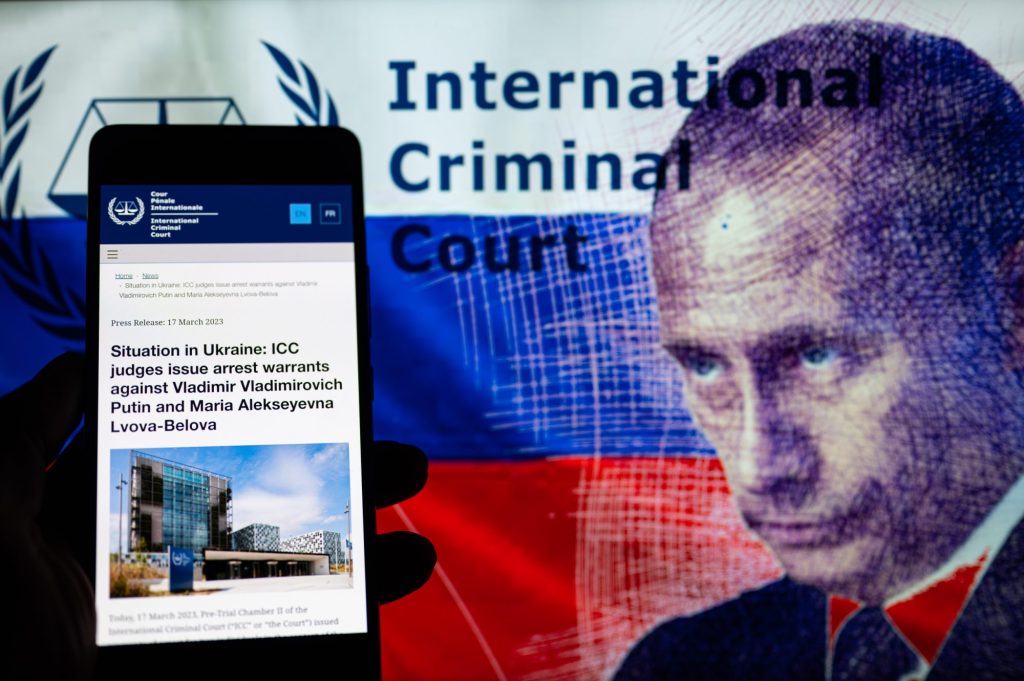
On March 17, the International Criminal Court (ICC) in The Hague indicted Russian President Vladimir Putin and issued an arrest warrant. This indictment is likely to have far-reaching consequences for Putin personally and for Russia.
The warrant states that Putin “is allegedly responsible for the war crime of unlawful deportation of population (children) and that of unlawful transfer of population (children) from occupied areas of Ukraine to the Russian Federation. There are reasonable grounds to believe that Putin bears individual criminal responsibility for the aforementioned crimes.”
The ICC is a comparatively new international organization. It was created in July 1998 and formally established in 2002. At present, 123 countries have ratified its statute. They include all the countries of South America, all EU countries, most of Oceania, and roughly half of Africa. All these countries are now theoretically committed to arresting Putin. No sovereign immunity will shield him.
ICC indictments are rare. To date, the court has only indicted 52 people, but it aims to prosecute top culprits. Earlier indictments have targeted former presidents Omar al-Bashir of the Sudan and Muammar Gaddafi of Libya. In this context, the indictment of Putin appears entirely natural.
Following their ICC indictments, al-Bashir and Gaddafi became international pariahs. Putin and his regime are not likely to fare any better. After this indictment, no serious politician or public figure will want to meet with or even talk to Putin. He cannot travel abroad without considering the possibility of arrest and extradition to The Hague.
Stay updated
As the world watches the Russian invasion of Ukraine unfold, UkraineAlert delivers the best Atlantic Council expert insight and analysis on Ukraine twice a week directly to your inbox.
In light of his new status as an indicted war crimes suspect, Putin will likely find that he is no longer invited to international forums such as G20 or the United Nations General Assembly. Since all power in Russia is concentrated to Putin, this means Russia has effectively lost its voice on the international stage.
Another consequence of the indictment is that no democratic political leader who values their own reputation will want to have any further contact with Putin. German Chancellor Olaf Scholz and French President Emanuel Macron will need to rethink their earlier policies of holding regular phone conversations with Putin. Likewise, there is no longer any realistic chance of a negotiated peace settlement between Putin’s Russia and Ukraine brokered by the international community. Meanwhile, Kremlin-friendly European politicians such as Hungary’s Prime Minister Viktor Orban will have to abandon their personal links with Putin.
There are limits to the impact of the ICC indictment, of course. Many influential countries in addition to Russia itself do not recognize the court, with the list including the United States, China, India, Saudi Arabia, and Turkey. However, even those countries that have yet to sign and ratify the ICC statute will be well aware that continuing to maintain close ties with Putin could now hurt their international standing.
Chinese President Xi Jingping has just confirmed that he will visit Putin in Russia on March 20-22. While few expect him to alter his plans in light of the ICC arrest warrant, his visit is unlikely to be good for China’s reputation. Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan has had quite intense contacts with Putin in recent years. As the leader of a NATO member state, will he maintain this level of engagement after Putin’s indictment? I doubt it.
Eurasia Center events

The implications of the ICC arrest warrant are not limited to the international arena. It is also likely to impact Putin’s standing within Russia, undermining his absolute power and leaving him more isolated than ever.
Russian investigative journalists have recently revealed that the increasingly reclusive Putin now travels in armored trains between his three main residences in Valdai, Novo-Ogaryovo, and Sochi, with special railway stations constructed at each location for his personal security. He rarely dares to meet anyone in person, only physically convening Russia’s Security Council three times over the past year. Now a wanted man, Putin’s paranoia looks set to worsen.
With Putin unable to play his usual active role in international negotiations, his value as Russia’s national leader will be greatly diminished. This will have a significant negative impact on Russia’s international standing that will continue for as long as Putin remains in office. Putin’s domestic political position will be seriously undermined, with members of the Russian elite drawing the inevitable conclusion that he is now a liability.
The indictment against Putin sends a powerful message to other senior figures within the Russian establishment, leaving them in no doubt that they are also vulnerable to possible prosecution. If the Russian President can be charged, they may also be indicted for their participation in Putin’s alleged crimes against humanity. Loyalty to Putin was once seen as the only way to get ahead in modern Russia; it now looks increasingly like a dangerous dead end.
The Russian leader is unlikely to appear in The Hague any time soon. Nevertheless, the ICC decision to indict him for war crimes is a highly consequential step that will deepen Russia’s international isolation while significantly weakening Putin’s personal position both at home and abroad.
Anders Åslund is a Senior Fellow at the Stockholm Free World Forum. He is co-author with Andrius Kubilius of the new book “Reconstruction, Reform, and EU Accession for Ukraine.”
Further reading
The views expressed in UkraineAlert are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Atlantic Council, its staff, or its supporters.

The Eurasia Center’s mission is to enhance transatlantic cooperation in promoting stability, democratic values and prosperity in Eurasia, from Eastern Europe and Turkey in the West to the Caucasus, Russia and Central Asia in the East.
Follow us on social media
and support our work
Image: Vladimir Putin arrest warrant seen in press release from the International Criminal Court in The Hague. On 17 March 2023 in Brussels, Belgium. (Photo Illustration by Jonathan Raa/NurPhoto)