Of the various parties embroiled in Russia’s ongoing war against Ukraine, few have attracted as much international attention as the paramilitary Wagner Group. Indeed, a veritable cottage industry has emerged dedicated to monitoring the Wagner network’s alleged involvement as unofficial agents of Russian foreign policy everywhere from Estonia to Sub-Saharan Africa.
The general consensus is that private military companies (PMCs) like Wagner Group must be countered because they advance Kremlin interests and help the Putin regime to project Russian power internationally. But a closer look suggests the Wagner Group and other Russian mercenary organizations may ultimately be liabilities and not assets for Putin.
For Wagner chief Yevgeny Prigozhin, 2023 already looks to be a tumultuous year. He has accused senior Russian military leaders of “treason” for allegedly holding up logistical and material support to Wagner mercenaries battling for control of Bakhmut in eastern Ukraine, and recently complained of being cut off altogether from the Kremlin.
Some commentators believe Prigozhin’s frequent jabs at members of the Russian elite could presage a contest for political power that may reach the heights of the Kremlin towers. Indeed, Prigozhin now says that he plans to remold Wagner into “an army with an ideology,” suggesting that he seeks to officially re-brand himself as an out-and-out political operator.
For all the speculation regarding the potential threat Prigozhin poses to the stability of the Putin regime, few have explored the Wagner leader’s relationship to the power structures that Putin himself depends upon for the perpetuation of his rule. In reality, the Wagner Group is as much a product of this system as it is a tool of Kremlin foreign and military policy. Western policymakers seeking to understand the role of Russian private paramilitaries should treat them as a symptom of the institutionalized corruption at the heart of Putin’s regime and not as just another instrument in Russia’s hybrid warfare toolbox.
Stay updated
As the world watches the Russian invasion of Ukraine unfold, UkraineAlert delivers the best Atlantic Council expert insight and analysis on Ukraine twice a week directly to your inbox.
Prigozhin has managed to carve a niche for himself by leveraging opaque corporate networks to facilitate Russian hard and soft power projection in Ukraine, Syria, and various conflict zones across Africa. This appears to be profitable work; his companies have reportedly raked in hundreds of millions of dollars from mineral extraction alone. White House officials have even claimed in recent months that Prigozhin directed Wagner fighters to capture the Ukrainian town of Soledar in order to secure access to nearby salt and gypsum mines. The notion that Prigozhin personally benefits from enabling the Kremlin’s foreign policy adventures appears to be a feature rather than a bug of Putin’s particular approach to governance.
Political scientists generally characterize Putin’s rule as a corrupt patron-client system in which elites are compensated for their allegiance with access to resources. Vladimir Gel’man of the University of Helsinki contends that Putin accepts bad governance by trusted elites to cultivate a loyal, informal power base separate from those formal institutions which might challenge his authority. Russia analyst Mark Galeotti likens this arrangement to a public-private “adhocracy” in which informal networks of enterprising business and political elites, rather than formal institutions, end up taking the initiative in divining and executing official policy.
The Wagner phenomenon reflects a political ecosystem that rewards the stewards of government policy with official as well as illicit perks in exchange for loyalty. Wagner benefits Putin by providing deniable cover for a wide range of military operations outside of Russia. In exchange, Prigozhin is allowed to pursue commercial ventures in the countries where his forces are active.
Eurasia Center events

Prigozhin’s trajectory is an indication that the Russian state’s claim to a monopoly on violence may be the next frontier to be challenged by Kremlin elites. The Wagner Group’s example appears to have encouraged everyone from Chechen strongman Ramzan Kadyrov to Russian natural gas giant Gazprom to organize PMCs of their own, a trend that some analysts argue could portend a “descent into warlordism.” Recent reports of a company owned by longtime Putin associate Gennadiy Timchenko hiring another PMC outfit not affiliated with Wagner to secure oil and gas infrastructure in Syria further suggest that Prigozhin is not the only person vying to supply PMC services to regime insiders.
International efforts to counter the Wagner network will require many of the same mechanisms used to combat corruption more generally. This will require governments to reflect on how their own institutions play into the interests of figures like Prigozhin, who has pursued journalists through the British courts despite being the subject of UK sanctions. Critics claim transnational imbalances in financial transparency that allow offshore jurisdictions to provide a veil of corporate secrecy to American and European nationals also help to obscure the Wagner network’s operations.
Efforts by the US Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control to target Wagner-linked shell companies registered in tax havens are a step in the right direction. But Western governments should also aim to hold accountable those individuals responsible for managing the network of corporate entities behind Wagner’s more mundane business operations.
One may reasonably question why Ukraine and its allies should go after Russian PMCs at all if their continued presence has the potential to undo Putin. Why not let them multiply and further weaken the foundations of the Putin regime? While potentially tempting, such an approach would involve considerable risks. If and when Putin leaves office, this is likely to create a power vacuum in which Russia’s nascent PMC class would flourish. Such an outcome could return Russia to a state of lawlessness reminiscent of the “wild nineties,” a period characterized by a proliferation of organized crime groups whose mercenary enforcers were often veterans of military campaigns in Afghanistan and Chechnya.
Putin often invokes the chaos of the 1990s to justify his authoritarian rule. Tolerating the presence of PMCs like the Wagner Group in the hope that they could unseat Putin risks reducing Russia to new depths of disorder and thereby facilitating the rise of aspiring autocrats in the years to come. Combating Russia’s private paramilitaries is essential not just in order to contain Putin, but to preempt the empowerment of future Russian leaders molded in his likeness.
Allen Maggard is a Russia analyst and specialist in the intersection of Russian political economy and the defense industry at C4ADS.
Further reading
The views expressed in UkraineAlert are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Atlantic Council, its staff, or its supporters.

The Eurasia Center’s mission is to enhance transatlantic cooperation in promoting stability, democratic values and prosperity in Eurasia, from Eastern Europe and Turkey in the West to the Caucasus, Russia and Central Asia in the East.
Follow us on social media
and support our work
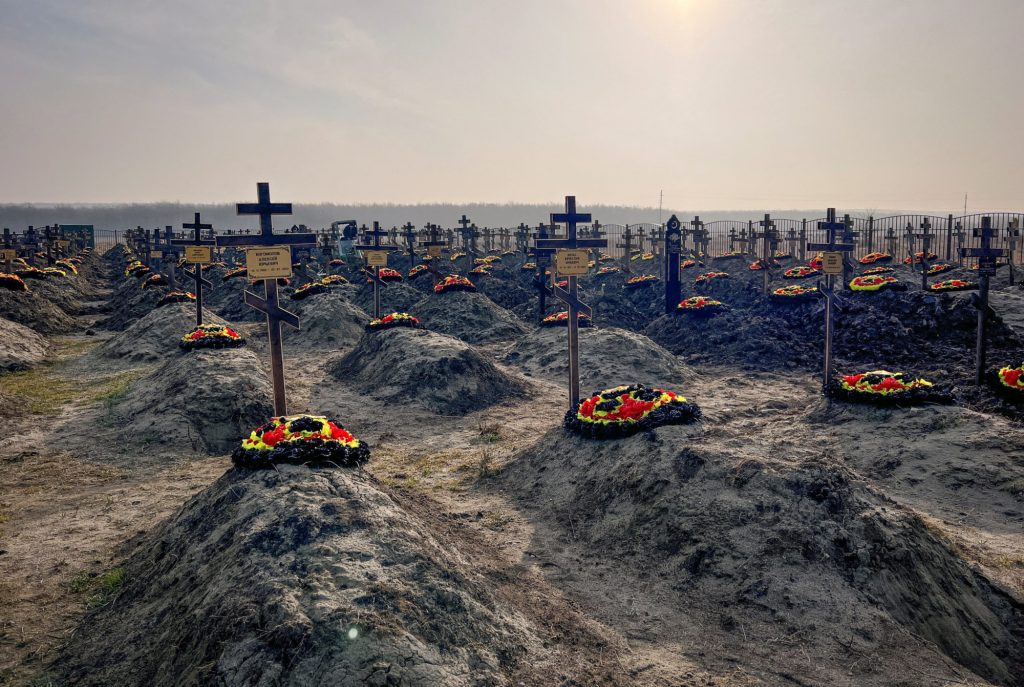
Image: Graves of Russian Wagner mercenary fighters are seen in a cemetery near the village of Bakinskaya in Krasnodar region, Russia. January 22, 2023. (REUTERS/Stringer)