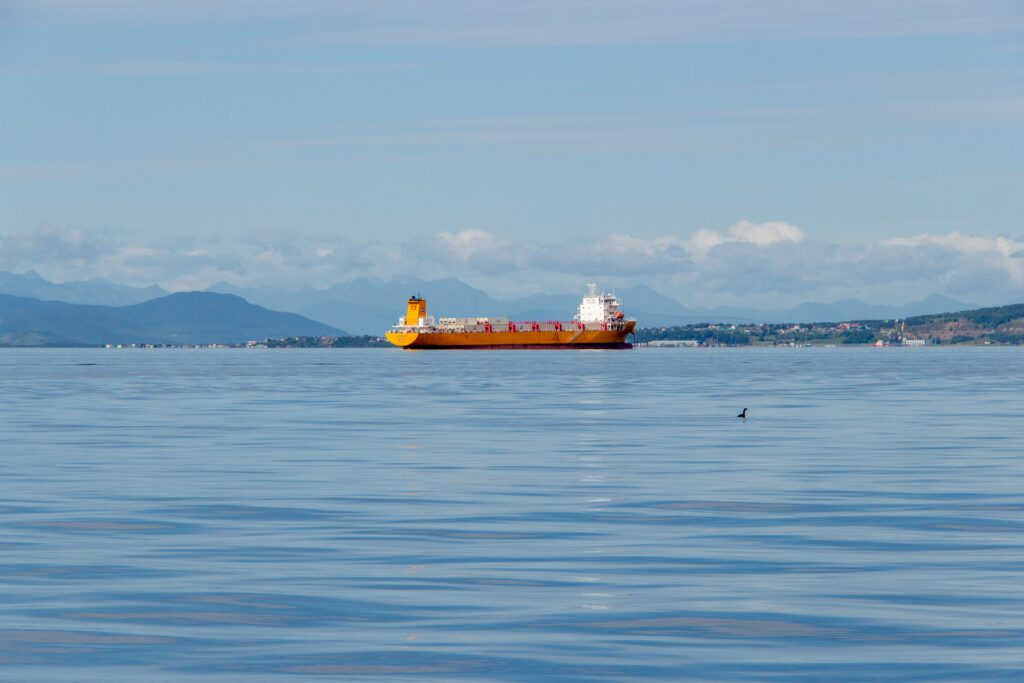
Ukraine seems to have found an effective asymmetrical response to the massive waves of deadly missile attacks that Russia has unleashed against Ukrainian cities since early January. A number of Russian oil refineries and oil terminals have been hit with precision strikes, attributed to new Ukrainian long-range drones.
By targeting fossil fuel exports—the financial lifeline of the Kremlin’s regime—this response has had an impact. In January Russia’s seaborne oil product exports fell 8.6 percent from a year earlier and 2 percent from the previous month to 10.8 million metric tons, owing to lower processing capacity and unplanned repairs.
Drone strikes at critical processing and export facilities bring financial pain to Russia. Repairs are costly and time-consuming, especially because of sanctions that limit access to Western technology, which is making the replacement of destroyed equipment difficult.
STAY CONNECTED
Sign up for PowerPlay, the Atlantic Council’s bimonthly newsletter keeping you up to date on all facets of the energy transition.
However, Ukraine’s efforts to repel Russian attacks would be made less challenging if Europe and the United States did even more to throttle Moscow’s oil and gas exports by utilizing the full power of sanctions.
The tragic loss of human life in Ukraine, including hundreds of children, is still too often paid for by cash that Russia receives from the export of oil and gas enabled by loopholes that persist in the sanctions regime imposed on Moscow by the United States and the European Union. Amid the ongoing struggle for peace and sovereignty in Ukraine, governments that believe in the rule of international law must do more. The United States, EU, and the Group of Seven (G7) industrialized nations should be consistent and strict in enforcing sanctions against Russian fossil fuels.
Western governments have strong tools to dry up the Kremlin’s war budget. They can do this by plugging the gaps in sanctions against Russian oil and gas exports, strengthening them further, and thereby severing the critical revenue stream supporting the Kremlin’s oppressive regime and its brutal war machine.
There are five specific actions that the G7 and EU can take in this direction: enforce price caps on Russian oil and oil products; prevent the expansion of Russia’s shadow fleet of oil tankers; close the refining loophole; fully ban Russian liquefied natural gas (LNG) imports; and take decisive actions to reduce demand for oil and gas in the long-term.
Civil society organizations are urging Western leaders to take these steps. More than 290 groups from across the globe addressed the G7 and EU leaders with this call in February, as Ukraine marked the tragic two-year anniversary of the full-scale invasion.
There is an urgent need to eliminate loopholes in sanctions against Russian fossil fuels to prevent further escalation of the Kremlin’s aggression in Europe outside of Ukraine.
The shadow of Russia’s military plans looms ominously. This is evident in the 2024 federal budget, with a staggering allocation of resources to the military-industrial complex, not seen since Soviet times. This is a startling shift in budgetary focus, with a third dedicated to the army. This militarization signifies a perilous path toward conflict intensification, threatening regional stability. In 2024, Russia’s “national defense” budget will expand to 10.8 trillion rubles ($110 billion), marking a 70 percent increase from 2023 and more than doubling from 2022. It is three times higher than the pre-war 2021 allocation.
Regrettably, Europe and the United States inadvertently contribute to this war chest. The refining loophole in Western sanctions against Russian oil exports, meticulously highlighted by Global Witness, remains a massive funding source feeding Russia’s aggression, a fact that should not be overlooked.
While Western governments have banned the imports of crude oil, petrol, diesel, and jet fuel that originate in Russia, their countries can still import refined oil products produced from Russian crude in other nations, like India, China, Turkey, or the United Arab Emirates. In 2023 sales of Russian crude oil to refineries in India went through the roof. These Indian refineries capitalized on selling the refined products to G7 markets, where direct supplies of Russian oil were banned. The refining loophole increases the demand for Russian crude oil and enables higher sales in terms of volume, while keeping its price up. As a result, the price of Russian crude oil does not collapse in the global market even with the Western sanctions.
OPEC members’ decision to restrict exports of additional volumes of oil to world markets benefits Putin, and contributes to Russia’s strategy to weaponize energy supply. The refining loophole also creates a space for cooperation between Russia and OPEC countries, which can import Russian oil to refine or mix it with other blends of crude to conceal origin and profit from it.
Similarly, Europe still buys significant volumes of Russian natural gas, not so much through pipelines, but increasingly in the form of LNG. Key Russian LNG importers such as France, Spain, and Belgium have little excuse for continuing to do business with Russia. The gas storage in Europe is ample, and projections indicate an energy surplus bolstered by record-breaking clean energy expansion and alternative LNG supplies set to come online in 2024.
In total, since the start of the full-scale invasion in Ukraine on February 24, 2022, Russia has amassed more than $650 billion in profits from fossil fuel exports. Yet, if international sanctions on Russia’s fossil fuel industry are maintained and rigorously enforced, the International Energy Agency projects that the Kremlin’s profits from oil and gas could plummet by 40 to 50 percent by 2030.
The West has to act collectively to cripple the Kremlin’s fossil fuel export lifeline to help end the war in Ukraine faster. The future of Ukraine’s security and human dignity hinges on this critical moment of action, and world leaders must take action now to stop funding Russia’s aggression.
Svitlana Romanko, Founder and Director of Razom We Stand
Oleh Savytskyi, Campaigns Manager at Razom We Stand
Related content
Learn more about the Global Energy Center

The Global Energy Center develops and promotes pragmatic and nonpartisan policy solutions designed to advance global energy security, enhance economic opportunity, and accelerate pathways to net-zero emissions.