The invasion of Ukraine was meant to advance Vladimir Putin’s vision of a revived Russian Empire. Instead, it is forcing neighboring countries to reassess their own relationships with Moscow and fueling growing calls for decolonization and derussification throughout a region that was once viewed by many international observers as an informal extension of Russia itself.
This embrace of decolonization is nowhere more evident than in Kazakhstan, the largest state in Central Asia and a regular target of imperialistic Russian rhetoric. In the year since Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine began, Kazakh society has actively sought to accelerate ongoing nation-building processes amid a notable rise in anti-imperialist sentiment. Meanwhile, the Kazakh authorities have made it clear that they do not condone Moscow’s military campaign in Ukraine and refuse to back the war.
Stay updated
As the world watches the Russian invasion of Ukraine unfold, UkraineAlert delivers the best Atlantic Council expert insight and analysis on Ukraine twice a week directly to your inbox.
One of the earliest indications that Kazakhstan would not align with Russia over the invasion of Ukraine was the decision in spring 2022 to cancel the country’s traditional World War II Victory Day celebrations. The cancellation was an unambiguous rebuff to the Putin regime, which has placed the Soviet victory over Nazi Germany at the heart of modern Russian national identity and expects regional leaders to demonstrate their loyalty via reverence for the Soviet war effort.
This snub was followed by an even more direct and public fallout in June 2022. While sharing a stage with Putin at a flagship annual economic forum in Saint Petersburg, Kazakh President Kassym-Jomart Tokayev declared that he would not recognize Russian-occupied areas of Ukraine.
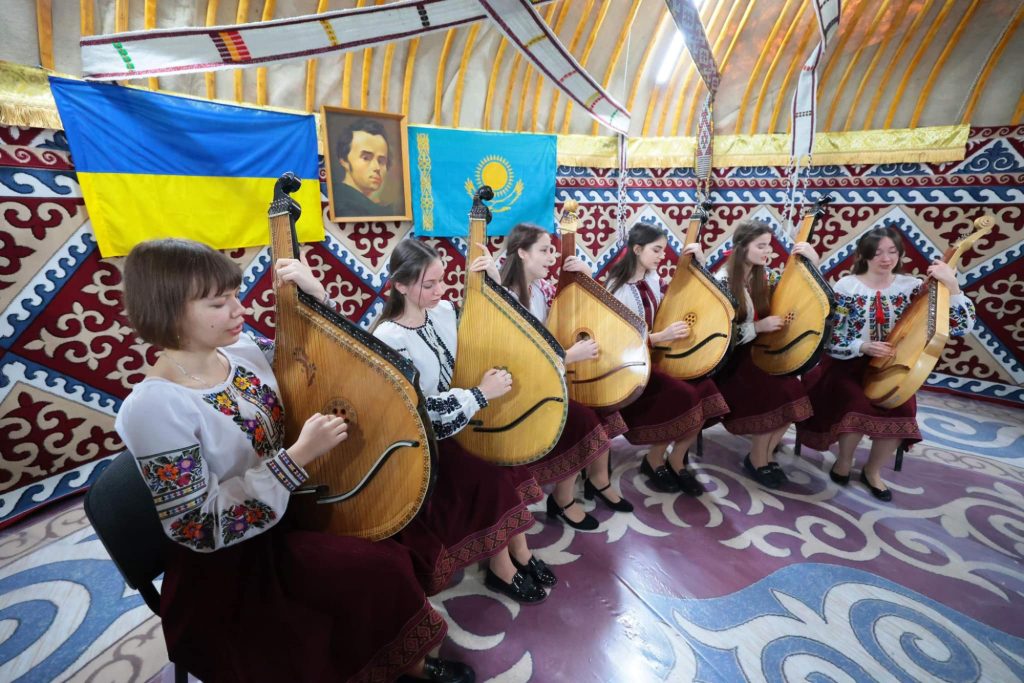
Perhaps the most eye-catching indication of Kazakh public support for Ukraine has been the “Yurt of Invincibility” initiative, which has seen a number of traditional Kazakh yurts set up in Ukrainian towns and cities in recent months to help Ukrainians cope with electricity blackouts caused by Russian bombing of the country’s civilian infrastructure.
Organized by the Kazakh business community and backed by private donations, the yurt initiative has proved highly popular among Ukrainians while sparking considerable anger in Russia. However, Kremlin attempts to elicit an official response from the Kazakh authorities were politely declined, with Kazakh Foreign Ministry spokesperson Aibek Smadiyarov stating there was “nothing to explain.”
It is not hard to imagine why the appearance of “Yurts of Invincibility” across Ukraine struck such a nerve in Russia. Manned by activists offering free electricity and internet access along with hot drinks, the yurts represent a humane response to the inhumanity of Russia’s brutal invasion. In a very real sense, these traditional Kazakh abodes serve as symbols of post-colonial solidarity between Kazakhstan and Ukraine.
Eurasia Center events

Russian discontent over the critical Kazakh response to the invasion of Ukraine has led to attacks on Kazakhstan from Russian officials and in the country’s Kremlin-controlled information space. Since the start of the invasion, pundits on Russia’s notoriously inflammatory political talk shows have begun speculating over the possibility of future Russian military intervention in Kazakhstan. During a November 2022 episode of prominent regime propagandist Vladimir Solovyov’s daily show, one commentator declared: “the next problem is Kazakhstan.” He went on to claim that “the same Nazi processes can start there as in Ukraine.”
These provocative statements were echoed by Russian Ambassador to Kazakhstan Alexei Borodavkin, who warned in December 2022 that “radical nationalist tendencies” were becoming more and more visible in Kazakhstan, before suggesting Russia was ready to “help” the Kazakh authorities address this issue.
The Russian Ambassador’s comments were particularly provocative as they closely mirrored the kind of language used by the Kremlin to justify the invasion of Ukraine. This played on longstanding Kazakh fears that Moscow may attempt to exploit the presence of a large ethnic Russian minority in Kazakhstan, which is concentrated in northern regions of the country bordering the Russian Federation.
Suggestions that ethnic Russians living in Kazakhstan are somehow oppressed have sparked a bitter response from many Kazakhs, who pride themselves on their tolerant attitude toward Russia and their respectful approach to the shared inheritance of the imperial past.
Unlike other post-Soviet states, Russian remains an official language in today’s Kazakhstan. The country also accepted hundreds of thousands of Russians fleeing mobilization into the Russian military in late 2022. Critics say this welcoming stance makes a mockery of Kremlin propaganda claims about a rising tide of Russophobia in today’s Kazakhstan.
The past year has witnessed historic shifts in allegiances and attitudes across the entire post-Soviet space. Ukraine’s heroic fight against Russian imperialism has prompted countries throughout the region to question the nature of their own ties to the Kremlin and seek geopolitical alternatives capable of countering Russian influence.
In Kazakhstan, the invasion has amplified anti-imperial sentiment and enhanced existing decolonization processes. These trends look set to gain further momentum in 2023. Geography alone dictates that Kazakhstan cannot realistically hope to cut all ties with Russia, but there is no escaping the fact that the full-scale invasion of Ukraine has seriously undermined Russian influence in a country where all roads once led to Moscow.
Kamila Auyezova is a research analyst who focuses on geopolitical and climate issues in Eurasia. You can find her on Twitter @KAuyezova.
Further reading
The views expressed in UkraineAlert are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Atlantic Council, its staff, or its supporters.

The Eurasia Center’s mission is to enhance transatlantic cooperation in promoting stability, democratic values and prosperity in Eurasia, from Eastern Europe and Turkey in the West to the Caucasus, Russia and Central Asia in the East.
Follow us on social media
and support our work
Image: A special Kazakh ‘Yurt of Invincibility’ has opened in Lviv to help those affected by Russia’s war in Ukraine. (Lviv Regional State Administrati via Reuters Connect)