggregate demands for consumer goods and services produced both in Africa and globally. The global aggregate demand could skyrocket if the income of a quarter of the world’s population increases by, say, 10, 20, 50, or 100 percent.
Second, over the next few decades, high-income and emerging economies will age rapidly and face severe labor shortages while Africa will have an ample supply. Hence, through effective labor migration policies, the world (especially high-income and emerging economies) can benefit significantly from Africa’s young labor force and keep itsdoors open for business for longer.
Population 65+ as a percentage of the total population
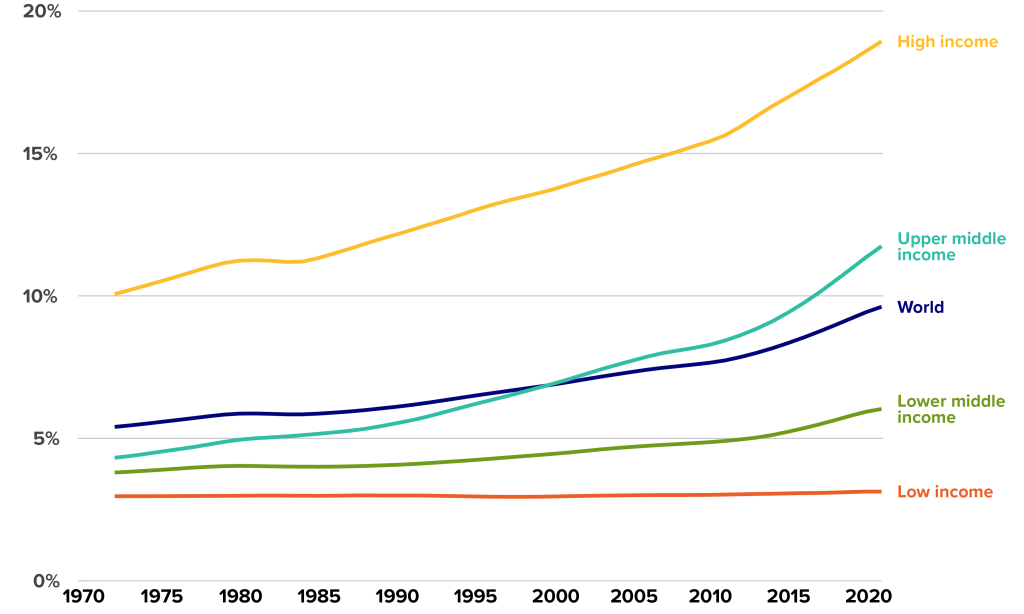
Source: World Bank.
But without sound institutions and policies and investments targeted toward human capital development and job creation, Africa’s young and rapidly growing population—pushed to migrate in search of economic opportunity—could become a source of political and social instability both for the continent and elsewhere in the world. Thus, it is imperative that delegations discuss these issues at the Annual Meeting in Marrakesh.
OCTOBER 10, 2023 | 5:48 PM GMT+1
On-the-ground signs that the IMF and client countries are diverging on monetary tightening priorities
The launch of an IMF working paper on inflation shocks over the past fifty years wound up showcasing conflicting priorities between the IMF and the academics, central bankers, and ministry officials in attendance—many of whom are from IMF client countries.
At the heart of the disagreement is not whether countries need to undertake monetary tightening to reduce inflation, but when it is appropriate to change course and lower interest rates in a way that public spending and investment become less costly. The IMF wants inflation to come back firmly to its target before easing is considered; the IMF official behind the working paper pointed to several “success” stories that actually resulted in hard, not soft, landings.
At the event, ministry and central bank officials pushed back that the current and persistent episode of inflation is not comparable to previous shocks, as the macroeconomic situation today is compounded by geopolitical, demographic, and climate risks. But for the IMF, economic orthodoxy pays off in the medium term. Given the wording and phrasing of attendees’ questions, macroeconomic officials from client countries and those facing other monetary pressures (such as pegging to the dollar) seem to be more concerned about delivering short-term economic prosperity and growth and hedging against external risks.
OCTOBER 10, 2023 | 5:23 PM GMT+1
Why a cookie-cutter approach won’t work for debt restructuring
Over the past six months, progress has been made in taking the sovereign debt restructuring framework forward.
That was the consensus of panelists in a discussion, hosted by the GeoEconomics Center at IMF-World Bank Week in Marrakesh. The progress is important as more low-income countries face debt distress—with the sovereign bonds of twenty-one countries trading above a one thousand basis point spread over US Treasuries. These countries urgently need a speedy restructuring process to help them get back on their feet.
Progress, however, really means the ability of various stakeholders in sovereign debt—debtor countries, bilateral official creditors, multilateral development banks, private-sector creditors, and civil society organizations—to be in a room (the Global Sovereign Debt Roundtable, launched in April 2023) and discuss issues. A better understanding has been reached among the participants especially when it comes to difficult issues like the cut-off points for calculating the amount of debt to be restructured, the role of multilateral development banks in sovereign debt restructuring, the treatment of domestic debt in restructuring, the principle of comparability of treatment between various classes of creditors, and the discount rate to be used to calculate the extent of debt reliefs granted to debtor countries.
But concrete agreements of terms still depend on case-by-case country applications. For example, in the case of Zambia, there has been agreement about using a discount rate of 5 percent, but the agreement is not universal—many private creditors think that is too low and unrealistic.
On the comparability of treatment—an issue that has held up the signing of a debt restructuring memorandum of understanding for Zambia after the announcement of agreed terms in Paris in June—agreement on concrete language has been achieved that paves the way for a deal between Zambia and its official bilateral creditors to be signed soon, reportedly by the end of the annual meetings. However, these terms cannot simply be replicated in other countries’ cases.
Participants and observers of the annual meetings should keep this in mind as they follow developments on the sovereign debt restructuring front in the next few days.
OCTOBER 10, 2023 | 4:40 PM GMT+1
Inside the IMF’s new approach to China
While the World Economic Outlook (WEO) made small downgrades in its forecast for China, the Fund’s view is even bleaker than the numbers suggest. Back in April, the WEO highlighted China’s rebound after its harsh zero-COVID shutdowns and confined its worries about the country’s property crisis to a single paragraph. This time, by IMF standards, both the WEO and Global Financial Stability Report take off the gloves and delve into the downsides, making clear that they see China as a potential risk to the global economy.
The WEO gives considerable attention to China in its opening chapter, highlighting the linked problems of the real estate downturn, soaring youth unemployment (each getting a chart), “subdued” consumer confidence, declining industrial output and business investment, and “weakening” exports. It even presciently singles out the debt issues at giant developer Country Garden, which today signaled a default on its international obligations. China is listed as a risk to the global economy, with the WEO’s “downside scenario” lowering China’s growth “as much as -1.6 percent in 2025.”
The GFSR builds a case for “financial stability concerns” in China. Its economic analysis closely tracks the WEO, but it adds on by addressing the financial vulnerabilities of some provincial governments (with a chart), the deep problems of local government financing vehicles exposed by the property crisis (three charts), and the recent worries about the country’s wealth management and trust industries. The report recommends to Beijing that “contingency planning should be developed to manage potential contagion” in the financial sector. Interestingly, both reports call for fiscal policy to be shifted toward supporting households—a step that the government has resisted—with the WEO suggesting such a policy would be preferable to “increasingly ineffective expensive investment in infrastructure.”
OCTOBER 10, 2023 | 4:04 PM GMT+1
A “big push” and a “first step” toward reaching Africa’s potential
If you keep up with our Bretton Woods 2.0 Project, you know that I’m a numbers guy. Here are a couple of the numbers from my latest issue brief that I’m keeping in mind as I talk with finance ministers and central bank governors on the ground in Marrakesh:
- Severe poverty rates globally declined drastically over the past five decades, from 45 percent to 10 percent. Yet, one-third of the African population still lives in severe poverty.
- Keeping in mind that the fifty-four African economies are heterogeneous, 44 percent of the African population doesn’t have access to electricity. Put into perspective: 80 percent of the total 750 million people who don’t have access to electricity in the world are in Africa.
- And finally, the continent leads in lack of access to other forms of basic infrastructure; 73 percent lack access to safely managed drinking water and sanitation services.
Because of its young and growing population, its massive natural resources, and its strategic location, Africa has tremendous potential that (if unleashed) could move hundreds of millions out of poverty and propel growth in the global economy. For this to happen, Africa needs a big push and deeper engagement from the Bretton Woods institutions and the global investment community. However, African leaders need to take the first step by instituting good governance practices that would attract investors to the continent. The combination of the “big push” and this “first step” can be transformative.
OCTOBER 10, 2023 | 4:00 PM GMT+1
Keep an eye out for small victories
Morocco has spared no effort to make feel delegates and guests welcome in Marrakesh. The conference venue has been constructed especially for this occasion, reminiscent of Bedouin tents, with ample outdoor features that remind delegates of the hot (and harsh) climate conditions that Moroccans and a large part of humanity face in their everyday lives.
In staying with the theme, as is usual for such meetings, there are lofty proclamations about how the world’s problems could be solved if everyone found a way to work together. Expectations abound that the ongoing revamp of the multilateral development banks’s business model and the proposed quota (or capital) increase for the IMF could provide urgently needed resources for climate change mitigation and poverty reduction in developing countries. Observing delegates from all corners of the world engaged in earnest conversations, one could be tempted to believe that larger solutions are in the realm of the possible.
Alas, like a Fata Morgana in the Sahara desert, appearances can be deceiving. Delegates were only given so much room to negotiate by leaders back home. And here the signs are not good, even beyond geopolitical tensions. Climate targets are not being met, and development assistance has been shrinking relative to what is needed. Increasing the capital base for multilateral lending (if agreed) will certainly help, but it is unlikely to be the game changer that many had hoped for.
Nevertheless, the Group of Twenty and Bretton Woods meetings still provide an important room for dialogue in troubled times. Behind the slogans and polished communiques, small victories are often won in private conversations, one country or issue at a time. The value of these meetings sometimes lies more in personal relationships that are established, a fact that was brought home during COVID-19 when professional networks ensured continuity in international dealings until in-person meetings became possible again.
With darker geopolitical and conjunctural clouds on the horizon, the sunny days of Marrakesh may soon fade from memory. But the hospitality of the Moroccan hosts will no doubt carry over to the next time the delegations meet to live up to almost impossible expectations yet again.
OCTOBER 10, 2023 | 1:34 PM GMT+1
Zambia may be days away from a debt restructuring plan. Here’s what it wants other countries to know about dealing with creditors.
With Zambia’s debt restructuring process capturing attention here on the ground in Marrakesh, Atlantic Council Senior Directors Josh Lipsky and Rama Yade pulled aside Zambian Finance Minister Situmbeko Musokotwane to get a sense of what is happening behind the closed doors of negotiations.
Musokotwane told them that the problems it has encountered in debt restructuring negotiations “to a large extent, [have] been resolved” and that his team is “hoping that [it] will sign the memorandum of understanding soon.” Such a deal is expected this week at the IMF-World Bank Annual Meetings.
“We’ve moved very far ahead” on it, he added.
With many countries around the world facing debt distress—after a series of economic crises shocked the world over the past few years—the Zambian finance minister provided advice for other countries gearing up to face their creditors in negotiations. “The most important thing is to recognize and accept you have a problem,” he said. “This sounds easy, but it’s not always the case, especially for governments that created a problem.” He added that properly recognizing debt problems will help a country “reach towards a solution.”
In addition, the finance minister advised that countries solidify their partnerships with Bretton Woods institutions because “they are the ones that are bridges between you and the creditors” and vouch for a country’s credibility and willingness to undertake reforms. But “it is not enough to have the IMF and World Bank speak for you,” he said. “You yourselves must demonstrate that you’re serious about correcting the situation. You must undertake the reforms.”
OCTOBER 10, 2023 | 11:58 AM GMT+1
With its young and talented population, Africa has great economic potential; but “demographics are not destiny”
For the first time in fifty years, the Annual Meetings of the World Bank-IMF are taking place in Africa. It’s good timing: The meetings come as the African Union begins its membership in the Group of Twenty, elevating its voice and influence in the global economic order. The fact that the Meetings are being held in Africa is also quite fitting: The continent and its citizens often disproportionately experience the effects of the world’s biggest challenges; but Africa is also home to remarkable opportunity.
In addition, the location of these Meetings is a testament to the resilience of the African continent’s people and the dynamism of its economies and cultures. That was a big theme echoed through the packed “tent” during an IMF opening session yesterday that was kicked off by Managing Director Kristalina Georgieva. At that same event, Moroccan Minister of Economy and Finance Nadia Fettah Alaoui emphasized the important contribution women are making to the dynamism of Morocco’s economy, pointing to a few of the government’s policies that aim to advance women’s economic empowerment and participation. Women trailblazers in African business and finance discussed how—through corporate leadership, investment innovation, and risk taking (along with effective policy)—countries on the continent can capitalize on the energy and talents of their young and entrepreneurial populations in order to foster inclusive growth.
However, as the panelists also noted, demographics are not destiny: Inclusive growth is going to take scale; it’s going to take financing and resources (and dealing with debt); it’s going to take technology, including artificial intelligence; it’s going to take investing in human capital; and it’s going to take effective governance and public trust.
Despite that tall order, there is optimism and inspiration on the ground in Marrakesh. Africa’s promise is clearly palpable.
OCTOBER 10, 2023 | 11:08 AM GMT+1
The recent developments that may throw a wrench into global financial stability
It was telling that the Global Financial Stability Report (GFSR) presentation started not with the usual presentation by the IMF’s financial counselor but went directly into a Q&A session, starting with a discussion of the sharp rise in government bond yields in recent weeks. The IMF’s Tobias Adrian put a brave face on this development, which came too late to be assessed for the GFSR, characterizing it as being in line with monetary tightening and adding that it is not being accompanied by disorderly market conditions.
On second look, however, the risks appear more concerning. The GFSR’s second chapter carries the explicit warning that, in an adverse scenario, a wide set of banks could experience significant capital losses, including several systemically important institutions in China, Europe, and the United States. Adrian’s concluding message, that policymakers could certainly prevent bad outcomes, sounds less reassuring in this context, given that the bond market sell-off was in part driven by political developments in some large countries.
OCTOBER 10, 2023 | 10:46 AM GMT+1
The global growth forecast hasn’t changed—but plenty more has in the World Economic Outlook
The latest World Economic Outlook released in Marrakesh today predicts unchanged global growth of 3 percent this year. Behind that unchanged forecast: The United States and China’s fluctuating growth essentially net out, with the United States receiving a 0.3 percentage-point upgrade and China receiving a 0.2 percentage-point downward revision.
But these forecasts are vulnerable to change courtesy of risks in both countries. The United States’ upward revision may not fully incorporate the impact of a longer period of 5 percent bond yields and 8 percent mortgage rates which have become more likely since late summer; while China’s 5 percent predicted growth is at the top of the current range of estimates of 2 to 5 percent. Both predictions may be optimistic.
What is clearer is the lower global growth trajectory over the next five years—down to 3.1 percent compared with the five-year rate of 3.6 percent estimated before the COVID-19 pandemic. The world economy is not expected to recover the pre-COVID growth trajectory—reflecting the enduring scarring caused by the past few years of global shocks.
OCTOBER 10, 2023 | 10:14 AM GMT+1
Will the World Economic Outlook’s “soft landing” forecast flame out?
The IMF’s World Economic Outlook foresees a soft landing for the global economy, but it also paints a distressing picture for emerging and developing countries and a pessimistic medium-term outlook. The IMF is right to point out the imbalances in the global outlook, but it overlooks how domestic inequality in advanced economies could throw the global economy off kilter. Pent-up anger at the rise in living costs will make it more difficult to conduct fiscal policy, exemplified by political dysfunction in the US Congress and the growing support for radical parties in some countries.
The recent sell-off in bond markets is at least in part a reflection of political uncertainty. The World Economic Outlook has again had the misfortune of coming out too soon after major market developments, but the IMF would do well to address the implications of higher long-term interest rates for the macro outlook and financial stability during the coming days in Marrakesh.
OCTOBER 10, 2023 | 9:32 AM GMT+1
What the “ups” and “downs” of the World Economic Outlook show about the world’s biggest economies
It finally happened. The IMF revised down China’s projected GDP growth for both 2023 and 2024. Many thought this would happen in July, and when it didn’t, all eyes were on today’s release of the World Economic Outlook. But is it revised down enough? Five percent for this year is still very optimistic. Our new report released last week, “Running out of Road: China Pathfinder 2023 Annual Scorecard,” shows just how much China is slowing post-COVID.
What’s interesting is that the US forecast was revised up (to 2.1 percent in 2023 and 1.5 percent in 2024). So this means that on the whole, global growth remains nearly unchanged from the previous forecasts, but the composition has shifted.
But remember: The World Economic Outlook was “put to bed” several weeks ago—so none of this takes into account the impact of the war in Israel. The IMF’s chief economist addressed the issue a few minutes ago saying there could be energy impacts, specifically when it comes to higher oil prices, but it’s just too early to say. The IMF seems to think the impact on energy prices is transitory, but the situation could escalate or expand and suddenly create another energy shock for the global economy. That’s an especially problematic situation for Europe, as it gears up to face the winter and tries to adapt to the lack of Russian energy.
On the bright side, India is forecasted to be the fastest-growing major economy—revised up to 6.3 percent in 2023. I’ll ask their finance minister, Nirmala Sitharaman, about this when I interview her in Marrakesh on Friday.
DAY ONE
OCTOBER 9, 2023 | 4:04 PM GMT+1
Six themes to watch as the Meetings kick off
As the IMF-World Bank Annual Meetings get underway, our experts put their heads together on the biggest themes to expect from the week. Below are their takes:
Martin said that the “accumulation of risks” and whether the world can achieve a soft landing after multiple economic shocks will dominate minds across the Meetings.
On debt restructuring conversations, Martin was skeptical that much would happen beyond “the usual kind of global sparring between China and the rest,” seeing as China has blocked attempts to restructure sovereign debt in the past. Hung said that “the international community here really should put the spotlight on China and put pressure on them to cooperate.”
Nicole listed climate adaptation and poverty reduction as key themes. Martin pointed specifically to financing for development and climate adaptation, reporting that there are “huge expectations” that there’s going to be agreement on financing multilateral development banks. Hung said to also keep an eye on new World Bank President Ajay Banga to see whether he can convince governments to increase their contributions to the Bank to facilitate climate- and development-related grants and loans to low-income countries.
Nicole called the Meetings “Banga’s first big show,” explaining that attendees will be watching to see what messages he raises. “But also, the expectations are really high in terms of what he will do with the private sector to really leverage and mobilize private finance,” given his experience in the sector, she said.
Martin pointed to arguments for restoring a division of labor between the IMF and World Bank, essentially letting the Bank focus on issues such as climate change and the IMF focus on macroeconomic issues. “I would expect this to make some waves,” Martin said. Nicole said that “the concern about mission creep… is real,” but there is still some “role for the IMF to play in development [and] in climate.” Hung agreed, saying that the IMF’s role in the climate-change issue lies in “advising governments of the risks they have to be prepared to deal with, the policy to mitigate the risks,” but “not financing.”
Each of the experts raised the topic of the proposed “equi-proportional” increase in the IMF’s quota resources, which will require countries to contribute more capital yet maintain the same voting shares—drawing criticism from members who feel as though they are undervalued, such as China and several emerging-market economies. It “may run into some resistance,” warned Martin. But, Nicole argued, “you can’t have inclusive growth if you don’t have inclusive governance.”
OCTOBER 9, 2023 | 2:14 PM GMT+1
Fragmentation is threatening developing economies in many ways. Climate is one of them.
This year’s IMF-World Bank Annual meetings—held in Africa for the first time in fifty years—must yield practical solutions and policy decisions that will protect low-income and developing economies against the multifaceted impacts of global geoeconomic fragmentation.
Africa’s fifty-four economies are home to nearly 1.4 billion people or 17.4 percent of the world’s population. However, they account for only about four percent of global carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. At the same time, twenty-two out of the world’s twenty-six poorest economies and twenty-three out of the world’s fifty-four lower-middle income economies are in Africa. Compared to others, these economies are heavily dependent on agriculture, forestry, and fishing for their economies, which is directly and negatively impacted by climate change.
To protect the livelihoods of billions in Africa and elsewhere, large CO2 emitters such as China, the United States, the European Union (EU), and other Group of Seven (G7) economies—together responsible for more than half of global CO2 emissions—must take serious steps to reduce their emissions and speed up their green transitions.
However, the global green transition is facing a headwind that has been gaining strength. Geoeconomic fragmentation between the world’s largest economies and increasing trade barriers worldwide are poised to threaten the global economy; for example, in relation to the trade of environmental goods—which are central to green transition—China and the countries that are part of the G7 and EU are highly dependent on each other. Geoeconomic fragmentation has the potential to massively interrupt that trade and, by extension, the energy transition.
The IMF hit on this topic in its World Economic Outlook this year, in a chapter dedicated to the impact of geoeconomic fragmentation on food security and the green transition. It estimates that with geoeconomic fragmentation, investments in renewable energy and electric vehicles may potentially decrease by up to 30 percent by the year 2030, in contrast to an unfragmented global supply chain. Such a decline would severely slow down the green transition, with significant negative impacts on the climate, especially for the low-income economies that bear disproportionate climate-change effects. This is in addition to the mushrooming economic costs of geoeconomic fragmentation for the continent in terms of higher food and energy prices as well as deadlocks in debt restructuring. Realistic solutions that will protect low-income and developing economies are needed.
OCTOBER 9, 2023 | 12:00 PM GMT+1
Two conflicting moods prevail as financial leaders gather
Flying into Marrakesh this weekend, I could see clearly how the city is split in two. The older part of the city—a medina originating from the eleventh century—is nestled within red clay walls that separate it from the newer parts of the city, where gleaming hotels line the roads and nearly every international brand is represented.
Finance ministers and central bank governors from over 180 countries are gathering right now in Marrakesh for the IMF-World Bank Annual Meetings, the first time the Meetings are being held on the African continent in fifty years. And the mood—just like the city—is split in two.
There’s optimism: The IMF is hinting that tomorrow it will revise its projections upwards and that there is now an increased chance of a “soft landing” not just for the United States, but for the entire global economy. But there’s also worry: War in Europe, and now in Israel, has reminded the fourteen thousand participants at these Meetings how quickly geopolitics can change their calculations.
It is not lost on anyone here that the last time these Meetings happened in Africa was 1973—just days before the start of the Yom Kippur War, which led to an oil embargo that sent the price of gas skyrocketing.
Once again, foreign policy and finance have become intertwined. And that’s why the Atlantic Council has come to the Meetings: to help map how Bretton Woods institutions can navigate this new era of geoeconomics.
OCTOBER 9, 2023 | 11:17 AM GMT+1
The pressure is rising on the IMF and World Bank to increase climate financing and restructure debt
Volatility in global financial markets spiked over the weekend after the Israeli government declared war following an attack from Hamas that killed hundreds of people. Oil prices rose by 5 percent at one point (before snapping back to about 3 percent), stock markets notched down worldwide, and safe haven flows pushed the US dollar and US Treasury bond prices up—adding more pressure on emerging bond markets. On average, sovereign bonds of emerging market countries trade at around eight hundred basis points above US Treasuries—with twenty-one countries facing a spread of around one thousand basis points: Basically, they’re in distress. In particular, Ethiopia is viewed as likely to default next, with spreads approaching five thousand basis points. Sri Lanka and Ghana still languish in their sovereign debt restructuring processes; meanwhile, Zambia seems like it may sign a MOU with official bilateral creditors at the end of this week’s Meetings.
These developments, coupled with escalating geopolitical rivalry, represent a somber backdrop for the opening of the IMF-World Bank Annual Meetings in Marrakesh—making it even more critical for the Bretton Woods Institutions to develop policies that address emerging market countries’ biggest challenges. Those policies should include mobilizing climate financing and speedily restructuring sovereign debt, among others.
OCTOBER 9, 2023 | 10:31 AM GMT+1
Take calls for international cooperation on commodities markets seriously
As the Marrakesh meetings proceed, it will be important not to lose sight of the bleak outlook contained in one of the very first documents released: The third chapter in the IMF’s World Economic Outlook on the potential risks posed by the fragmentation of commodities markets. The analysis (summarized here) warns about the impact of deepening global divisions on commodities trade. This trend—affecting everything from wheat to lithium—could increase inflationary pressures, reduce global growth, and even slow the energy transition.
As the world witnessed after the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, wheat shortages and rising fuel prices hit the poor hardest. As the chapter points out, “the average low-income country imports more than 80 percent of the wheat it consumes,” and over forty percent of those imports come from only three countries. That means that additional shortages caused by “global fragmentation” could sharply increase food insecurity across the developing world. And while the model shows that the overall “global economic costs appear modest” from such disruptions, low-income countries that rely heavily on agricultural imports would be “disproportionately affected.”
Given that in the aftermath of COVID-19 the number of people living in extreme poverty rose for the first time in decades, there should be concern that deepening geopolitical tensions will only increase the plight of low-income communities. In addition, a slower “green transition” will only add to the burden on developing countries as they are among those already feeling the most pain from climate change. It is something to keep in mind as the Meetings this week inevitably produce calls for international cooperation.
OCTOBER 9, 2023 | 9:52 AM GMT+1
The private sector has a tall order to fill on climate investment
Chapter 3 of the IMF’s Global Financial Stability Report emphasizes the need to mobilize private financing and investment to emerging market and developing countries—who would need two trillion dollars annually by 2030 to fight climate change and adapt to its effects, five times more than currently planned $400 billion in climate investments planned for the next seven years. As public investment is limited, private funds will have to make up for 80 percent to 90 percent of the needed climate investment. Private climate investment needs to be scaled up dramatically to fit this tall order; for example, climate investments account for only a portion of the more than $2.5 trillion of assets under the management of environmental, social, and governance mutual funds.
In the chapter, the IMF then proceeded to review a list of oft-repeated measures by emerging market and developing countries to attract private investment—such as strong macroeconomic policies; deepening financial markets; policy predictability within a robust governance framework; better climate data, taxonomy, and disclosure; and risk sharing and guarantees by multilateral development banks. These are good policy ideas, but they’re not easy to implement—and they have not yet been able to generate the level of private climate investment that is needed. Against this backdrop, attention has turned to the World Bank’s Private Sector Investment Lab—comprised of chief executive officers of financial institutions and former officials aiming to bring more private financing to emerging market countries—watching to see whether the investment lab will be able to come up with concrete and actionable ideas.
OCTOBER 9, 2023 | 7:24 AM GMT+1
The world needs realistic fiscal solutions now
In IMF managing director Kristalina Georgieva’s curtain raiser speech last week, she called attention to the estimated global economic loss of $3.6 trillion caused by global shocks since 2020. More distressingly, she pointed out, the losses have been distributed very unequally, falling disproportionately on vulnerable developing and low-income countries while only one country—the United States, with the help of expensive fiscal rescue measures—has seen its gross domestic product rebound over pre-COVID levels. Now, fiscal risks are acute for all countries, and there is an urgent need for governments to rebuild fiscal space to be in a position to react to and rebound from future shocks. Furthermore, deteriorating international cooperation—due to rising geopolitical competition and distrust—has fragmented the global economy, slowing its growth.
While having described very concisely the challenges, Georgieva didn’t fully detail realistic policy measures to help the world rebound from this decade’s shocks and crises. There is an urgent need to raise two trillion dollars (needed annually, according to estimations) to help developing and low-income countries adapt to climate change and meet sustainable development goals. Formulating these policies at this week’s meetings is mission critical for the IMF and World Bank: Their failure to spur change within the next ten years would position the world on a trajectory toward increasing fiscal risks.
Further reading
Mon, Oct 9, 2023
The United States just sent a strong message to the IMF
New Atlanticist By Martin Mühleisen
A recent speech by a US Treasury Department official gave a tough appraisal of the IMF and its leadership. Martin Mühleisen explains what is behind the Biden administration’s change of tone.
Mon, Oct 9, 2023
The Bretton Woods institutions under geopolitical fragmentation
Issue Brief By Martin Mühleisen
Given China’s current resource advantage, Western countries need to make better use of the IMF and World Bank where doing so is in their interest. If applied more broadly, this approach could provide incentives for other governments to return to multilateral institutions, instead of China, for support.
Mon, Oct 9, 2023
How the IMF can navigate great power rivalry
Issue Brief By Hung Tran
Fragmentation resulting from geopolitical competition between large economies is posing a serious challenge to the fulfillment of IMF's core missions. Here's how it can respond.
Image: The Atlantic Council's GeoEconomics Center arrives at the IMF-World Bank Annual Meetings in Marrakesh.



