Watch the event
Event transcript
Uncorrected transcript: Check against delivery
Speaker
Samantha Power
Administrator, United States Agency for International Development (USAID)
Moderator
Jonathan Capehart
Pulitzer Prize-winning journalist, the Washington Post and MSNBC
VICENTE GARCIA: Hello. Welcome to this special Pride edition of #ACFrontPage. I’m Vicente Garcia, senior director of engagement and external affairs at the Atlantic Council, and we’re delighted for today’s conversation featuring USAID Administrator Samantha Power on a topic important to me as a member of the LGBTQI+ community, but also to the Atlantic Council in our mission to shape the global future together through US global leadership and global engagement.
Today’s conversation will be led by Pulitzer-winning journalist Jonathan Capehart, who is the host of his own show on MSNBC, serves on the Washington Post Editorial Board, and a frequent commentator on PBS, and the list goes on. We welcome participation by those here joining us today in person during our Q&A session, but also welcome those joining online by using the hashtag #ACFrontPage.
Administrator Power, thank you for joining us here today. We’re very eager to hear from you about the Biden administration’s and USAID’s priorities at addressing global LGBTQI+ human rights. And so now I’ll turn it over to Jonathan to lead our discussion. Thank you.
JONATHAN CAPEHART: Thank you very much, Vicente, for the invitation to be here. Thank you all. One more thing, Vicente. As someone who reads teleprompter for a living, I really felt for you because that print is so small.
SAMANTHA POWER: Yeah, seriously. We’re just old, dude.
JONATHAN CAPEHART: I know, it’s true, given the distance. But thank you very much for that introduction. And, Administrator Power, thank you very much for being here and taking the time to be a part of this important conversation.
So, as you well know, within the first month of taking office President Biden issued a memorandum that directed various parts of the US government responsible for foreign policy, such as USAID, to prioritize efforts to advance LGBTQI+ rights around the world. How are those efforts going? And what have been the biggest challenges?
SAMANTHA POWER: Thank you so much. And thanks to everybody for turning out. It’s a great energy in the room, great energy this month, and much needed, because we harness this energy to try to do this work in the world.
Well, first to say that USAID is one of fifteen agencies that is being responsive to President Biden’s direction to promote and protect and respect the human rights of LGBTQIA+ people around the world. And I’d say I feel very fortunate every day, no matter what issue I’m working on, to be at USAID, because we have this toolkit. We have programming in public health on maternal and child health. Of course we have PEPFAR, where we work with the State Department and CDC, which has, of course, made a major difference, saving twenty-five million lives and 5.5 million babies is the estimate for the good that it has done over time. And that’s had a particular effect on LGBTQIA+ communities around the world.
But beyond that, we do agriculture. We do economic growth and inclusion, livelihoods work. We’ve helped vaccinate the world. In many parts of the world, if you are LGBTQIA+, coming forward to seek social services may risk something near and dear to you, depending on the legal environment in which you’re working.
When the fallout from COVID occurred and you saw such economic devastation around the world, given the fact that LGBTQIA+ people are often working in the informal sector and may have had, in some instances, less backup, the kinds of crises that have befallen the planet have a disparate impact on marginalized communities and those that have, in a sense, faced preexisting conditions, you might say, including discrimination, stigmatization, violence, et cetera.
So we went forth. We have tripled the size of our staff. We have the great Jay Gilliam, who many of you work with, as our lead LGBTQIA+ coordinator at USAID. That position had been unfilled in the previous administration. This fiscal year we’ve had a dedicated pool of resources of around sixteen million dollars, which does everything from spot emergency assistance to people who need legal defense because they’re being rounded up in some cases or evicted to working really closely with the State Department to help identify people who would be eligible for asylum or to become refugees because of their vulnerability, because of their sexual orientation or gender identity.
So, you know, I’d say you see a massive surge in programming, in attention. But for me, I think the—and the thing that Jay has helped us so much with and the team, if you believe in development in 2023—I mean, and actually seeing development outcomes that matter and reversing development setbacks that have occurred—it’s not enough to have, like, a little pot of money, or a big pot of money, even, dedicated to LGBTQIA+. All the programming we do on food security, on education, on health, needs to be—and the list goes on—needs to be attentive and intentional about going out of our way to make sure that we are not just practicing development but inclusive development.
And the biggest challenges—I’m sure we’ll get into them, and I know many in the audience are seized with them—is criminalization, and even in countries that already have criminalized LGBTQIA+ status, you know, new moves, desire to render more salient laws that may be on the books but being ignored by some communities, work in places like Uganda, because of the introduction of the anti-homosexuality act, vigilantes and citizens and others taking what’s happening in the legal space or in the parliament and getting signed into law and viewing it as license to do whatever the hell they want to vulnerable people.
And so it’s not just happening in Uganda. That’s, of course, something that has happened very recently. But we see the instrumentalization of the human-rights agenda that so many in the world aspire to see progress, that being turned on its head. And in places where anti-democratic forces are ascendant or are getting either support or abetted or at least not counteracted by authorities, you see those voices getting louder. And even when there’s not a law and that kind of legal ballast behind those voices, that, in and of itself, is terrifying and exclusionary and a deterrent, again, for these communities to come forward and access these programs at the very time where we’re really seeking to make sure that we’re leaving no one behind.
JONATHAN CAPEHART: So since you brought up Uganda and also your point about, you know, USAID has all of these programs. But there are countries where just presenting yourself to make yourself—avail yourself of these programs could put you in danger. So the question is what is the United States government doing or can it do to push back on what’s happening in countries like Uganda?
SAMANTHA POWER: Well, to start—and I would start with what I consider a statement of the obvious but, nonetheless, I think does need to be said because it’s not always the way things are done, which is you start from the proposition of nothing about you without you. This question of tactics and how to prevail or how to counteract are super complicated, right.
Imagine, like, being part of the Biden administration and the tactical questions about how we moved the Inflation Reduction Act and, you know, convinced Joe Manchin to be part of the—I mean, when we’re operating in someone else’s country, you know, understanding, you know, the complex ecosystem in which we work, drawing, I should say, at USAID very heavily on the expertise of our local staff, two-thirds of—at least-two thirds of USAID staff abroad are nationals of the countries in which we work so they can be a great resource, but fundamentally it is the communities that are going to be affected by these laws that provide cues to us on how vocal to be, how much to signal in a deterrent way in advance of the movement of a piece of legislation, which risks then putting the United States at the center of a national drama and potentially triggering nationalism and other forces or some, you know, historical, you know, dynamics—let’s put it that way.
And so—but even what I’ve just said is kind of simplistic because there is no one view. I mean, even within an organization people are debating at fever pitch, you know, what the right approach is. This is just really, really hard.
But we do come in with humility and really try to be in lockstep with the groups who we may have funded in the past or may be funding currently, and in the case of the anti-homosexuality act in—that Uganda has moved forward with President Biden was very clear that the law should be repealed. Came out with a public statement. Has talked—and this is one of the approaches that we have taken not only in Uganda but in other places that are threatening to put in place similar laws—talking about the effects, Jonathan, on this incredibly successful partnership that we’ve had in combating HIV/AIDS.
There’s one report in Uganda that shows that service utilization is down by more than 60 percent since the law was introduced and that’s people who are afraid of coming forward for vital health services because they’re afraid it could lead to their arrest or it could lead to their eviction or it could lead to vigilante violence.
And so here we are, you know, trying to get this epidemic under control by 2030 and we’re part of this grand global coalition and at the same time these steps are being taken that would set back not only the health of LGBTQI+ communities but the health in this instance of all Ugandans.
And so, in a sense, you know, really looking at what the practical effects are of being seen to license community involvement in discrimination, stigmatization, and even law enforcement as you see citizens, again, taking things into their own hands but trying to find also arguments that have broad appeal in terms of services or programs that a broad swath of the societies in which we work are enthusiastic about, you know, showing the link between those—for example, private sector investment. There’s not one country in which USAID works that isn’t interested in fueling economic growth recovering from COVID, getting young people to work.
Well, what does it mean if the multinational companies that we and the Commerce Department and the State Department have been working with to try to encourage them to invest in these countries? Their own anti-discrimination policies and values are not going to make that an attractive place for investment.
So it’s a combination of, you know, the State Department taking steps now potentially to sanction individuals involved in this measure in Uganda. That’s been something that’s been messaged publicly and, again, these sort of practical effects that are going to extend practical harms, that are going to extend beyond if this law is not repealed.
JONATHAN CAPEHART: And so let’s talk about another country. I was thinking when you say, in response to my question about Uganda, talking to the groups on the ground, getting their input into what USAID and what the US government should do, let’s talk about Ukraine. There’s a war going on, but hopefully at some point that war will end and reconstruction will begin. Where does the LGBTQI+ community play—come into the conversation about rebuilding? Both from making sure that they are whole in Ukrainian society, but also that their rights are protected and respected?
SAMANTHA POWER: Well, this is a complex issue and a complex question, and I could come at it a few different ways. But, first, let me just say that, you know, part of Putin’s motivation, as we well know, for invading Ukraine was watching Ukrainian society, the Ukrainian government, move at really rapid pace to integrate itself into Europe. And, yes, that carries with it a lot of economic benefit for young people in Ukraine, but much of the impetus behind what was, you know, between really 2013 and last year, such a shift, right, in an orientation that went in one direction and then shifted in another direction. Much of it was values-based.
That doesn’t mean everybody was with all aspects of the European agenda, or the European program, or the European Convention on Human Rights immediately. We’ve seen that, of course. But, you know, part of what Ukraine is fighting for and part of what Russia is trying to squelch is liberalization, is broad understanding of who human rights protections apply to. Now, again, that’s a kind of general statement.
What we do—then, shall I say, of course, following Russia’s invasion Ukraine’s work to liberalize and build checks and balances and build in human rights protections, although not making headlines in the American or even the European headline, that work has accelerated. Which is, frankly, remarkable that a country that’s fighting for its life and its people can walk and chew gum at the same time. But meaning, you know, you see [LGBTQI+] protections progressing not only through legislative measures, and regulation, and as we vet—as the Ukrainians vet and we support programs to vet judges, you know, their human rights credentials being assessed in this much more comprehensive way.
But also, again, as the economy—parts of the economy actually flourish—I know this is hard to believe. But, like, the tech sector grew by, I think, seven or eight percent last year. You know, that itself, young people being out and being integrated in the world, there’s just things happening in the society that I think is going to put Ukraine, you know, and above all [LGBTQI+] communities and individuals, in a much more supportive legal and social ecosystem as the whole rationale for the war is about integrating into Europe. And the criteria by which—that Ukraine is going to need to meet, the roadmap and so forth, is going to entail much stronger protections than have existed in the past.
To your point, I think, if I understood it, about reconstruction, again, that’s incumbent on this intentionality that I was talking about. USAID is a critical partner. I was just meeting with the minister of finance yesterday talking about reconstruction out of the recent conference in the United Kingdom. You know, as we think about procurement and nondiscrimination in procurement, you know, how are those checks and those protections built in? As we think right now about health services and making sure that those are restored every place we can, even places close to the front line or as territory is liberated, how does USAID support flow in a manner where we are constantly vigilant to how inclusive those services are, and whether or not they are provided?
I mean, you know, we’ve actually managed to distribute I think it’s something like sixteen million antiretrovirals in Ukraine, you know, just since the war, you know, has started. So, you know, in terms of the mainstream PEPFAR and HIV/AIDS programs, like, those have continued. We’ve managed to be able to keep those afloat. And that took real intentionality on the part of our health team and our Ukraine team.
But I think, again, the principle that we want to bring to everything we do in terms of inclusive development is just that it’s a design feature of any program that we do that we are looking to make sure we are going out of our way, just as we would for religious minorities and on behalf of religious freedom or for women in countries where women are discriminated against, to make sure that we are reaching the full spectrum of beneficiaries, and that any kind of social deterrent or normative factors are ones that we try to circumvent to make sure that we are being inclusive because that’s going to be in the interests of all—again, all individuals living in a country economically and in terms of their ability to—in this instance, to integrate into Europe.
JONATHAN CAPEHART: So what would you—what do you say to people who question why supporting LGBTQI+ rights should be a part of American foreign policy? Because you could see there might be some people around the world, or even in our own country, who think, you know, I’m down with the community, but why make that part of our foreign policy.
SAMANTHA POWER: Well, I think one way to take that question, which we do hear a lot and you might even say increasingly in certain quarters, but—is to imagine the counterfactual. You know, imagine a world in which US taxpayer resources are expended in a manner that, you know, in a sense perpetuates or deepens exclusion of individuals who are really vulnerable. I mean, that would be bad. And not only that, it would have the flavor, I think, in many of the countries we work, for a country that for all of our imperfections has long stood for human rights, it would have—it would have the effect, I believe, of being seen to kind of legitimate some of the rhetoric and actions and legal measures that are being put forward.
So, you know, there’s not, like, some place of neutrality here, right? We are the United States. We, you know, for many, many years in a very bipartisan way have stood for human rights. We have stood behind the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, which doesn’t have exceptions or footnotes excluding particular communities. We stand for implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals, which explicitly say that no person should be left behind—again, without footnotes or caveats. So I think there are really hard questions about tactics, about in some places how vocal to be to not, again, put ourselves at the center of a narrative, because that in some sense is just what people who would seek to repress or terrorize vulnerable communities would like to see happen. So, again, it’s very, very difficult on the ground to find the right balance of tools.
You know, if you look at the Anti-Homosexuality Act in Uganda, the—you know, we spoke out with thirty-one countries. We spoke out with the United Nations independent expert that US diplomacy, when I was the UN as ambassador, was absolutely critical in securing the creation of that position. And the fact that that position has been renewed three times now, including most recently last year, speaks to, again, changing norms. The fact that international instruments more and more are including—sometimes explicitly, sometimes less so—[LGBTQI+] rights as human rights, the fact that we see same-sex marriage legalized this last year in Estonia and Slovenia, but also decriminalization in places as varied as Barbados and Singapore means that these principles are getting traction.
And these international instruments—and this is a critical part of President Biden’s agenda—are really important, Jonathan, because it gives citizens in a country, you know, where on the books there’s lots of happy talk about human rights, but it gives [LGBTQI+] organizations and individuals, you know, something to hang their arguments on; something to say, look, but the United Nations Human Rights Council just appointed this individual, this individual says this. And so when we can act in company, in a coalition, I think that’s always advantageous, and that is something we seek to do.
When the norms themselves—I was part of getting the Security Council for the first time in what at that time was the seventy-five-year history of the UN to condemn the targeting of individuals on their—on the basis of their sexual orientation—that had never happened before—and hearing from around the world what it meant for the United Nations Security Council to have done that. I mean, this was something that was a consensus document; you know, the Russian Federation, a number of African governments that had laws that were not respectful of these human rights on the books went along with that.
And so, again, thinking tactically about how to do it and how these norms become more salient in international law, I think, is very important. But it is in our interest to have maximum economic inclusion that’s consistent with our economic objectives as a country and our foreign-policy interests. It is in our interest to fight repression against whomever it is being carried out. And it is in our foreign-policy interest to stand up for our values.
President Biden’s polling, I think, reflects broad approval, surging poll numbers; I think a tripling in global polls about—when the question is posed, do you think Joe Biden will do the right thing, a tripling from his predecessor. And if you talk to people around the world and sort of get a sense of why, the fact that human rights are so central to President Biden’s argument and democracy and the importance of democracy delivering, that’s a major distinguishing feature not only of this administration but really of US foreign policy from some of the big geopolitical actors who are more and more active.
So if we go quiet, just in the same way that if we were to go quiet on the rights of Christians in societies in which they are being persecuted, and just defer to prevailing, you know, what is taken as prevailing popular sentiment, I think we would really shortchange what is distinguishing about American foreign policy.
JONATHAN CAPEHART: One more question from me before we open it up to Q&A, and that’s this. Everything you say is, you know, terrific and wonderful in terms of what the administration is doing, American values. But I just wonder, when you travel around the world or talk to your counterparts, particularly those in, say, Uganda and elsewhere, how do you respond to what they might say, such as, you know, well, your own country’s, you know, no—you know, no garden party. You’ve got book bans and drag-queen story hours being banned and don’t-say-gay laws. And we’re awaiting a Supreme Court decision, possibly tomorrow, definitely by Friday, on whether a cake decorator can say, no, I’m not going to decorate your cake because your same-sex marriage, you know, goes against my beliefs.
How do you deal with that when that is thrown back in your face from foreign leaders?
SAMANTHA POWER: You know, we have a policy that Jay has helped shepherd through USAID which will be the first-of-its-kind LGBTQIA+ policy that’ll be out soon. And one of its many, I think, important features is it speaks of the importance of going forth in a spirit of humility and ally-ship. And I’ve already spoken, I think, a little bit about the ally-ship point.
But in general—you know, you didn’t mention the insurrection. You know, like—
JONATHAN CAPEHART: Well, I mean, it wasn’t—
SAMANTHA POWER: There’s plenty—there’s—
JONATHAN CAPEHART: It wasn’t an LGBTQIA+ insurrection. So I figured I’d just leave—
SAMANTHA POWER: No, that’s a good point.
JONATHAN CAPEHART:—leave that out. But go on.
SAMANTHA POWER: No, but what I mean is in general we are standing up for democracy and human rights as we are facing domestically very, very significant challenges. And I’ve broadened the aperture a little bit from your question, though your question is very valid, you know, as focused on our discussion, our topic for today.
But I don’t even think we can think about LGBTQIA+ rights outside of the broader context of the anti-democratic movements that exist all over the world, including—you know, which include not recognizing results of elections, including resorting to violence, including, you know, some cases partnering with, you know, outside repressive actors who would seek to widen divisions within democracies.
So, you know, the statistics, it’s—you know, I think it’s sixteen years of freedom in decline around the world. And what we see is attacks on minorities generally—sometimes religious minorities; sometimes LGBTQI+ communities—are often the canary in the coal mine about a broader set of measures and a broader kind of consolidation of power away from the people and in the center. And certainly, a diminishment of checks and balances. I think that’s the abiding feature. And minority rights and the rights of marginalized communities fundamentally are checks on majoritarianism in our country and globally.
So, you know, I think if you go—and I’m not saying that we don’t have, you know, as you put it, kind of thrown back at us things that are happening in this country. But I think really since President Obama, and very much carried through with President Biden, we tend to kind of preempt that moment by situating the dialogue about [LGBTQI+] rights in our own struggles, and not leaving the elephant in the room, you know, over here. But to say, look, we’re—this is—we’re in the midst of, you know, many of these same challenges. There are forces in our countries—in our country that would also wish to go back to what is remembered as a simpler time.
And, you know, often I think that actually sets the stage for a more productive conversation, because it’s not a finger-wagging—you know, you may condemn something that has happened and use the leverage of the United States to demand, you know, a repeal. But it is not from a glass house that we are having conversations like this. And I was just in Africa, and I’ll be traveling again. I mean, the dialogue that we have is a humble dialogue. But it is one that has a North Star that I think can animate us both and that is rooted, fundamentally, not only in American values, at their core, but in international instruments and in universal values.
JONATHAN CAPEHART: And so we’re going to open it up to questions. There is a microphone, oh, I thought it was on a stand. It’s an actual person. Thank you. Thank you very much. We’re going to go until about—if I can find my thing—until about quarter to four. So the microphone is there. Short questions, so we can get more answers in. Go ahead.
Q: Hi, Administrator Power. My name is Ryan Arick. I’m an assistant director here at the Atlantic Council. I’m really thrilled to have you here today.
I wanted to ask a question related to US development assistance to Ukraine, and specifically how we’re looking at the LGBTQI+ angle as far as our assistance during the ongoing war. I would appreciate your thoughts. Thank you.
SAMANTHA POWER: You want to go one by one, or?
JONATHAN CAPEHART: Yeah.
SAMANTHA POWER: OK.
JONATHAN CAPEHART: Quickly.
SAMANTHA POWER: OK. So in brief, one of the things you’ll see, again, in the forthcoming policy, is a broad emphasis on thinking within USAID and within our humanitarian emergency programing about inclusion and about proactive outreach and services. I think there’s been—we’ve always, of course, been for an inclusive process to find and to serve beneficiaries. But to think—you know, to think that all beneficiaries will come forward equally in all communities is not accurate. And so, you know, how this plays out in any specific crisis area, you know, that’s going to be fundamentally up to our engagement with our implementing partners, like the World Food Program, like the ICRC and others. But there is a broad embrace of inclusive response and a broad recognition that gravity alone is not going to get you there.
Again, we’re quite far along in Ukraine because I think the government has every incentive—you know, not saying that there isn’t discrimination that occurs in Ukraine, or that some of those fears don’t still exist. But there are a lot of incentives pulling policy and enforcement in a constructive direction, given the European journey that they are very committed to. But imagine, you know, in other parts of the world where there isn’t that, you know, legal framework or that political will at high levels and so that’s why crisis is going to be very important.
The other thing I’d say is, of course, just continuing our HIV/AIDS work full speed ahead, any work we do in human rights, thinking—so, again, there’s the dedicated LGBTQI+ work and then there’s making sure that all of our programming in these other areas is inclusive of that.
So just—and, finally, just we’ve done a lot with hotlines. There’s so much trauma, so much need for psychosocial service and care. We work very closely with Mrs. Zelensky as well, who has really pushed mental health and so forth. So you will see both in our development programming and in our emergency humanitarian programming, provided the resources are there, which we have to work with Congress to continue to mobilize, but a very significant allocation as well to recognizing the trauma and then the unique traumas that may apply to different communities, including this one.
JONATHAN CAPEHART: OK. We’ve got six questions, ten minutes. So what I want to really try to do is two questions at a time. And, Madam Administrator, if you could—a little more brief—to the first two, ask the questions and then we’ll have the administrator answer. Quick questions.
Q: Hi, Administrator Power. My name is Katie. I’m a graduate student at Johns Hopkins SAIS right in Dupont Circle.
And my question for you kind of revolves around the other countries we haven’t talked about. We’ve talked a lot about Ukraine, Uganda. But what should the USAID and other people in the United States what other countries should we focus on for human rights violations, especially in the community?
JONATHAN CAPEHART: OK. Great.
I’m going to get one more.
Q: Hi, Administrator. My name is Divya. I’m an undergraduate at Stanford University and I’m currently an intern at the Cyber and Infrastructure Security Agency.
My question for you is how and if you have handled and talked about tech governance in regards to LGBTQI+ rights and misinformation, perhaps, regarding HIV/AIDS, vaccines, and more.
JONATHAN CAPEHART: OK. Two simple questions—in nine minutes. I’m going to—I’m keeping us on time.
SAMANTHA POWER: So on the first question, I would say that there is a spate now of laws, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa but not only, that are at various stages of legislative movement. Let’s put it that way.
Now, what focus entails, again, you know, I think filtering it through what do our partners on the ground think would be most advantageous for any particular individual or entity or institution to do, as we’ve discussed, it’s—you know, figuring that out is no easy proposition. But I think the New York Times recently did a study that did a lay down of how many country—what stage of passage, you know, these laws were.
I mean, it’s kind of—it’s kicked up what’s happened in Uganda and even our response to it has kicked up, you know, more vocal leadership to push through further exacerbating criminalization measures as, by the way, have really important positive decisions that have been made in Africa.
That, in turn, has generated a backlash and we’ve seen something very similar here, of course, over many, many decades where anti-discrimination ordinances, for example, in Florida—you know, I mean, decades ago—then kicked off major—you know, very, very pronounced counter reactions, massive fundraising, et cetera. That’s happening, too, where for a step forward it then, you know, ignites, you know, certain forces and antibodies and then you see, you know, proactive moves that really can set back those rights.
So, again, the tactics I think we’d have to be very, very case specific. But, you know, where I would—especially for those of you who are in civil society or not in the government per se, the actual support for the organizations. And you’ll have the chance, as well, in this country—those of you who are active in the LGBTQI+ community—through the Welcome Corps at the State Department—this is—I’m sorry I’m going on, but this is a very exciting development that we will actually have the chance—in addition to processing people who are being persecuted on the grounds of their sexual orientation or gender identity, we will have the chance as community members to welcome these individuals. Now, that infrastructure is being built and it’s not, you know—you know, yet where there’s a number for you to call, but all of us will have a—well, there’s a number to call for Welcome Corps, but I’m saying very specifically—
SAMANTHA POWER: For—from this—OK. I was told that we were—we were still some weeks away from that. Well, what is the number that people should call, then, if they want—
AUDIENCE MEMBER: There’s a link on—
SAMANTHA POWER: What is the link?
AUDIENCE MEMBER: RainbowRailroad.org.
SAMANTHA POWER: OK. That’s the State Department program?
AUDIENCE MEMBER: No.
SAMANTHA POWER: No, no, no, OK. So I’m—sorry, I was talking—
AUDIENCE MEMBER:—to Welcome Corps.
SAMANTHA POWER: OK, great. OK. So RainbowRailroad.org will refer you. I think the State Department piece we are still moving out to make sure that these partnerships can be ignited in rapid fire.
And then the second question, Jonathan, was?
JONATHAN CAPEHART: I wrote in my notes tech governance.
SAMANTHA POWER: Tech governance.
JONATHAN CAPEHART: Yes.
SAMANTHA POWER: Yes is the short answer. I’ve engaged them—
JONATHAN CAPEHART: We have—we have five minutes and five questions to go.
SAMANTHA POWER: Yes. I have—I have engaged them on disinformation generally, and this is a very important subcomponent. Discrimination isn’t new. Persecution isn’t new. The amount of disinformation, including deepfakes showing President Biden vilifying LGBTQI+—I mean, you know, these things are really exacerbating an already very challenging situation.
JONATHAN CAPEHART: OK. And so we have one, two, three, four, five questions, five minutes. Lord Jesus. All right.
Here’s what I want to do. I want you each to ask your very brief question so your question at least gets articulated, and then Administrator Power will answer. Real quickly.
SAMANTHA POWER: All five.
JONATHAN CAPEHART: All five. All five. Because now we have four minutes.
Q: Thank you very much.
Very quickly, what would you say to other countries that stand on principle of noninterference, we don’t get to tell other governments how to treat their people? Very briefly. Thank you.
JONATHAN CAPEHART: OK. Thank you.
Q: Yes. My name is Bishop Joseph Tolton.
Domestically in our country, White supremacy one can argue is cradled by the far religious right in our country. These actors are also responsible for the racialization of homophobia across Africa. Are there whole-of-government conversations about how to hold these actors accountable for their racialized efforts?
JONATHAN CAPEHART: Great question.
Q: Hi. David Stacy, Human Rights Campaign.
As you know, nondiscrimination is a touchstone of equality, and the administration right now is reviewing the requirements for grantees and cooperative agreements and across the foreign assistance agencies. Can you speak to the need to do that and USAID’s role in helping the other agencies do something where we’re applying it across the board with all of the agencies on an equal basis?
Q: Hi. Mark Bromley with Council for Global Equality.
You spoke about the value of both dedicated LGBTQI+ funding and integrated funding, and we’re excited that that fifteen million is increased to twenty-five million this year. But on the integration point, how are you thinking about measuring integration for LGBTQI+ persons, particularly in places where, you know, being [LGBTQI+] may be criminalized, it’s difficult/dangerous to measure? How do we make sure that’s more than lip service and that that integration is really happening? Because that is where the true value lies.
JONATHAN CAPEHART: OK. Last question.
Q: Hi there. My name is Bryce Dawson from Counterpart International.
You mentioned the difficulties of minimizing intrusion and tactically advocating for LGBTQI+ rights in other nations, as well as mentioned potential procurement policies to ensure [LGBTQI+] protections. Do you have any in the pipeline that you’re working on or anything in the future?
JONATHAN CAPEHART: I want to thank everyone for their—for their questions, all five of you or seven altogether. Madam Administrator, you have two minutes.
SAMANTHA POWER: Thirty seconds.
Well, you know, I think that in general we—in our engagements on human rights issues, we hear a lot about noninterference. I mean, there’s no question. I heard about it a lot at the UN. We hear it often from, you know, countries like the Russian Federation that have invaded another country and tried to take over the other country. We hear it from countries that are providing surveillance technology, you know, to other countries, or fueling disinformation in the countries in which we are working.
So, you know, it is a shield. It is an important one to take seriously, because we also, of course, respect sovereignty, and territorial integrity, and so forth. So USAID is active across sectors and involved in these countries. And this agenda, I think, is—and, by that, it’s the human rights agenda more broadly—is central to how we believe as well that we will get the most out of the programs that we are doing across sectors.
And that brings me—and that’s the kind of conversation we have. Is, like, I was using Uganda as an example about making sure that we are also making the pragmatic case for people who are very skeptical because, again, they—there is a kind of seamlessness to the way our work across governance and human rights in citizen security and in the broad sweep of development sectors—from agriculture, to education, to health, et cetera—they do come together in service of development objectives. And that’s what the SDG’s also enshrine.
And then I’m not going to be able to do justice to the other questions in full, beyond I think the point about measuring integration is very important. You know, for those who are not making their identity known to us, that’s not going to be something that, you know, we will be able to measure in that sense. But I think these are the kinds of things that we are working through, through this policy, to make sure that this isn’t just, yes, here’s our standalone programming, and then by everything else we do, you know, operates in the way that we’ve always done it.
And so it’s not going to be, you know, instant, where everything is happening all at once. But all of our missions have to have inclusive development advisors or somebody—and this will be evident out of the policy—but somebody who is a focal point for working on LGBTQI+ rights and programming. So we’re hopeful that that, plus our new office of chief economist, will help us develop a kind of methodology that will be responsive to this concern that somehow it’s going to be invisible and not done, which is certainly our objective is for it to be done and, when appropriate, visible. And certainly, at least visible to us so we know whether we’re achieving what we’re setting out to achieve.
And then, lastly, I would just say, because it’s coming, the point about nondiscrimination among beneficiaries is just really important. And that guidance will be forthcoming, we hope, soon.
JONATHAN CAPEHART: Do you have any thoughts on the other question about—I wrote it down real fast, but I know I got it wrong—about the racialized religious efforts on LGBTQI+ rights that have been happening?
SAMANTHA POWER: Well, I guess all I would say on that—because there are others in our government, I think, who are working on the kind of conversation that was asked about—is just this is another part of the response to the noninterference charge, is—that we do hear from people who don’t want to be engaged on human rights issues. And that is that there are a lot of actors from outside who are very active actually in pushing certain forms of legislation that would have these discriminatory, and these exclusionary, and these dangerous effects. And so, again, the noninterference claim is usually made in a selective way.
JONATHAN CAPEHART: And with that, and just two minutes overtime, Samantha Power, nineteenth administrator of USAID. Thank you very, very much for being here.
SAMANTHA POWER: Thank you.
Watch the event
Further reading
Mon, Jun 21, 2021
Tony Blinken on the Putin summit and why the ‘democratic recession’ matters for LGBTQI rights
New Atlanticist By Daniel Malloy
The US secretary of state spoke at an Atlantic Council Front Page event in honor of Pride Month, setting out the department’s priorities on LGBTI issues.
Thu, Jun 24, 2021
Ukraine offers hope in an increasingly homophobic neighborhood
UkraineAlert By Adrian Hoefer, Shelby Magid
While Ukrainian attitudes towards the LGBTQI community are still far behind the levels of acceptance encountered elsewhere in the West, Ukraine’s modest progress offers hope in a region where intolerance is on the rise.
Tue, Mar 23, 2021
Protecting the world’s trans population requires political representation
New Atlanticist By
There is one group of women that has been left behind in conversations about gender-based issues: trans women. Global leaders must change the narrative to advance a trans-inclusive agenda
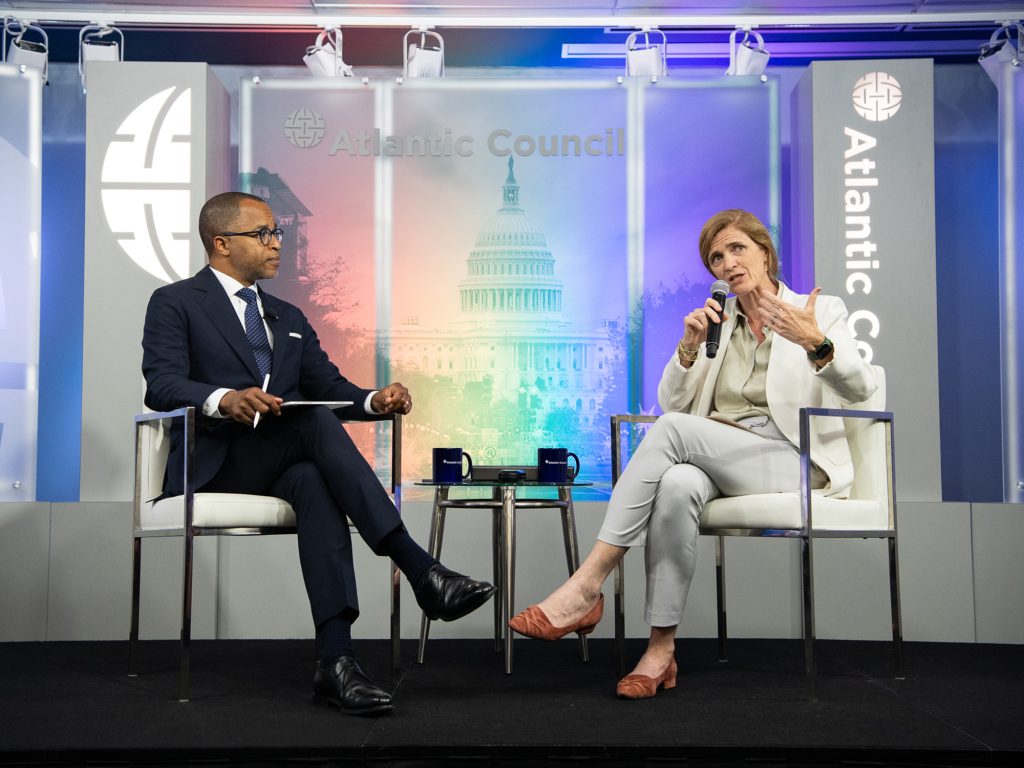
Image: USAID Administrator Samantha Power speaks at an Atlantic Council Front Page event on June 28, 2023.