Cleveland, Ohio: Promoting a local and just energy transition
Introduction
Cities and states are at the forefront of US efforts to achieve decarbonization goals, manufacture low-carbon technologies, and identify opportunities to align the energy transition with economic opportunities for businesses and workers. These subnational strategies align with ambitious nationwide objectives, including reducing US greenhouse gas emissions 50–52 percent below 2005 levels by 2030, achieving 100-percent carbon pollution-free electricity by 2035, and attaining a net-zero emissions economy by 2050. Achieving these targets will require cities and states across the United States to adopt decarbonization technologies, policies, and strategies. The leadership of state, local, and tribal leaders in climate action is pivotal for ensuring the long-term and sustainable decarbonization of the US economy.
Cleveland, Ohio, a mid-sized lakefront city with a rich manufacturing history, was once the fifth-largest city in the United States. However, as was the case with many Midwestern cities, Cleveland’s deindustrialization led to its economic decline. Yet Cleveland has an opportunity to establish itself as a leader in low-carbon and equitable growth. The city is pioneering valuable lessons learned and best practices to share with other cities facing similarly challenging conditions. It provides an example of how cities can leverage the benefits of the low-carbon transition to address climate change while providing public health, social, and economic opportunities for everyday Clevelanders—and to use this transition as an opportunity to reestablish itself as an industrial powerhouse in a low-carbon economy.
Cleveland is building toward a decarbonization agenda that envisions a city and region that are more equitable, sustainable, and livable. Yet while there are important voices advocating for an environmentally and socially sustainable future, it has proven challenging to build the critical mass of support required for structural, long-term change in Cleveland. Progress toward a comprehensive decarbonization vision, therefore, has been uneven in both the city and the surrounding region, including Cuyahoga County.
Nonetheless, key stakeholders continue to press forward to ensure that the Cleveland region will have a decarbonized future for all its citizens. For that to occur, the city’s public, private, philanthropic, and civil-society leaders will have to build upon their existing efforts, expanding and deepening the coalition of groups and interests that want to transform Cleveland’s economy in a decarbonized direction.
Following his election in 2021, Cleveland’s mayor, Justin Bibb, reaffirmed his predecessor’s commitment to sustainability and climate action. He announced a goal to transition Cleveland to 100-percent renewable energy by 2030, funded an initiative focusing on the circular economy, and stressed environmental justice as a core priority of his administration, among other actions. The city launched its Climate Action Plan in 2013, and updated the plan in 2018 to provide a framework for the city’s approach to tackle climate change across five focus areas: energy efficiency, clean energy, sustainable transportation, food systems, and clean water and vibrant green space. The plan also addressed cross-cutting priorities across the focus areas of social and racial equity, good jobs, climate resilience, and business leadership. The city is currently working on updating the 2018 iteration and expects to release an updated version in 2024. Members of the Greater Cleveland Partnership, the city’s Chamber of Commerce, for example, have begun to monitor their scope-one and scope-two emissions due to increasing customer demand for sustainability. And a steering committee, consisting of representatives from leading organizations in the region, has been formed to support an update to the city’s essential targets and goals—and, ultimately, to advance a unified vision for the city.
Cleveland: Basics
The Cleveland-Elyria Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA), defined as the core city of Cleveland plus the surrounding Cuyahoga, Geauga, Lake, Lorain, and Medina Counties, had a population of 2.1 million people in 2020. The once-thriving city of Cleveland has experienced substantial population decline, from nearly one million residents in 1950 to 364,000 in 2022. The city’s population loss was the surrounding Cuyahoga County’s gain (Cuyahoga is by far the largest county among the five in the MSA), although it too has declined in population, from around 1.7 million in 1970 to 1.24 million people in 2022. The core city’s population decline stemmed from several forces that were common to US cities in the postwar era, including net out-migration, underinvestment in public infrastructure, and a shifting economic base, especially industrial-plant closures. Many of these demographic shifts resulted from the long-term decline, starting in the 1960s, of Cleveland’s industrial and manufacturing bases, which continue to be the backbone of Cleveland’s economy.
Such changes also landed unequally on Cleveland’s population. As just one of many possible examples, the construction of highways through Cleveland starting in the 1950s split the city unevenly, and to the detriment of poorer minority communities. Today, the legacy of Cleveland’s unequal economic geography remains, in particular for the city’s Black population, which remains concentrated in neighborhoods characterized by lower incomes, employment, and educational attainment. Within the city of Cleveland, 31.4 percent of residents live below the poverty line.
Decarbonization: State and local
With respect to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, the city of Cleveland has made some progress in mitigating its climate impact. Cleveland’s GHG emissions stood at 11.65 million tons in 2018, down 7 percent from 2010 levels, with an 11-percent improvement in emissions per dollar of gross domestic product (GDP). Cleveland’s GHG reductions occurred as regional eGrid emissions fell on coal-to-gas switching, as well as the increased adoption of clean energy. At the state level, Ohio’s use of coal in the electricity sector halved to 59 terawatt hours (TWh) over the same time period, while its natural gas usage rose 545 percent to 46 TWh to 2018; generation from clean energy sources, such as nuclear energy and wind, also rose sharply from 2010 to 2018. As is true of other US cities, greenhouse gas emissions in the greater Cleveland region are lowest toward the city center and highest toward the region’s periphery, owing to the roles played by population density, mixture of uses, commute lengths, and housing sizes.
While at the city level, Cleveland has notched key gains toward decarbonization, it faces state-level headwinds. Policymakers in Ohio’s state government appear willing to tilt energy markets toward fossil fuels. State officials have implemented restrictive legislation concerning the transition to renewable power sources, instituting onerous property-setback requirements for wind turbines and making approval processes for wind and solar projects much more difficult. As a result, Ohio’s electricity grid fuel mix will constrain Cleveland’s decarbonization ambitions. Ohio’s electricity generation is dominated by coal and natural gas, with clean energy sources such as nuclear, wind, and solar accounting for a very low proportion of overall output. In 2022, Ohio garnered only 15.4 percent of all electricity generation from nuclear, wind, or solar sources, versus nearly 51 percent for natural gas and nearly 32 percent for coal. Because clean electricity accounts for only a small fraction of Ohio’s total generation, there will be fewer decarbonization benefits to Cleveland from the electrification of vehicles or heating of buildings.
At the same time, there are countervailing forces at work within the state. The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) of August 2022 has already generated new investments totaling $8.03 billion and more than five thousand good-paying clean energy jobs in Ohio, per research from the nongovernmental organization Climate Power, suggesting the clean energy transition’s economic potential there. Reflective of Ohio’s industrial history, Honda, LG Energy, and EdgeEnergy have invested in the electric vehicle economy and First Solar and Invenergy have invested in solar manufacturing. Federal support also aims to reduce energy bills through the Home Energy Rebate program and energy-efficiency grants.
While investment outcomes are typically tracked at the state level, local organizations in Cleveland are attempting to catalyze clean energy investments into the city. The GO Green Energy Fund, headquartered in Cleveland, is not only the nation’s first Black-led green bank program, it is also leading an initiative to secure $250 million in funding from IRA to support residential solar uptake for low-income residents across twenty counties, including Cuyahoga. In addition to solar, the fund is also examining other clean energy technologies, such as appliances and weatherization. With state policymakers evincing little interest in advancing decarbonization, local groups are aggressively pursuing federal funding from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
Cleveland: Decarbonization pillars
Despite the constraints at the state level on decarbonization parameters, Cleveland and other local jurisdictions are setting forth strategies to reduce carbon emissions where possible. Cleveland’s efforts can be summarized with four key pillars: environmental justice; industry and manufacturing; transportation; and conservation. The pillars are generally aligned with the cross-cutting focus areas outlined in the city’s 2018 version of the Climate Action Plan (these include environmental justice, the green economy including business leadership, climate resilience, clean energy and efficient buildings, transportation, land and water conservation, and food security).
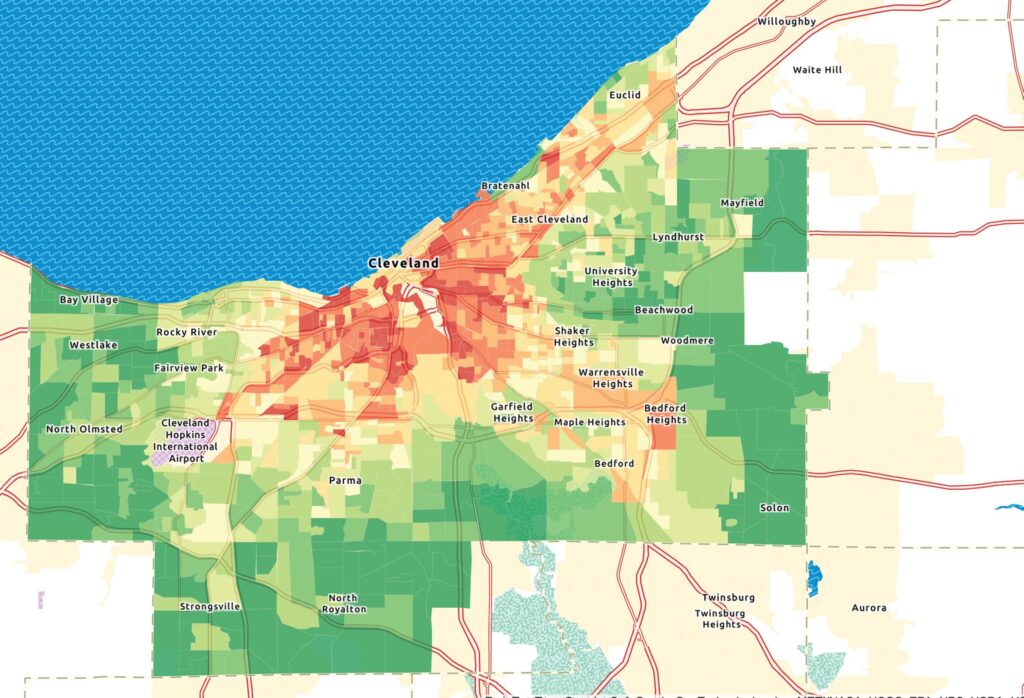
The map depicts cumulative environmental justice burden index scores for each block group in Cuyahoga County, using data from the US EPA’s EJSCREEN Environmental Justice Mapping and Screening Tool, combining environmental and demographic socioeconomic indicators. The areas in red experience the highest environmental justice burden and green experiencing the lowest burden. The highest environmental justice burdens are experienced in neighborhoods located in or near former industrial facilities or interstates. Source: ArcGIS
Environmental justice
As occurred in other US cities, Cleveland’s economic development historically disadvantaged poor and minority communities. East Cleveland, a suburb, was redlined on racial grounds and now has the lowest median income in Ohio, a 50.3-percent child-poverty rate, and 40 percent of its Black population living in poverty. The city’s decarbonization strategy includes a commitment to ensure that decarbonization efforts are equitable. For example, Mayor Bibb announced a $15-million investment for three disadvantaged neighborhoods to actualize the concept of a walkable or bikeable “fifteen-minute city,” and intends to allocate $50 million from the American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA) funding to prepare a thousand acres of vacant land to attract development and revive well-paying jobs in the city.
The historical legacy of discriminatory practices has cast a long shadow over Cleveland, amplifying the adverse impacts of economic and environmental outcomes such as high energy costs. Electricity and gas bills in Cleveland consume 6.6 percent of the average household income, nearly double the national average of 3.6 percent. Within the region, there are efforts to provide relief while pursuing decarbonization. The city of Cleveland, for example, is implementing a pilot program to install solar panels on the homes of low- and moderate-income families. Such efforts overlap with those by co-ops such as the Solar United Neighbors, Cuyahoga County Solar Cooperative, and Cleveland Solar Cooperative, which also develop solar assets in low- to medium-income neighborhoods.
Industry and manufacturing
Industry and manufacturing played a pivotal role in both Cleveland’s growth and its decline, but also should play an important role in the city’s rejuvenation efforts. Industry and manufacturing are Cleveland’s largest electricity consumers, using about 60 percent of the city’s total electricity. Energy efficiency is a central pillar of Cleveland Cliffs’ environmental strategy (the company, which is headquartered in Cleveland, is the largest flat-rolled steelmaker in the United States). Its Cleveland Works plant produces hot-rolled, cold-rolled, and hot-dip galvanized sheet and semi-finished slabs, and has the capacity to manufacture more than three million tons of raw steel annually using its two blast furnaces. Working closely with the Department of Energy’s Better Plants program, Cleveland Cliffs is committed to achieving a 10-percent reduction in energy intensity over ten years and announced a target to purchase two million MWh annually of renewable power.
Transportation
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is a vital step in reducing the city’s emissions, but its effectiveness in achieving decarbonization goals relies on the electricity grid. The absence of signals from the state pertaining to grid decarbonization fosters hesitation regarding investments in, and adoption of, decarbonization technologies like EVs. Cleveland’s EV adoption remains limited, accounting for merely 2.2 percent of new vehicle registrations in the Cleveland-Akron metro area, in contrast to comparable cities such as Columbus (3.7 percent), Detroit (4 percent), and Indianapolis (3.1 percent). The slow growth of EVs can be attributed partly to the lack of state-level EV tax incentives in Ohio, a contrast with other states such as Washington, Oregon, and California that are offering substantial incentives, leading to higher levels of EV registration rates in cities such as Seattle (17.2 percent), Portland (13.1 percent), and San Francisco (32.9 percent).
EV-charging infrastructure in Cleveland remains underdeveloped, although the mayor’s office has initiated the installation of its first free EV-charging station in the Lee-Harvard neighborhood, with plans for multiple additional installations throughout the city. The Greater Cleveland Regional Transit Authority’s 2020–2030 strategic plans include measures to introduce electric-powered buses, integrate alternative power at stations, provide EV charging at its facilities, and support multimodal connections to its transit systems. At the state level, there are plans to install EV-charging infrastructure across a corridor of 1,870 miles, facilitating a more comprehensive charging network across the region. Additionally, the Northeast Ohio Areawide Coordinating Agency (NOACA) has identified forty-seven locations for charging stations, spanning five counties in the region.
The city of Cleveland’s Mobility Plan demonstrates a proactive approach toward improving the city’s bike and pedestrian infrastructure, a step toward realizing Mayor Bibb’s fifteen-minute city framework, which has the potential to reduce vehicular traffic and associated emissions. This plan is multifaceted, aiming to bolster transit-oriented development, inject investment into Cleveland’s neighborhoods, and encourage multimodal transportation options. Currently, the city’s bicycle lanes are disjointed, catering to pockets of the city. Bike Cleveland, a local nongovernmental organization (NGO), has identified twenty-seven miles of potential new or improved bike facilities to enhance biking connectivity and safety.
Conservation
The conservation of land resources is integral to any vision that seeks to improve Cleveland’s livability, local economy, and environmental sustainability, while contributing to climate adaptation and energy efficiency. Among other benefits, conserving land helps mitigate climate-change impacts, contributing to local air and water quality and reducing urban heat-island effects. As with so many other aspects of the Cleveland case study, its conservation story is a combination of a troubling history and promising future.
For many decades, Cleveland was known as the Forest City for the extent and diversity of its tree canopy. Trees provide shade, reducing the heat-island effect, and can thus lower energy demand and associated emissions for keeping buildings cool. Since the 1950s, the city of Cleveland has lost half its tree cover, now estimated at around 18 percent of what the Cleveland Tree Coalition estimates as a possible upper limit. The city continues to lose trees at the rate of seventy-five acres per year. Unsurprisingly, the lowest coverage levels are in the city’s poorest neighborhoods contributing to poor air quality and access to shade, a result of systematic underinvestment in the city’s tree canopy there. An Urban Forestry Commission has been reconstituted under the aegis of the city government. It has the express goal of reversing the loss of tree cover through identifying appropriate policy remedies and generating public and civil-society buy-in to reforestation of the city.
The city’s history shows that a concerted, collaborative effort can accomplish this major conservation and decarbonization goal. The Cuyahoga River, which flows through Cleveland, is an iconic example of the city’s ability to achieve such an ambitious aim. The river is known for the 1969 fire that helped spark the mass environmental movement across the United States. Over decades, the determined efforts of federal, state, and local officials—as well as industry, civil society, and the Cleveland-Cuyahoga County Port—have brought the Cuyahoga back from its near-dead status of half a century ago.
Conclusion and recommendations
For the city of Cleveland and the surrounding region to successfully decarbonize, leaders from the public, private, and philanthropic sectors, plus those from civil society, will need to sustain and strengthen the coalitions that are moving the region in this direction. There are many promising signs on this front, as shown by the growing efforts of the Climate Action Plan steering committee and efforts to update the 2018 version of the plan. The city has made progress toward ensuring a just transition to a clean energy community, promoting low-carbon industrial production, advocating for an increase in EV adoption and charging infrastructure, and conserving tree cover, but much more work is needed to realize its climate and decarbonization agenda. The city will need to overcome remaining challenges by continuing engagement with all stakeholders: at the household and business levels to promote wider adoption of low-carbon technologies such as heat pumps, EVs, and charging systems; with the city’s utility, Cleveland Public Power, to develop a clean-energy grid; and through recognition by industry and large firms that decarbonization strategies are a better way of doing business.
Despite the state of Ohio’s recalcitrant policies toward renewable energy, there is much opportunity for Cleveland in this domain. For example, the city and region have numerous synergies between onshore and offshore wind on the one hand and steelmaking on the other. Great Lakes offshore wind must overcome several hurdles, including permitting challenges, height restrictions on wind turbines, cost inflation, and more, yet the Cleveland region nonetheless has a unique opportunity to accelerate decarbonization and economic development by leveraging its existing industrial base for wind development.
Finally, an oft-repeated message in consultations with key stakeholders is that the city and region need to realize the opportunities and benefits of recent federal legislation like the Inflation Reduction Act, CHIPS Act, and Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, as seen by recent investments in other regions of Ohio. There is enormous public funding available for investment from these acts. Leaders will need to bring the right groups of stakeholders together to aggressively pursue federal incentives and funding.
AUTHORS
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The Atlantic Council would like to thank the Natural Resources Defense Council for its support of this work.
The authors would like to thank the following local and state stakeholders who provided valuable insights that informed this report:
- Deepa Vedavyas, director of resiliency and sustainability, NOPEC
- Jennifer Lumpkin, manager of local partnerships, Cleveland, Alliances for Great Lakes
- Joel Brammeier, president and CEO, Alliance for the Great Lakes
- Emily Keller, manager of sustainability initiatives, Greater Cleveland Partnerships
- Jacob Schwemlein, director for Drive Electric Ohio, Clean Fuels Ohio
- Tim Cho, senior manager of federal grants and special projects, Clean Fuels Ohio
- Hannah Ruscin, program manager, Clean Fuels Ohio
- Eleanor Jersild, senior manager of compliance and operations, Clean Fuels Ohio
- Paige Lampman, Professional Services Manager of Projects, Clean Fuels Ohio
- Joe Flarida, Executive Director, Power a Clean Future Ohio
- Jacob VanSickle, Executive Director, Bike Cleveland
- SeMia Bray, Co-Director Black Environmental Leaders Association
- Elena Stachew, Northeast Ohio Strategy Consultant, Power a Clean Future Ohio
- Kirt Conrad, Chief Executive Director, Stark Area Regional Transit Authority
- Sarah E. O’Keeffe, Director, Sustainability and Climate Justice, Mayor’s Office of Sustainability, City of Cleveland
- Max Zandi, former young global professional, Atlantic Council Global Energy Center
- Grant Goodrich, executive director, Great Lakes Energy Institute, CWRU
This report was written and published in accordance with the Atlantic Council policy on intellectual independence. The authors are solely responsible for its analysis and recommendations. The Atlantic Council and its donors do not determine, nor do they necessarily endorse or advocate for, any of this report’s conclusions.
RELATED CONTENT

The Global Energy Center develops and promotes pragmatic and nonpartisan policy solutions designed to advance global energy security, enhance economic opportunity, and accelerate pathways to net-zero emissions.
Image: Cleveland, Ohio, USA skyline on the river.




